Abstract
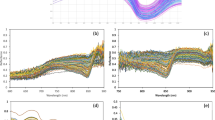
The total soluble nitrogen (TSN) content in sugar beets strongly hinders sugar extraction. Traditionally, the amount of TSN is not measured directly, but inferred from the amount of amino nitrogen (~30% of the TSN) in the beet. Betaine, the other main TSN component, accounts approximately for another 30%. Betaine also interferes with sugar crystallization, and it is a highly interesting metabolite in pharmaceutics and agronomics. The aim of this study was to develop non-invasive near-infrared (NIR) applications to measure the TSN and betaine content in beets in a fast and reliable way. Sugar beets were harvested for up to five harvest periods, and pulp samples were measured with a NIR system. Calibration models reached correlations (R) between laboratory and predicted values of 0.823 for TSN and 0.947 for betaine, respectively. The prediction of independent validation sets showed also high correlation coefficients for both TSN (R = 0.756) and betaine (R = 0.837). These NIR applications could be very helpful in the assessment of beet quality in breeding programs and industrial processes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beiss, U. 1994. Betain content in sugar beet. Zuckerindustrie 119(2): 112–117.
Burba, M., U. Nitzschke, and R. Ritterbusch. 1984. Die N-Assimilation der Pflanze unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Zuckerrübe. Zuckerindustrie 109(7): 613–629.
Burba, M., and H. Schiewek. 1993. The nonsugar and ion balance of thick juice as bases for a quality assessment of sugar beets: Part 2. Zuckerindustrie 118(12): 921–936.
Burba, M. 1996. Harmful nitrogen as a criterion of beet quality. Zuckerindustrie 121(3): 165–173.
Burba, M., T. Huijbregts, and E. Hilscher. 2001. On the determination ot total soluble nitrogen in sugarbeet by Near Infrared Spectrometry. NIRS. Zuckerindustrie 126(5): 367–375.
Choluj, D., R. Karwowska, A. Ciszewska, and M. Jasińska. 2008. Influence of long-term drought stress on osmolyte accumulation in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) plants. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum 30: 679–687.
Craig, S. 2004. Betaine in human nutrition. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 80: 539–549.
Day, C.R., and S.A. Kempson. 2016. Betaine chemistry, roles, and potential use in liver disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1860(6): 1098–1106.
Dutton, J., and T. Huijbregts. 2006. Root Quality and Processing. In Sugar Beet, ed. A.P. Draycott, 409–442. Oxford: Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Fox, G., and M. Manley. 2009. Hardness methods for testing maize kernels. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 57(13): 5647–5657.
Freckleton, R.P., A.R. Watkinson, D.J. Webb, and T.H. Thomas. 1999. Yield of sugar beet in relation to weather and nutrients. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 93(1): 39–51.
Givens, D.I., and E.R. Deaville. 1999. The current and future role of near infrared reflectance spectroscopy in animal nutrition: a review. Australian Journal of Agricultural Research 50: 1131–1145.
Gzik, A. 1996. Accumulation of proline and pattern of α-amino acids in sugar beet plants in response to osmotic, water and salt stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany 36: 29–38.
Hallauer, A.R., and J.B. Miranda. 1981. Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Ames: Iowa State University Press.
Hanson, A.D., and R. Wyse. 1982. Biosynthesis, Translocation, and Accumulation of Betaine in Sugar Beet and Its Progenitors in Relation to Salinity. Plant Physiology 70(4): 1191–1198.
Heppner, S., K. Thielecke, K. Buchholz, and D. Wullbrandt. 2000. Potential applications of NIR spectrometry in the sugar industry. Zuckerindustrie 125(5): 325–330.
Hoffmann, C. 2005. Changes in N composition of sugar beet varieties in response to increasing N supply. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science 191: 138–145.
Hoffmann, C., and B. Märländer. 2005. Composition of harmful nitrogen in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) - amino acids, betaine, nitrate—as affected by genotype and environment. European Journal of Agronomy 22: 255–265.
Hoffmann, C., 2006. Zuckerrüben als Rohstoff. Göttingen, Post-doctoral Thesis.
