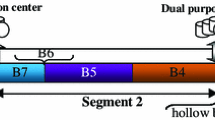
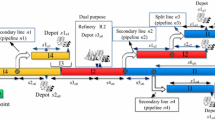
Abstract
Pipelines represent the most reliable and economical mode of fluid transportation in the petroleum supply chain. They are often multi-product systems and are extensively used to carry different types of petroleum derivatives from refineries to distribution depots. This paper addresses the optimal scheduling of a treelike pipeline that connects several refineries to multiple depots and that meets the customer demands over a multi-period planning horizon. A continuous time scheduling formulation based on a mixed integer linear programing framework is presented which allows intermediate nodes to act as dual purpose stations. The problem goal is to satisfy local market requirements on time while keeping the inventory levels at depot tanks within feasible ranges. Solutions to three case studies show remarkable reductions in the CPU time with regards to previous contributions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boschetto SN, Magatão L, Brondani WM et al (2010) An operational scheduling model to product distribution through a pipeline network. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:5661–5682
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2004) Optimal scheduling of multiproduct pipeline systems using a non-discrete MILP formulation. Comput Chem Eng 28:2053–2068
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2008) Dynamic scheduling of multiproduct pipelines with multiple delivery due dates. Comput Chem Eng 32:728–753
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2010) Operational scheduling of refined products pipeline networks with simultaneous batch injections. Comput Chem Eng 34:1687–1704
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2012a) A rigorous mathematical formulation for the scheduling of tree-structure pipeline networks. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:5064–5085
Cafaro DC, Cerdá J (2012b) Rigorous scheduling of mesh-structure refined petroleum pipeline networks. Comput Chem Eng 34:158–203
Cafaro VG, Cafaro DC, Mendéz CA et al (2012) Detailed scheduling of single-source pipelines with simultaneous deliveries to multiple offtake stations. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:6145–6165
Cafaro VG, Cafaro DC, Mendéz CA et al (2015a) MINLP model for the detailed scheduling of refined products pipelines with flow rate dependent pumping costs. Comput Chem Eng 72:210–221
Cafaro VG, Cafaro DC, Mendéz CA et al (2015b) Optimization model for the detailed scheduling of multi-source pipelines. Comput Ind Eng 88:395–409
Castro PM (2010) Optimal scheduling of pipeline systems with a resource-task network continuous-time formulation. Ind Eng Chem Res 49:11491–11505
Castro PM (2017) Optimal scheduling of multiproduct pipelines in networks with reversible flow. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:9638–9656
Castro PM, Mostafaei H (2017) Product-centric continuous-time formulation for pipeline scheduling. Comput Chem Eng 104:283–295
Chen H, Wu C, Zuo L et al (2017a) Optimization of detailed schedule for a multiproduct pipeline using a simulated annealing algorithm and heuristic rules. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:5092–5106
Chen H, Zuo L, Wu C et al (2017b) Optimizing detailed schedules of a multiproduct pipeline by a monolithic MILP formulation. J Pet Sci Eng 159:148–163
Fabro JA, Stebel SL, Rossato D et al (2014) A MILP (mixed integer linear programming) decomposition solution to the scheduling of heavy oil derivatives in a real-world pipeline. Comput Chem Eng 66:124–138
Ghaffari-Hadigheh AR, Mostafaei H (2015) On the scheduling of real world multiproduct pipeline with simultaneous delivery. Optim Eng 16:571–604
Hane CA, Ratliff HD (1995) Sequencing inputs to multi-commodity pipelines. Ann Oper Res 57:73–101
Herrán A, de la Cruz JM, de Andrés B (2010) Mathematical model for planning transportation of multiple petroleum products in a multi-pipeline system. Comput Chem Eng 34:401–413
Jones WMC, Paddock KF (1982) Transport by pipeline. In: Hobson GD (ed) Modern petroleum technology-Part I. Wiley, London
Magatão L, Arruda LVR, Neves FA (2004) A mixed integer programming approach for scheduling commodities in a pipeline. Comput Chem Eng 28:171–185
Magatão L, Arruda LVR, Neves F, Jr. (2011) A combined CLP-MILP approach for scheduling commodities in a pipeline. J Sched 14:57–87
Magatão SNB, Magatão L, Polli HL et al (2012) Planning and sequencing product distribution in a real-world pipeline network: an MILP decomposition approach. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:4591–4609
Magatão SNB, Magatão L, Neves F et al (2015) A novel MILP decomposition approach for scheduling product distribution through a pipeline network. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:5077–5095
MirHassani SA, Jahromi F (2011) Scheduling multi-product tree-structure pipelines. Comput Chem Eng 35:165–176
Mostafaei H, Castro PM (2017) Continuous-time scheduling formulation for straight pipeline. AICHE J 63:1923–1936
Mostafaei H, Ghaffari-Hadigheh AR (2014) A general modeling framework for the long-term scheduling of multiproduct pipelines with delivery constraints. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:7029–7042
Mostafaei H, Alipouri Y, Shokri J (2015a) A mixed-integer linear programming for scheduling a multi-product pipeline with dual-purpose terminals. Comput Appl Math 34:979–1007
Mostafaei H, Alipouri Y, Zadahmad M (2015b) A mathematical model for scheduling of real-world tree-structured multi-product pipeline system. Math Methods Oper Res 81:53–81
Mostafaei H, Castro PM, Ghaffari-Hadigheh A (2015c) A novel monolithic MILP framework for lot-sizing and scheduling of multiproduct tree-like pipeline networks. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:9202–9221
Mostafaei H, Castro PM, Ghaffari-Hadigheh AR (2016) Short-term scheduling of multiple source pipelines with simultaneous injections and deliveries. Comput Oper Res 73:27–42
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2003) Scheduling of a multiproduct pipeline system. Comput Chem Eng 27:1229–1246
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2004) Efficient MILP formulations and valid cuts for multiproduct pipeline scheduling. Comput Chem Eng 28:1511–1528
Rejowski R, Pinto JM (2008) A novel continuous time representation for the scheduling of pipeline systems with pumping yield rate constraints. Comput Chem Eng 32:1042–1066
Relvas S, Matos HM, Barbosa-Póvoa A et al (2006) Pipeline scheduling and inventory management of a multiproduct distribution oil system. Ind Eng Chem Res 45:7841–7855
Relvas S, Boschetto Magatão SN, Barbosa-Póvoa A et al (2013) Integrated scheduling and inventory management of an oil products distribution system. Omega 41:955–968
Sasikumar M, Prakash PR, Patil SM (1997) PIPES: a heuristic search model for pipeline schedule generation. Knowl Based Syst 10:169–175
Stebel SL, Magatao SNB, Arruda LVR et al (2012) Mixed integer linear programming formulation for aiding planning activities in a complex pipeline network. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:11417–11433
Taherkhani M, Seifbarghy M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R et al (2017) Mixed-integer linear programming model for tree-like pipeline scheduling problem with intermediate due dates on demands. Oper Res Int J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-017-0329-2
Zaghian A, Mostafaei H (2016) An MILP model for scheduling the operation of a refined petroleum products distribution system. Oper Res Int J 16:513–542
Zhang HR, Liang YT, Liao Q et al (2017) A hybrid computational approach for detailed scheduling of products in a pipeline with multiple pump stations. Energy 119:612–628
Zyngier D, Kelly JD (2009) Multi-product inventory logistics modeling in the process industries. Optim Logist Chall Enterp 30:61–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taherkhani, M. An MILP approach for scheduling of tree-like pipelines with dual purpose terminals. Oper Res Int J 20, 2133–2161 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0400-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0400-7