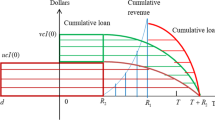
Abstract
In practice, to promote sales and alleviate the default risk of customers, the retailer frequently offers its good credit customers full trade credit while offers bad credit customers partial trade credit. In other words, both types of customers receive a credit period simultaneously, but the bad credit customers must pay a fraction of the purchase cost at the time of buying productions as a collateral deposit. By contrast, for the sake of self-interest, the supplier chooses to provide the partial trade credit for its retailer on account of reducing the credit risk. Numerous researchers assume that the retailer has the powerful decision-making right and he/she can obtain the full trade credit, however, very few academicians have studied that the supplier offers the retailer partial trade credit, which is more realistic and significant. In this paper, we establish an economic order quantity model for a retailer who receives a partial trade credit by its supplier, and offers a full or partial trade credit to its good or bad credit customers respectively based on the cost minimization of the retailer. Then, the optimal ordering strategy of the retailer under different conditions is given. Finally, through numerical examples and sensitivity analysis, we derive the influence of related parameters on retailer’s order decision and managerial insights.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annadurai K, Uthayakumar R (2012) Analysis of partial trade credit financing in a supply chain by eoq-based model for decaying items with shortages. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 61(9–12):1139–1159
Chen SC, Teng JT (2014) Retailer’s economic order quantity when the supplier offers conditionally permissible delay in payments link to order quantity. Int J Prod Econ 155:284–291
Chen SC, Teng JT, Skouri K (2014) Economic production quantity models for deteriorating items with up-stream full trade credit and down-stream partial trade credit. Int J Prod Econ 155(5):302–309
Chung KJ (1998) A theorem on the determination of economic order quantity under conditions of permissible delay in payments. Comput Oper Res 25(1):49–52
Giri BC, Maiti T (2013) Supply chain model with price- and trade credit-sensitive demand under two-level permissible delay in payments. Int J Syst Sci 44(5):937–948
Goyal SK (1985) Economic order quantity under conditions of permissible delay in payments. J Oper Res Soc 36(4):335–338
Huang YF (2003) Optimal retailer’s ordering policies in the eoq model under trade credit financing. J Oper Res Soc 54(9):1011–1015
Huang YF (2006) An inventory model under two levels of trade credit and limited storage space derived without derivatives. Appl Math Model 30(5):418–436
Huang YF, Hsu KH (2008) An eoq model under retailer partial trade credit policy in supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 112(2):655–664
Jaggi CK, Verma M, Kausar A (2010) Customer based two stage credit policies in a supply chain. Int J Logist Transp Res 1(2):1–12
Liao J, Huang K, Chung K, Ting P, Lin S, Srivastava HM (2017) Lot-sizing policies for deterioration items under two-level trade credit with partial trade credit to credit-risk retailer and limited storage capacity. Math Methods Appl Sci 40(6):2122–2139
Lou KR, Wang WC (2013) Optimal trade credit and order quantity when trade credit impacts on both demand rate and default risk. J Oper Res Soc 64(10):1551–1556
Mahata GC (2012) An epq-based inventory model for exponentially deteriorating items under retailer partial trade credit policy in supply chain. Expert Syst Appl 39(3):3537–3550
Mahata GC, Mahata P (2011) Analysis of a fuzzy economic order quantity model for deteriorating items under retailer partial trade credit financing in a supply chain. Math Comput Model 53(9–10):1621–1636
Pan YQ (2015) An EPQ model for muti-items under partial trade credit and limited storage capacity. In: Intelligent control and automation, pp 4976–4981
Sarkar B, Saren S (2015) An inventory model with trade-credit policy and variable deterioration for fixed lifetime products. Ann Oper Res 229(1):1–26
Soni HN, Joshi M (2013) A fuzzy framework for coordinating pricing and inventory policies for deteriorating items under retailer partial trade credit financing. Pergamon Press Inc, Oxford
Soni HN, Patel KA (2012) Optimal strategy for an integrated inventory system involving variable production and defective items under retailer partial trade credit policy. Decis Support Syst 54(1):235–247
Taleizadeh AA, Lashgari M, Akram R, Heydari J (2016) Imperfect economic production quantity model with upstream trade credit periods linked to raw material order quantity and downstream trade credit periods. Appl Math Model 40(19–20):8777–8793
Teng JT (2009) Optimal ordering policies for a retailer who offers distinct trade credits to its good and bad credit customers. Int J Prod Econ 119(2):415–423
Teng JT, Chang CT (2009) Optimal manufacturer’s replenishment policies in the epq model under two levels of trade credit policy. Eur J Oper Res 195(2):358–363
Teng JT, Min J, Pan Q (2012) Economic order quantity model with trade credit financing for non-decreasing demand. Omega 40(3):328–335
Thangam A (2012) Optimal price discounting and lot-sizing policies for perishable items in a supply chain under advance payment scheme and two-echelon trade credits. Int J Prod Econ 139(2):459–472
Tirole J (2006) The theory of corporate finance. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Wang Y, Sun X, Meng F (2016) On the conditional and partial trade credit policy with capital constraints: a Stackelberg model. Appl Math Model 40(1):1–18
Wu C (2016) Optimal trade credit period and lot size policies under default risk. In: Control conference, pp 9660–9665
Wu J, Chan YL (2014) Lot-sizing policies for deteriorating items with expiration dates and partial trade credit to credit-risk customers. Int J Prod Econ 155(5):292–301
Wu J, Ouyang LY, Cárdenas-Barrón LE, Goyal SK (2014) Optimal credit period and lot size for deteriorating items with expiration dates under two-level trade credit financing. Eur J Oper Res 237(3):898–908
Wu J, Al-Khateeb FB, Teng JT (2016) Inventory models for deteriorating items with maximum lifetime under downstream partial trade credits to credit-risk customers by discounted cash-flow analysis. Int J Prod Econ 171(Part1):105–115
Zhang C, Fan LW, Tian YX, Yang SM (2018) Optimal Credit Period and Lot Size Policies for a Retailer at Risk of Customer Default Under Two-Echelon Partial Trade Credit. IEEE Access 6:54295–54309. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2871838, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8470937/
Zia NP, Taleizadeh AA (2015) A lot-sizing model with backordering under hybrid linked-to-order multiple advance payments and delayed payment. Transp Res Part E 82:19–37
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank anonymous referees for their positive and constructive comments to improve the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Tian, Yx., Fan, Lw. et al. Optimal ordering policy for a retailer with consideration of customer credit under two-level trade credit financing. Oper Res Int J 21, 2409–2432 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-019-00505-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-019-00505-0