Abstract
This work was aimed to study the risk assessment of the different doses of transgenic sugarcane syrup employing a variety of short term genotoxic bioassays in mice. These assays were employed for the first time in this work to assess the possible genetic lesions induced by genetically modified crops (GMC). The genotoxic bioassays used: were estimation of cell proliferation activity, analysis of chromosomal abnormalities in mice bone-marrow cells, analysis of micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes in mice, analysis of mice primary spermatocytes and analysis of mice spermhead abnormalities. Analysis of amino acids revealed that there were significant differences between the tested sources (transgenic and non transgenic plants). However, aspartic acid, seriene, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, alanine, cystine, valine, methionine and isoleucine showed highly differences.
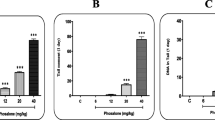
There were statistically significant differences in mitotic index and cell proliferation in bone marrow of animals treated (fed) with sugarcane transgenic syrup. It ranged from 1.1 to 6.5 % for the doses 5 and 0.5 g/kg b.wt., respectively. Analysis of chromosomal abnormalities in mice bone-marrow cells revealed that there were significant differences. The different types of aberrations observed were: stickiness, fragments, RCF or robertsonian centric fusion, deletion and ring chromosomes. Aberrations were significantly increased with the increasing dose of the tested syrup. Regarding the analysis of micronucleated polychromatic erthrocytes, the data showed that no significant increases in micronucleated polychromatic erythrocytes were achieved. The analysis of diakinesis stage revealed that transgenic sugarcane syrup was proven to be a positive inducer of chromosomal aberrations, giving important evidence that its effect reached germinal cells of mice and affected the genome, giving evidence that the present transgenic sugarcane syrup was found to clastogenic at the level of germinal cells. Examination of sperm head abnormalities showed that there were unknown substances in transgenic sugarcane syrup which interacted with sperm head differentiation. Variety of short-term genotoxic bioassays employed in this work have been extensively used for assessment of genetic lesions induced by environmental contaminants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler ID (1984) Cytogenetic test in Mammals, In: Mutagenicity testing a practical approach (Venitt S.; J. M. Parry and J. M. Eds).IRL press Oxford.
Au WW, Hsu TC (1980) The genotoxic effects of adriamycninmatic and germinal cells of mouse. Mutation Res. 79: 351–61.
Bender MA, Griges HG, Bedford US (1974) Recombinational DNA repair sister chromatid exchanges. Mutat Res. 24: 117–123.
Brewen JG, Preston RJ (1974) Cytogenetic effects of environmental mutagens in mammalian and extrapolation to man. Mutat Res. 26:297–300.
Bruce WR, Furrer R, Wyrobeck AJ (1974) Abnormalities in the shape of marine sperm after acute testicular x-irradiation. Mutat. Res. 23:381–386.
Bruce WR, Heddle JA (1979) The mutagenic activity of 61 as determined by the micronucleus, salmonella and sperm abnormality assay. Car. J. Genet. Cytol. 23: 319–333.
Brusick D (1999) Principles of genetic toxicology. Plenum press, N. Y.
Cohen JJ, Duke RC (1984) Glucocorticoid activation of a calciumdependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J. Immunol. 132: 38.
El-Seedy AS (2004) Cytogenetic alteration and tumour induction in mice by urethane and indoxan. M.Sc. Thesis., Dept. of Genetics, Faculty of Agriculture, Alexandria University.
Evans HJ (1978) What is sister chromatid exchanges? Chromosome Today 6: 315–326.
FAO/WHO (1991) Strategies for Assessing the Safety of Foods Produced by Biotechnology. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Consultation. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. http://www.fao.org/es/esn/gm/biotec-e.htm
FAO/WHO (1996) Biotechnology and Food Safety. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Consultation. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 61. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy. http://www.fao.org/es/esn/gm/biotec-e.htm
FAO/WHO (2000) Safety Aspects of Genetically Modified Foods of Plant Origin. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Foods Derived from Biotechnology, Geneva, Switzerland. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. http://www.fao.org/es/esn/gm/biotece.htm.
FAO/WHO (2001) Evaluation of Allergenicity of Genetically Modified Foods. Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Foods Derived from Biotechnology, Geneva, Switzerland. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome. http://www.fao.org/es/esn/gm/biotece.htm
FAO/WHO (2003) Launch expert report on diet, nutrition and prevention of chronic diseases. Public Health Nutr. 6(4):323–325.
Gallapudi B, Kamara OP (1979) Application of simple Gimsa-staning method in the micronucleus test. Mutat. Res. 64: 45–46.
Heddle HJ, Bruce WR (1977) One the use of multiple assays for mutagenicity, especially the micronucleus, salmonella and sperm abnormality assayas, in: D. Scott, B.A. Bridges and F.M. Sobel (eds). Progress and Genetic Toxicology, Elsevier, Springer-Verlag, New York; pp: 265–274.
