Abstract
Background
Stomach wall uptake (SWU) of tracer in 99mTc-MIBI myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) occasionally leads to imaging artifacts, thereby lowering the diagnostic accuracy. It is less-studied phenomenon for possible link with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) intake. This prospective work looked for association of SWU with PPI intake and compared its incidence with H2 antagonists (H2A) users and patients not on either gastroprotective medication.
Methods
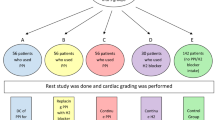
One hundred fifty-six patients undergoing one day stress/rest 99mTc-MIBI SPECT-MPI were distributed into four groups: control group (n = 48, not on any gastroprotective medication), PPI group (n = 47, on PPI treatment), H2A group (n = 19, on H2A therapy), and intervention group (N = 42, PPI discontinued for 3 days before MPI). Poststress planar images were analyzed for clinically relevant SWU.
Results
Clinically relevant SWU was seen in 36% of PPI group patients compared to 8% in the control group, 10.5% in the H2A group, and 9.5% in the intervention group, respectively, with statistically significant difference. Only 1/40 patients undergoing exercise stress showed clinically relevant SWU compared to 26/116 patients undergoing adenosine stress (P = .020).
Conclusion
Patients on PPIs scheduled for vasodilator stress MPI may discontinue PPIs for 3 days, or replace with H2A to reduce the incidence of clinically relevant SWU associated with PPI therapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MPI:
-
Myocardial perfusion imaging
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery disease
- MIBI:
-
Methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile
- SWU:
-
Stomach wall uptake
- PPIs:
-
Proton pump inhibitors
- H2A:
-
H2 antagonists
- SPECT:
-
Single photon emission computed tomography
- TMT:
-
Treadmill test
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
References
Burrell S, MacDonald A. Artefacts and pitfalls in myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med Technol 2006;34:193-211.
Peace R, Lloyd J. The effect of imaging time, radiopharmaceutical, full fat milk and water on interfering extra-cardiac activity in myocardial perfusion single photon emission computed tomography. Nucl Med Commun 2005;26:17-24.
Boz A, Yildiz A, Güngör F, Karayalçin B, Erkiliç M. The volume effect of the stomach on intestinal activity on same-day exercise-rest Tc-99m tetrofosmin myocardial imaging. Clin Nucl Med 2001;26:622-5.
Germano G, Chua T, Kiat H, Areeda JS, Berman DS. A quantitative phantom analysis of artefacts due to hepatic activity in technetium-99m myocardial perfusion SPECT studies. J Nucl Med 1994;35:356-9.
Hofman M, McKay J, Nandurkar D. Efficacy of milk versus water to reduce interfering infra-cardiac activity in 99mTc-sestamibi myocardial perfusion imaging. Nucl Med Commun 2006;27:837-42.
Hambye AS, Delsarte P, Vervaet A. Influence of the different biokinetics of sestamibi and tetrofosmin on the interpretation of myocardial perfusion imaging in daily practice. Nucl Med Commun 2007;28:383-90.
Côté C, Dumont M. The clinical meaning of gastric-wall hyperactivity observed on sestamibi cardiac single-photon emission computed tomography. Can Assoc Radiol J 2004;55:178-83.
Gholamrezanezhad A, Moinian D, Eftekhari M, Mirpour S, Hajimohammadi H. The prevalence and significance of increased gastric wall radiotracer uptake in sestamibi myocardial perfusion SPECT. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 2006;22:435-41.
Goel S, Bommireddipalli S, DePuey E. Effect of proton pump inhibitors and H2 antagonists on the stomach wall in 99mTc-sestamibi cardiac imaging. J Nucl Med Technol 2009;37:240-3.
Mouden M, Rijkee K, Schreuder N, Timmer J, Jager P. Influence of proton-pump inhibitors on stomach wall uptake of 99mTc-tetrofosmin in cadmium–zinc–telluride SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging. Nucl Med Commun 2015;36:143-7.
Javadi H, Jallalat S, Semnani S, Mogharrabi M, Nabipour I, Tabib S, et al. The association of increased stomach wall radiotracer uptake with prolonged use of Omeprazole capsules on myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) using 99mTc-sestamibi SPECT. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur 2013;16:91-4.
Henzlova M, Duvall W, Einstein A, Travin M, Verberne H. ASNC imaging guidelines for SPECT nuclear cardiology procedures: Stress, protocols, and tracers. J Nucl Cardiol 2016;23:606-39.
Van Dongen AJ, Van Rijk PP. Minimizing liver, bowel, and gastric activity in myocardial perfusion SPECT. J Nucl Med 2000;41:1315-7.
Hurwitz GA, Clark EM, Slomka PJ, Siddiq SK. Investigations of measures to reduce interfering abdominal activity on rest myocardial images with Tc-99msestamibi. Clin Nucl Med 1993;18:735-41.
Sood A, Singh D, Dutta U, Mittal BR, Parmar M, Kaur G, et al. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in facilitating early hepatic clearance of radiotracer among patients undergoing 99mTc-sestamibi myocardial perfusion scintigraphy: A randomized double blind placebo controlled parallel trial. J Nucl Cardiol 2019;45:78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-019-01597-z.
Vanderhoff BT, Tahboub RM. Proton pump inhibitors: An update. Am Fam Phys 2002;66:273-80.
Sachs G. Proton pump inhibitors and acid-related diseases. Pharmacotherapy 1997;17:22-37.
Chaudhry AS, Kochhar R, Kohli KK. Genetic polymorphism of CYP2C19 & therapeutic response to proton pump inhibitors. Indian J Med Res 2008;127:521-30.
Klotz U, Schwab M, Treiber G. CYP2C19 polymorphism and proton pump inhibitors. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2004;95:2-8.
Redzic ZB, Hasan FA, Al-Sarraf H. Effects of omeprazole treatment on nucleoside transporter expression and adenosine uptake in rat gastric mucosa. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2009;87:402-10.
Yip L, Kwok YN. Role of adenosine A2A receptor in the regulation of gastric somatostatin release. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2004;309:804-15.
Acknowledgment
The authors kindly acknowledge the invaluable inputs and guidance from Prof Inderjit Singh Anand, Cardiologist, Minneapolis, MN (USA) and Prof Suresh Kumar Sharma, Department of Statistics, Panjab University, Chandigarh (India).
Disclosure
Drs Harpreet Singh, Ashwani Sood, Bhagwant Rai Mittal, Neeraja Bollampally, Arun Kumar Reddy Gorla, Vaishnavi Dasagrandhi, Madan Parmar have nothing to disclose. No financial support was received for the publication of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors of this article have provided a PowerPoint file, available for download at SpringerLink, which summarizes the contents of the paper and is free for re-use at meetings and presentations. Search for the article DOI on SpringerLink.com.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, H., Mittal, B.R., Sood, A. et al. Association of use of proton pump inhibitors and H2 antagonists with stomach wall uptake in 99mTc-methoxy-isobutyl-isonitrile (MIBI) myocardial perfusion imaging. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 27, 1611–1619 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-019-01733-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-019-01733-9