Abstract
Background
We previously described the feasibility of myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) with nearly half the radiation dose using ordered-subset expectation maximization with resolution recovery (OSEM-RR) processing. This study sought to determine if the findings can be expanded to obese patients.
Methods
Fifty obese patients (>100 kg) referred for MPI underwent stress-rest or rest-stress studies with a half dose of Tc-99m sestamibi in a 1-day protocol using OSEM-RR processing. Image quality and clinical results were compared with matched patients (by age, sex, weight, presence/probability of coronary artery disease) evaluated with standard “full-dose” Tc-99m sestamibi, mostly in a 2-day protocol. Dose activities were adjusted individually by weight.
Results
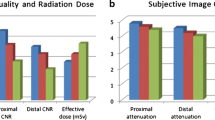
Mean Tc-99m activity was 33.4 ± 13.9 mCi in the half-dose group and 60 ± 10 mCi in the full-dose group (P < .0001). Respective mean effective doses per study were 10 ± 4 and 18 ± 3 mSv (P < .0001). Overall image quality was good-to-excellent in 94% of the half-dose group and 80% of the full-dose group (P < .045). There was no between-group difference in rate or size of ischemia or infarction, except for stress left ventricular ejection fraction.
Conclusions
MPI with half the radiation dose is feasible in obese patients. Image quality is better than for full-dose MPI, and the procedure can be performed in 1 day.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Einstein JE, Moser KW, Thompson RC, Cerqueira MD, Henzlova MJ. Radiation dose to patients from cardiac diagnostic imaging. Circulation 2007;116:1290-305.
Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang Y, Ross JS, Chen J, Ting HH, et al. Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures. N Engl J Med 2009;361:849-57.
Chen J, Einstein AJ, Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang Y, Ross TS, et al. Cumulative exposure to ionizing radiation from diagnostic and therapeutic cardiac imaging: A population-based analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;56:702-11.
Committee to Assess Health Risks from Exposure to Low Levels of Ionizing Radiation, National Research Council. Health risks from exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation: BEIR VII Phase 2. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2006.
Berrington de Gonzalez A, Kim K-P, Smith-Bindman R, McAreavey D. Myocardial perfusion scans. Projected population cancer risk from current levels of use in the United States. Circulation 2010;122:2403-10.
Hendel RC, Berman DS, Di Carli MF, Heidenreich PA, Henkin PE, Pellikka PA, et al. Appropriate use criteria for cardiac radionuclide imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 2009;53:2201-29.
Ward RP, Al-Mallah MH, Grossman GB. American society of nuclear cardiology review of the ACCF/ASNC appropriateness criteria for single-photon emission computed tomography myocardial perfusion imaging (SPECT MPI). J Nucl Cardiol 2007;14:e26-38.
Cequeira MD, Allman KV, Ficaro EP, Hansen CL, Nichols KJ, Thompson RC, et al. Recommendations for reducing radiation exposure in myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Cardiol 2010;17:709-18.
Beller GA. Importance of consideration of radiation doses from cardiac imaging procedures and risks of cancer. J Nucl Cardiol 2010;17:1-3.
Henzlova MJ, Cerqueira MD, Hansen CL, Taillefer R, Yao S. ASNC imaging guidelines for nuclear cardiology procedures: Stress protocols and tracers. J Nucl Cardiol 2009;16. doi: 10.1007/s12350-009-9062-4.
DePuey EG, Taillefer R, Gadiraju R, Anstett F. A clinical evaluation of two resolution recovery methods for reduced scan time of gated MPI SPECT. Presented as a Late Breaking Clinical Trial Abstract, ASNC, St. Luke’s-Roosevelt, New York, NY, 2006.
Borges-Neto S, Pagnanelli RA, Shaw LK, Honeycutt E, Shwartz SC, Adams CL, et al. Clinical results of a novel wide beam reconstruction method for shortening scan time of Tc-99m cardiac SPECT perfusion studies. J Nucl Cardiol 2007;14:555-65.
DePuey EG, Gadiraju R, Clark J, Thompson L, Anstett F, Shwartz S. Ordered subset expectation maximization and wide beam reconstruction “half time” gated myocardial perfusion SPECT functional imaging: A comparison to “full-time” filtered backprojection. J Nucl Cardiol 2008;15:547-63.
Ali I, Ruddy TD, Almgrahi A, Anstett FG, Wells RG. Half time SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging with attenuation correction. J Nucl Med 2009;50:554-62.
Duvall WL, Croft LB, Godiwala T, Ginsberg T, Henzlova MJ. Reduced isotope dose with rapid SPECT MPI imaging: Initial experience with a CZT SPECT. J Nucl Cardiol 2010;17:1009-14.
DePuey EG, Bommireddipalli S, Clark J, Leykekhman A, Thompson LB, Friedman M. A comparison of the image quality of full time myocardial perfusion SPECT vs. wide beam reconstruction half time and half dose SPECT. J Nucl Cardiol 2011;18:273-80.
“Evolution for cardiac” (White Paper). GE Healthcare, 2007. http://www.gehealthcare.com.
Zafrir N, Yuzefovich B, Mats I, Solodky A, Blazar A, Battler A. A novel method to reduce the acquisition time of myocardial perfusion SPECT scan: A comparative study. [Abstract] Presented at the ICNC 9, Barcelona, Spain, May 2009.
Zafrir N, Solodky A, Ben-Shlomo A, Mats I, Nevzorov R, Battler A, Gutstein A. Feasibility of myocardial perfusion imaging with half the radiation dose in obese patients using ordered subset expectation maximization with resolution recovery software. J Nucl Cardiol 2012;19. doi:10.1007/s12350-012-9552-7.
Holly TA, Abbott BG, Al-Mallah M, Calnon DA, Cohen MC, DiFilippo FP, et al. ASNC guidelines for nuclear cardiology procedures. Single photon emission computed tomography. J Nucl Cardiol 2010;17:941-73.
DePuey EC, Garcia EV. Updated imaging guidelines for nuclear cardiology procedures. J Nucl Cardiol 2001;8:G5-56.
Radiation dose to patients from radiopharmaceuticals (addendum 2 to ICRP publication 53). ICRP publication 80. Ann ICRP 1998; 28:1-126.
Berman DS, Avidov A, Kang X, Hayes SW, Friedman D, Sciammarella MG, et al. Prognostic validation of a 17-segment score derived from a 20 segment score for myocardial perfusion SPECT interpretation. J Nucl Cardiol 2004;11:414-23.
Iskandrian AE. Risk assessment of stable patients (panel 3) in winter green panel summaries. J Nucl Cardiol 1999;6:93.
Conflict of interest
The authors have indicated that they have no financial conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zafrir, N., Bental, T., Solodky, A. et al. Feasibility of myocardial perfusion imaging with half the radiation dose in obese patients using ordered-subset expectation maximization with resolution recovery software. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 20, 111–119 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-012-9650-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-012-9650-6