IFBC (1990) Biotechnologies and food: Assuring the safety of foods produced by genetic modification. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 12: S1–S196.
Kuiper HA, Kleter GA, Noteburn HPJM, Kok EJ (2001) Assessment of the food safety issues related to genetically modified foods. Plant J. 27: 503–528.
Miroslave R, Jeggo P, Wagner R (1982) Chromosomal rearrangement and carcinogensis. Mutat. Res. 98:249–64.
Moore S, Stein HW (1958) Chromatography of amino acids on sulfonated polystyrene resins. Anal. Chem. 30:1185.
Muscat J, El-wynder E (1992) Tobacco, alcohol, asbestos and occupational risk factors for laryngeal cancer. Cancer 69: 2244–2251.
(NRC) National Research Council of National Academies (U.S.) Committee on Defining Science -based Concerns Associated with Products of Animal Biotechnology (2002) Animal Biotechnology: Science-based concerns. The National Academies Press, Washington D.C.,U.S.
OECD (1993) Safety Evaluation of Foods Derived by Modern Biotechnology: Concepts and Principles. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, Paris, http://www.oecd.org/pdf/M00034000/M00034525.pdf
OECD (1996) Food safety evaluation. Organization of Economic Cooperation and Development, Paris. http://www.oecd.org/pdf/ M00034000/M00034525.pdf
Oud JL, De Jong JH, De Rooiz DG (1979) Asequential analysis of meiosis in the male mouse using a restricted spermatocytes population obtained by a hydroxyurea, triaziquone treatment. Chromosomal. 71:237–248.
Schmid W (1975) The micronucleus test. Mutat. Res., 31: 9–15.
Seehy MA (1989a) Sister chromatid exchanges induced by lannate. Bull. High Inst. Pulic Health., XIX,4: 993–1000.
Seehy MA (1989b) Detection of sister chromatid exchanges in Allium cepa: A modified Staining technique. J. Agric. Sci., Mansoura Univ. 14(3): 1573–1577.
Seehy MA, Osman MA (1989) Evaluation of nystain genotoxicity: II Bone-marrow chromosomes: micronucleus test: primary spermatocytes and sister chromatid exchange. Bull Alex. Fac. Medicine, XXV, 6:1631–1636.
Seehy MA, Hafez A (1992) Genotoxicity of contraceptives. 1st International Conference on Environmental Mutagenesis on Human Population at Risk, Egypt. Cairo, January, 19–24.
Seehy MA, Youssef MK, El-Metainy AY, Badr EA (1989) Genetical and biochemical alterations induced by chlorpyrifos and paraquat dichloride. J. Agric. Sci., Mansoura Univ., 14(l): 186–197.
Seehy MA, Hafez A, Saber A (2007) Evaluation of fast foods genotoxicity. Egypt. J. Genet. Cytol. (In press).
Seehy M, Marwa (2003) DNA damage induced by Decis in human lymphocytes and experimental rodent’s genome. M.Sc. Thesis., Dept. of Genetics, Faculty of Agriculture, AlExanderia University.
Seehy M Marwa (2007) Micro and macro DNA lesions induced by some foods. Ph. D. degree, Dept. Genetics, Faculty of Agriculture, AlExanderia University.
Soares ER, Sheridan W, Haseman JK, Segall M (1979) Increases frequency of aberrant sperm as indicators of mutagenic damage in mice. mutat. Res. 64: 27–35.
Swanson CP, Mere T, Young WJ (1982) Cytogenetics: the chromosomes in division, inheritance and evolution. Prentice Hall of India New Delhi. 68.
Topham JC (1980a) The deletion of carcinogen induced sperm head abnormalities in mice. Mutat. Res. 69:149–155.
Topham JC (1980b) Chemically induced transmissible abnormalities in sperm head shape. Mutat. Res. 70:109–114.
Virgilio I, M Shuster (1996) fhit gene alternations in head and neck squamons cell carcinomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93: 9770–9775.
Wyrobeck AJ, Bruce WR (1975) Chemical induction of sperm abnormalities in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 71:4425–4429.
Wyrobeck AJ, Gordon LA, Burkhart LG, Francis MW, Kapp RW, Letz G, Malling HV, Topham JC, Whorton MD (1983 a) An evaluation of the mouse sperm morphology test and other sperm testes in non-human mammals: a report of the gene-tox program. Mutat. Res. 115: 1–72.
Wyrobeck AJ, Gordon LA, Burkhart LG, Francis MW, Kapp RW, Letz G, Malling HV, Topham JC, Whorton MD (1983 b) An evaluation of human sperm as indicators of chemically induced alternation of spermatobenic function. Mutat. Res. 115:73–148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badawy, O.M., El-Seehy, M.M., Saadalla, M.M. et al. Biosafety and risk assessment of transgenic sugarcane plants. Sugar Tech 10, 234–242 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-008-0042-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-008-0042-9