Hoffmann, C., T. Huijbregts, N. van Swaaij, and R. Jansen. 2009. Impact of different environments in Europe on yield and quality of sugar beet genotypes. European Journal of Agronomy 30: 17–26.
Igne, B., L.R. Gibson, G.R. Rippke, and C.R. Hurburgh. 2007. Influence of Yearly Variability of Agricultural Products on Calibration Process: A Triticale Example. Cereal Chemistry Journal 84(6): 576–581.
Kenter, C., C. Hoffmann, and B. Märländer. 2006. Effects of weather variables on sugar beet yield development (Beta vulgaris L.). European Journal of Agronomy 24(1): 62–69.
Liebe, S., and M. Varrelmann. 2016. Effect of Environment and Sugar Beet Genotype on Root Rot Development and Pathogen Profile During Storage. Phytopathology 106(1): 65–75.
Mackay, I., A. Horwell, J. Garner, J. White, J. McKee, and H. Philpott. 2011. Reanalyses of the historical series of UK variety trials to quantify the contributions of genetic and environmental factors to trends and variability in yield over time. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 122(1): 225–238.
Mäkelä, P. 2004. Agro-industrial uses of glycinebetaine. Sugar Tech 6(4): 207–212.
Marketandmarkets. 2015. Betaine Market by Type (Synthetic Betaine and Natural Betaine), Form (Betaine Anhydrous, Cocamidopropyl Betaine, Betaine Monohydrate), Application (Food & Beverages, Animal Feed, Cosmetics, Detergents), and by Geography - Global Forecast to 2020. http://www.marketsandmarkets.com.
Piepho, H.P., A. Büchse, and K. Emrich. 2003. A Hitchhikers Guide to Mixed Models for randomized experiments. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science 189: 310–322.
Pojić, M., J. Mastilović, and N. Majcen. 2012. The Application of Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Wheat Quality Control. In Infrared Spectroscopy - Life and Biomedical Sciences, ed. T. Theophile, 167–184. Rijeka: InTech.
van der Poel, P.W., H. Schiweck, and T. Schwatz. 1998. Sugar technology beet and cane sugar manufacture. Berlin: Dr. Albert Bartens KG.
Roggo, Y., L. Duponchel, and J.-P. Huvenne. 2004. Quality evaluation of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) by near-infrared spectroscopy. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 52(5): 1055–1061.
Schiweck, H., G. Kozianowski, J. Anderlei, and M. Burba. 1994. Calculation of the nonsugar mass in thick juice from beta analyses - Proposal of a formula to assess the technical quality of sugar beets. Zuckerindustrie 119(4): 268–282.
Shaw, B., T.H. Thomas, and D.T. Cooke. 2002. Responses of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) to drought and nutrient deficiency stress. Plant Growth Regulation 37: 77–83.
Smed, E., A.W.M. Huijbregts, D. Hadjiantoniou, and G. Vallini. 1996. Influence of agronomic factors on non conventional parameters of the internal quality of sugar beet. In Proceedings of the 59th IIRB Congress 385–389.
Stockfisch, N., H.-J. Koch, and B. Märländer. 2002. Effects of Weather on Growth and Dry Matter Yield of Sugar Beet. Pflanzenbauwissenschaften 6(2): 63–71.
VSN International. 2011. GenStat for windows, 14th ed. Hempstead: VSN International.
Williams, P. 2010. The analysis of wheat by near-infrared spectroscopy. In Handbook of vibrational spectroscopy, ed. E.C.Y. Li Chan, P.R. Griffiths, and J.M. Chalmers. New Jersey: John Wiley.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Christiane Lakenbrink for the HPLC determination of betaine in pulp samples, Dr. Hartwig Wellmann for kind assistance with the TSN determination, and Kathrin König and Enrico Ziehe for excellent technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martínez-Arias, R., Müller, B.U. & Schechert, A. Near-Infrared Determination of Total Soluble Nitrogen and Betaine in Sugar Beet. Sugar Tech 19, 526–531 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-016-0496-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-016-0496-0