Abstract
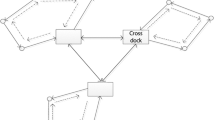
Cross-docking is a useful logistic practice used by many companies to reduce logistical costs. Cross-docking facilities are responsible for transferring products from suppliers to retailers and vice versa. Furthermore, vehicle routing is an important issue with regard to cross-docks. This paper investigates, for the first time, a vehicle routing problem in a distribution network with a cross-docking center by considering both forward and reverse logistics in an integrated model. In this regard, two strategies are presented to tackle the forward and reverse logistics. A mathematical model is developed for each strategy in order to find the best solution to transfer products from suppliers to retailers and then return products from retailers to suppliers through cross docks with minimum transportation cost. As the resulting mathematical model is NP-hard, a simulated annealing based heuristic algorithm is developed to optimize the model. Finally, these strategies are compared in terms of cost and the results demonstrate that the second strategy is superior to the first one.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agustina D, Lee CKM, Piplani R (2014) Vehicle scheduling and routing at a cross docking center for food supply chains. Int J Prod Econ 152:29–41
Alshamrani A, Mathur K, Ballou RH (2007) Reverse logistics: simultaneous design of delivery routes and returns strategies. Comput Oper Res 34(2):595–619
Chen P, Guo Y, Lim A, Rodrigues B (2006) Multiple cross docks with inventory and time windows. Comput Oper Res 33(1):43–63
Chopra S, Meindl P (2007) Supply chain management. Strategy, planning and operation. Pearson, London
Dethloff J (2001) Vehicle routing and reverse logistics: the vehicle routing problem with simultaneous delivery and pick-up. OR-Spektrum 23(1):79–96
Dondo R, Cerdá J (2013) A sweep-heuristic based formulation for the vehicle routing problem with cross-docking. Comput Chem Eng 48:293–311
Dondo R, Méndez CA, Cerdá J (2011) The multi-echelon vehicle routing problem with cross docking in supply chain management. Comput Chem Eng 35(12):3002–3024
Farahani RZ, Rezapour S, Drezner T, Fallah S (2014) Competitive supply chain network design: an overview of classifications, models, solution techniques and applications. Omega 45:92–118
Hosseini SD, Shirazi MA, Karimi B (2014) Cross-docking and milk run logistics in a consolidation network: a hybrid of harmony search and simulated annealing approach. J Manuf Syst 33(4):567–577
Kassem S, Chen M (2013) Solving reverse logistics vehicle routing problems with time windows. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 68:57–68
Kheirkhah A, Rezaei S (2016) Using cross-docking operations in a reverse logistics network design: a new approach. Prod Eng Res Devel 2(10):175–184
Kim H, Yang J, Lee KD (2009) Vehicle routing in reverse logistics for recycling end-of-life consumer electronic goods in South Korea. Transp Res Part D Transp Environ 14(5):291–299
Kirkpatrick S, Gelatt CD, Vecchi MP (1983) Optimization by simulated annealing. Science 220(4598):671–680
Lee YH, Jung JW, Lee KM (2006) Vehicle routing scheduling for cross-docking in the supply chain. Comput Ind Eng 51(2):247–256
Li Y, Lim A, Rodrigues B (2004) Crossdocking: JIT scheduling with time windows. J Oper Res Soc 55:1342–1351
Lim A, Miao Z, Rodrigues B, Xu Z (2005) Transshipment through crossdocks with inventory and time windows. Naval Res Logist (NRL) 52(8):724–733
Ma H, Miao Z, Lim A, Rodrigues B (2011) Crossdocking distribution networks with setup cost and time window constraint. Omega 39(1):64–72
Moghadam SS, Ghomi SF, Karimi B (2014) Vehicle routing scheduling problem with cross docking and split deliveries. Comput Chem Eng 69:98–107
Mousavi SM, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R (2013) A hybrid simulated annealing algorithm for location and routing scheduling problems with cross-docking in the supply chain. J Manuf Syst 32(2):335–347
Mousavi SM, Vahdani B, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Hashemi H (2014) Location of cross-docking centers and vehicle routing scheduling under uncertainty: a fuzzy possibilistic–stochastic programming model. Appl Math Model 38(7):2249–2264
Musa R, Arnaout JP, Jung H (2010) Ant colony optimization algorithm to solve for the transportation problem of cross-docking network. Comput Ind Eng 59(1):85–92
Ramos TRP, Gomes-Salema MI, Barbosa-Povoa AP (2009) A multi-product, multi-depot vehicle routing problem in a reverse logistics system: comparative study of an exact formulation and a heuristic algorithm. In: Livro de actas da 14º congresso da APDIO, IO2009, pp 195–202
Rogers DS, Tibben-Lembke RS (1999) Going backwards: reverse logistics trends and practices, vol 2. Reverse Logistics Executive Council, Pittsburgh, PA
Ryan TA, Joiner BL (1976) Normal probability plots and tests for normality. Minitab Statistical Software: Technical Reports. The Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA. Available from MINITAB
Santos FA, Mateus GR, Da Cunha AS (2013) The pickup and delivery problem with cross-docking. Comput Oper Res 40(4):1085–1093
Taguchi G (1986) Introduction to quality engineering. Asian Productivity Organization, Tokyo
Vahdani B, Zandieh M (2010) Scheduling trucks in cross-docking systems: robust meta-heuristics. Comput Ind Eng 58(1):12–24
Vahdani B, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Zandieh M, Razmi J (2012) Vehicle routing scheduling using an enhanced hybrid optimization approach. J Intell Manuf 23(3):759–774
Wen M, Larsen J, Clausen J, Cordeau JF, Laporte G (2009) Vehicle routing with cross-docking. J Oper Res Soc 60(12):1708–1718
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the editor and anonymous reviewers whose comments have helped to improved our paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaboudani, Y., Ghodsypour, S.H., Kia, H. et al. Vehicle routing and scheduling in cross docks with forward and reverse logistics. Oper Res Int J 20, 1589–1622 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0396-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12351-018-0396-z