Abstract
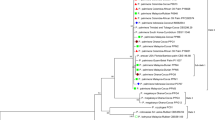
Sugarcane leaf scald caused by Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson is an extremely destructive disease. In 2017, suspected symptoms of sugarcane leaf scald was observed, in Baoshan, Mengding and Jinping, Yunnan Province, China. The bacteria was isolated from the symptomatic stalks and was subsequently identified as the causal agent using Koch’s postulates. BLASTN analysis showed that the amplified nucleotide sequences of 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoD genes from all isolates shared 100% sequence identity with the nucleotide sequences of corresponding genes of X. albilineans strain GPE PC73 (Acc no. FP565176). Based on symptom diagnosis in the field, colony morphology, validation of Koch’s postulates and molecular identification of 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoD genes, the disease was confirmed as sugarcane leaf scald caused by X. albilineans. Partial 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoD gene sequence analysis of 36 X. albilineans strains from Yunnan and Guangxi provinces, China, was determined. The results revealed that the gyrB gene was the most sensitive in differentiating X. albilineans strains from Yunnan and Guangxi provinces.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Daugrois, J.H., R. Boisne-Noc, P. Champoiseau, and P. Rott. 2012. The revisited infection cycle of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of leaf scald of sugarcane. Functional Plant Science and Biotechnology 6: 91–97.
Davis, M.J., P. Rott, P. Baudin, and J.L. Dean. 1994. Evaluation of selective media and immunoassays for detection of Xanthomonas albilineans, causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald disease. Plant Disease 78: 78–82.
Davis, M.J., P. Rott, C.J. Warmuth, M. Chatenet, and P. Baudin. 1997. Intraspecific genomic variation within Xanthomonas albilineans, the sugarcane leaf scald pathogen. Phytopathology 87: 316–324.
Davis, M.J., C.J. Warmuth, R. Philippe, C. Michèle, and B. Pierre. 1995. Worldwide genetic variations in the sugarcane leaf scald disease pathogen, Xanthomonas albilineans. Journal-American Society of Sugar Cane Technologists 15: 71.
Hoy, J.W., and M.P. Grisham. 1994. Sugarcane leaf scald distribution, symptomatology, and effect on yield in Louisiana. Plant Disease 78: 1083–1086.
Klett, P., and P. Rott. 1994. Inoculum sources for the spread of leaf scald disease of sugarcane caused by Xanthomonas albilineans in Guadeloupe. Journal of Phytopathology 142: 283–291.
Küpfer, M., P. Kuhnert, B.M. Korczak, R. Peduzzi, and A. Demarta. 2006. Genetic relationships of Aeromonas strains inferred from 16S rRNA, gyrB and rpoB gene sequences. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 56: 2743–2751.
Li, W.F., and Y.K. Huang. 2012. Modern diagnosis, detection and control technology of sugarcane disease. Beijing: China Agriculture Press.
Lin, L.H., M.S. Ntambo, P.C. Rott, Q.N. Wang, Y.H. Lin, H.Y. Fu, and S.J. Gao. 2018. Molecular detection and prevalence of Xanthomonas albilineans, the causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald, in China. Crop Protection 109: 17–23.
Pascual, J., M.C. Macián, D.R. Arahal, E. Garay, and M.J. Pujalte. 2010. Multilocus sequence analysis of the central clade of the genus Vibrio by using the 16S rRNA, recA, pyrH, rpoD, gyrB, rctB and toxR genes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 60: 154–165.
Ricaud, C., B.T. Egan, J.A.G. Gillaspie, and C.G. Hughes. 1989. Disease of sugarcane: major disease. New York: Elsevier.
Rott, P., M. Arnaud, and P. Baudin. 1986. Serological and lysotypical variability of Xanthomonas albilineans (ashby) Dowson, causal agent of sugarcane leaf scald disease. Journal of Phytopathology 116: 201–211.
Rott, P., M.J. Davis, and P. Baudin. 1994. Serological variability in Xanthomonas albilineans, causal agent of leaf scald disease of sugarcane. Plant Pathology 43: 344–349.
Rott, P., L. Fleites, G. Marlow, M. Royer, and D.W. Gabriel. 2011. Identification of new candidate pathogenicity factors in the xylem-invading pathogen Xanthomonas albilineans by transposon mutagenesis. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 24: 594–605.
Rott, P., D. Soupa, Y. Brunet, P. Feldmann, and P. Letourmy. 1995. Leaf scald (Xanthomonas albilineans) incidence and its effect on yield in seven sugarcane cultivars in Guadeloupe. Plant Pathology 44: 1075–1084.
Soler, L., M.A. Yanez, M.R. Chacon, M.G. Aguilera-Arreola, V. Catalán, M.J. Figueras, and A.J. Martinez-Murcia. 2004. Phylogenetic analysis of the genus Aeromonas based on two housekeeping genes. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 54: 1511–1519.
Stackebrandt, E., and B.M. Goebel. 1994. Taxonomic note: a place for DNA-DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 44: 846–849.
Tamura, K., G. Stecher, D. Peterson, A. Filipski, and S. Kumar. 2013. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Molecular Biology and Evolution 30: 2725–2729.
Tsushima, S., H. Shinohara, T. Nakazato, S. Ando, T. Sugisawa, and Y. Tabei. 2006. Phylogenetic analysis of Xanthomonas albilineans strains from Okinawa, Japan, through a comparison of the gyrB and rpoD genes in geographically distinct strains. Journal of Phytopathology 154: 683–687.
Urwin, R., and M.C. Maiden. 2003. Multi-locus sequence typing: a tool for global epidemiology. Trends in Microbiology 11: 479–487.
Young, J.P., H.L. Downer, and B.D. Eardly. 1991. Phylogeny of the phototrophic rhizobium strain BTAi1 by polymerase chain reaction-based sequencing of a 16S rRNA gene segment. Journal of Bacteriology 173: 2271–2277.
Zhang, R.Y., H.L. Shan, W.F. Li, X.Y. Cang, X.Y. Wang, J. Yin, Z.M. Luo, and Y.K. Huang. 2017. First report of sugarcane leaf scald caused by Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson in the province of Guangxi, China. Plant Disease 101: 1541.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Sugar Crop Research System (CARS-170303), Yunling industry and technology leading talent training program ‘Prevention and Control of Sugarcane Pests’ (2018LJRC56) and Yunnan Province Agriculture Research System (YNGZTX-4-92).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RYZ wrote the manuscript. XYW analyzed the date. XYW, WFL, JL, HLS, XYC, ZML and JY performed experimental work. YKH conceived and designed the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, RY., Wang, XY., Shan, HL. et al. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Xanthomonas albilineans (Ashby) Dowson Based on Multiple Gene Sequences in Yunnan Province, China. Sugar Tech 21, 794–801 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-019-00713-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-019-00713-0