Abstract
Background
To determine the capability of 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy to detect early cardiac involvement and predict clinical worsening in transthyretin (TTR) gene mutation patients.
Methods
Eleven mutated subjects with normal interventricular septum (IVS) thickness, NT-proBNP level and no cardiac symptoms underwent three seriate 99mTc-DPD scans (visually and semiquantitatively analyzed), and was followed-up for 5-8-years.
Results
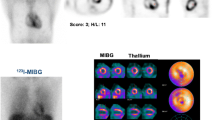
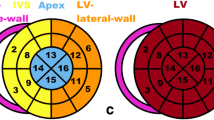
Six patients showed no myocardial accumulation in all scans. Increased IVS thickness occurring in one patient 4 years after the last scan was the only abnormal finding in these patients; no cardiac symptoms developed during the follow-up. In three patients, cardiac radiotracer uptake was found at enrollment; other laboratory/instrumental abnormal findings occurred later and cardiac symptoms developed during the follow-up period. Two patients had a negative 99mTc-DPD scan at enrollment and showed cardiac uptake in the following scans. Increased mean left-ventricular (LV) wall thickness was found 3 years after positive scintigraphy; NT-proBNP increased later in one patient. These patients developed cardiac symptoms during the follow-up period.
Conclusions
99mTc-DPD scan detects cardiac involvement in subjects with TTR gene mutation earlier than ECG, echocardiography and biochemical markers, occurring some years before the fulfillment of current diagnostic criteria for cardiac amyloidosis. A positive 99mTc-DPD scan predicts cardiac symptoms onset.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TTR:
-
Transthyretin
- IVS:
-
Interventricular septum
- Hattr:
-
Hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis
- FAP:
-
Familial amyloid polyneuropathy
- FAC:
-
Familial amyloidotic cardiomyopathy
- DPD:
-
3,3-diphosphono-1, 2-propanodicarboxylic acid
- NT-proBNP:
-
N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide
- PYP:
-
Pirophosphate
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiogram
- EF:
-
Ejection fraction
References
Rapezzi C, Quarta CC, Obici L, Perfetto F, Longhi S, Salvi F, et al. Disease profile and differential diagnosis of hereditary transthyretin-related amyloidosis with exclusively cardiac phenotype: An Italian perspective. Eur Heart J 2013;34:520-8.
Ando Y, Coelho T, Berk JL, Cruz MW, Ericzon BG, Ikeda S, et al. Guideline of transthyretin-related hereditary amyloidosis for clinicians. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2013;8:31.
Glaudemans AW, van Rheenen RW, van den Berg MP, Noordzij W, Koole M, Blokzijl H, et al. Bone scintigraphy with (99m)technetium-hydroxymethylene diphosphonate allows early diagnosis of cardiac involvement in patients with transthyretin-derived systemic amyloidosis. Amyloid 2014;21:35-44.
Castaño A, Drachman BM, Judge D, Maurer MS. Natural history and therapy of TTR-cardiac amyloidosis: Emerging disease-modifying therapies from organ transplantation to stabilizer and silencer drugs. Heart Fail Rev 2015;20:163-78.
Maurer MS, Schwartz JH, Gundapaneni B, Elliott PM, Merlini G, Waddington-Cruz M, et al. Tafamidis treatment for patients with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 2018;379:1007-16.
Benson MD, Waddington-Cruz M, Berk JL, Polydefkis M, Dyck PJ, Wang AK, et al. Inotersen treatment for patients with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 2018;379:22-31.
Adams D, Gonzalez-Duarte A, O’Riordan WD, Yang CC, Ueda M, Kristen AV, et al. Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 2018;379:11-21.
Arbustini E, Merlini G. Early identification of transthyretin-related hereditary cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2014;7:511-4.
Castano A, De Luca A, Weinberg R, Pozniakoff T, Blaner WS, Pirmohamed A, et al. Serial scanning with technetium pyrophosphate (99mTc-PYP) in advanced ATTR cardiac amyloidosis. J Nucl Cardiol 2016;23:1355-63.
Di Bella G, Pizzino F, Minutoli F, Zito C, Donato R, Dattilo G, et al. The mosaic of the cardiac amyloidosis diagnosis: role of imaging in subtypes and stages of the disease. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2014;15:1307-15.
Kristen AV, Scherer K, Buss S, aus dem Siepen F, Haufe S, Bauer R, et al. Noninvasive risk stratification of patients with transthyretin amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2014;7:502-10.
Rapezzi C, Quarta CC, Guidalotti PL, Longhi S, Pettinato C, Leone O, et al. Usefulness and limitations of acid scintigraphy in the aetiological diagnosis of amyloidotic cardiomyopathy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011;38:470-8.
Rapezzi C, Quarta CC, Guidalotti PL, Pettinato C, Fanti S, Leone O, et al. Role of (99m)Tc-DPD scintigraphy in diagnosis and prognosis of hereditary transthyretin-related cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2011;4:659-70.
Minutoli F, Di Bella G, Sindoni A, Vita G, Baldari S. Effectiveness of skeletal scintigraphy in transthyretin-related amyloidosis. Int J Cardiol 2013;168:4988-9.
Minutoli F, Di Bella G, Mazzeo A, Donato R, Russo M, Scribano E, et al. Comparison between (99m)Tc-diphosphonate imaging and MRI with late gadolinium enhancement in evaluating cardiac involvement in patients with transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013;200:W256-65.
Russo M, Mazzeo A, Stancanelli C, Di Leo R, Gentile L, Di Bella G, et al. Transthyretin-related familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: Description of a cohort of patients with Leu64 mutation and late onset. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2012;17:385-90.
Hutt DF, Quigley AM, Page J, Hall ML, Burniston M, Gopaul D, et al. Utility and limitations of 3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid scintigraphy in systemic amyloidosis. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 2014;15:1289-98.
Kristen AV, Haufe S, Schonland SO, Hegenbart U, Schnabel PA, Röcken C, et al. Skeletal scintigraphy indicates disease severity of cardiac involvement in patients with senile systemic amyloidosis. Int J Cardiol 2013;164:179-84.
Gillmore JD, Maurer MS, Falk RH, Merlini G, Damy T, Dispenzieri A, et al. Nonbiopsy diagnosis of cardiac transthyretin amyloidosis. Circulation 2016;133:2404-12.
Minutoli F, Di Bella G, Vita G, Laudicella R, Bogaert J, Baldari S. Non invasive cardiac imaging in patients with systemic amyloidosis: A practical approach with emphasis on clinical contribution of bone-seeking radiotracers. Clinical and Translational Imaging 2017;5:545-59.
Mazzeo A, Russo M, Di Bella G, Minutoli F, Stancanelli C, Gentile L, et al. Transthyretin-related familial amyloid polyneuropathy (TTR-FAP): A single-center experience in sicily, an Italian endemic area. J Neuromuscul Dis 2015;2:S39-48.
Gertz M, Merlini G. Definition of organ involvement and response to treatment in AL amyloidosis: An updated consensus opinion (abstr CP B). Amyloid 2010;17(Suppl 1):48-9.
Graceffa A, Russo M, Vita GL, Toscano A, Dattola R, Messina C, et al. Psychosocial impact of presymptomatic genetic testing for transthyretin amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Neuromuscul Disord 2009;19:44-8.
Banypersad SM, Moon JC, Whelan C, Hawkins PN, Wechalekar AD. Updates in cardiac amyloidosis: A review. J Am Heart Assoc 2012;1:e000364.
Schiller NB, Shah PM, Crawford M, DeMaria A, Devereux R, Feigenbaum H, et al. Recommendations for quantitation of the left ventricle by two-dimensional echocardiography. American Society of Echocardiography Committee on Standards, Subcommittee on Quantitation of Two-Dimensional Echocardiograms. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1989;2:358-67.
Perugini E, Guidalotti PL, Salvi F, Cooke RM, Pettinato C, Riva L, et al. Noninvasive etiologic diagnosis of cardiac amyloidosis using 99mTc-3,3-diphosphono-1,2-propanodicarboxylic acid scintigraphy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2005;46:1076-84.
Puille M, Altland K, Linke RP, Steen-Muller MK, Kiett R, Steiner D, et al. 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy in transthyretin-related familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:376-9.
Di Bella G, Minutoli F, Piaggi P, Casale M, Mazzeo A, Zito C, et al. Usefulness of combining electrocardiographic and echocardiographic findings and brain natriuretic peptide in early detection of cardiac amyloidosis in subjects with transthyretin gene mutation. Am J Cardiol 2015;116:1122-7.
Vita G, Vita GL, Stancanelli C, Gentile L, Russo M, Mazzeo A. Genetic neuromuscular disorders: living the era of a therapeutic revolution. Part 1: Peripheral neuropathies. Neurol Sci 2019;40:661-9.
Galat A, Van der Gucht A, Guellich A, Bodez D, Cottereau AS, Geundouz S, et al. Early phase 99mTc-HMDP scintigrapgy for the diagnosis and typing of cardiac amyloidosis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2017;10:601-3.
Hutt DF, Fontana M, Burniston M, Quigley AM, Petrie A, Ross JC, et al. Prognostic utility of the Perugini grading of 99mTc-DPD scintigraphy in transthyretin (ATTR) amyloidosis and its relationship with skeletal muscle and soft tissue amyloid. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2017;18:1344-50.
Acknowledgements
None.
Disclosure
Minutoli F, Di Bella G, Mazzeo A, Laudicella R, Gentile L, Russo M and Baldari S have nothing to disclose and they have no relevant or material financial interests that can relate to the research described in this paper. Vita G. discloses having been on advisory board for Alnylam Therap., Akcea Therap, and Pfizer. He is also principal investigator in clinical trials sponsored by Alnylam Therap and Ionis Therap.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors of this article have provided a PowerPoint file, available for download at SpringerLink, which summarizes the contents of the paper and is free for re-use at meetings and presentations. Search for the article DOI on SpringerLink.com.
All editorial decisions for this article, including selection of reviewers and the final decision, were made by guest editor Nagara Tamaki, MD.
Funding
Minutoli F, Di Bella G, Mazzeo A, Laudicella R, Gentile L, Russo M, Vita G and Baldari S declare that they did not receive any financial support for this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minutoli, F., Di Bella, G., Mazzeo, A. et al. Serial scanning with 99mTc-3, 3-diphosphono-1, 2-propanodicarboxylic acid (99mTc-DPD) for early detection of cardiac amyloid deposition and prediction of clinical worsening in subjects carrying a transthyretin gene mutation. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 28, 1949–1957 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-019-01950-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-019-01950-2