Abstract
Background
Cadmium Zinc Telluride (CZT) SPECT camera technology has the potential to reduce patient’s radiation exposure and shorten imaging time. This study evaluated the correlation of low stress tracer dose, rapid CZT SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) to coronary angiography in a <200-lbs population to further validate its ability to achieve both goals while preserving diagnostic accuracy.
Methods
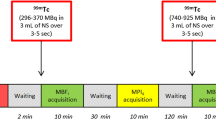
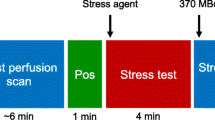
All patients who had a low-dose stress (≤15 mCi) Tc-99m sestamibi SPECT MPI study using a CZT camera (GE Discovery NM 530c) with 3- to 5-minute image acquisition over a 2-year period followed by a coronary angiogram within 2 months were included. Patients with a history of coronary revascularization, left ventricular dysfunction, and LBBB or paced rhythms were excluded. Both MPI studies and coronary angiograms were interpreted by blinded readers and coronary artery disease (CAD) was defined as ≥70% stenosis.
Results
A total of 71 patients were included with a mean age of 64 years, 55% male, and a BMI of 25.4 kg/m2 with an average stress dose of 13.3 mCi. Exercise stress was performed in 54% of patients and vasodilator pharmacologic stress in 46%. Sensitivity was 89%, specificity was 66%, and accuracy was 78% for detecting obstructive CAD.
Conclusions
In this group of non-obese patients undergoing low stress dose imaging, high-efficiency CZT SPECT imaging demonstrated a high sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy for detecting obstructive epicardial CAD with a greatly reduced imaging time.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garcia EV, Faber TL, Esteves FP. Cardiac dedicated ultrafast SPECT cameras: New designs and clinical implications. J Nucl Med 2011;52:210-7.
Einstein AJ, Moser KW, Thompson RC, Cerqueira MD, Henzlova MJ. Radiation dose to patients from cardiac diagnostic imaging. Circulation 2007;116:1290-305.
Henzlova MJ, Duvall WL. The future of SPECT MPI: Time and dose reduction. J Nucl Cardiol 2011;18:580-7.
Sharir T, Ben-Haim S, Merzon K, Prochorov V, Dickman D, Berman DS. High-speed myocardial perfusion imaging initial clinical comparison with conventional dual detector anger camera imaging. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2008;1:156-63.
Sharir T, Slomka PJ, Hayes SW, DiCarli MF, Ziffer JA, Martin WH, et al. Multicenter trial of high-speed versus conventional single-photon emission computed tomography imaging: Quantitative results of myocardial perfusion and left ventricular function. J Am Coll Cardiol 2010;55:1965-74.
Esteves FP, Raggi P, Folks RD, Keidar Z, Askew JW, Rispler S, et al. Novel solid-state-detector dedicated cardiac camera for fast myocardial perfusion imaging: Multicenter comparison with standard dual detector cameras. J Nucl Cardiol 2009;16:927-34.
Buechel RR, Herzog BA, Husmann L, Burger IA, Pazhenkottil AP, Treyer V, et al. Ultrafast nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging on a new gamma camera with semiconductor detector technique: First clinical validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:773-8.
Herzog BA, Buechel RR, Katz R, Brueckner M, Husmann L, Burger IA, et al. Nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging with a cadmium-zinc-telluride detector technique: Optimized protocol for scan time reduction. J Nucl Med 2010;51:46-51.
Gimelli A, Bottai M, Giorgetti A, Genovesi D, Kusch A, Ripoli A, et al. Comparison between ultrafast and standard single-photon emission CT in patients with coronary artery disease: A pilot study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2011;4:51-8.
Songy B, Lussato D, Guernou M, Queneau M, Geronazzo R. Comparison of myocardial perfusion imaging using thallium-201 between a new cadmium-zinc-telluride cardiac camera and a conventional SPECT camera. Clin Nucl Med 2011;36:776-80.
Duvall WL, Croft LB, Godiwala T, Ginsberg E, George T, Henzlova MJ. Reduced isotope dose with rapid SPECT MPI imaging: Initial experience with a CZT SPECT camera. J Nucl Cardiol 2010;17:1009-14.
Duvall WL, Croft LB, Ginsberg ES, Einstein AJ, Guma KA, George T, et al. Reduced isotope dose and imaging time with a high efficiency CZT SPECT camera. J Nucl Cardiol 2011;18:847-57.
Nkoulou R, Pazhenkottil AP, Kuest SM, Ghadri JR, Wolfrum M, Husmann L, et al. Semiconductor detectors allow low-dose-low-dose 1-day SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging. J Nucl Med 2011;52:1204-9.
Nakazato R, Tamarappoo BK, Kang X, Wolak A, Kite F, Hayes SW, et al. Quantitative upright-supine high-speed SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging for detection of coronary artery disease: Correlation with invasive coronary angiography. J Nucl Med 2010;51:1724-31.
Duvall WL, Sweeny JM, Croft LB, Barghash MH, Kulkarni NK, Guma KA, et al. Comparison of high efficiency CZT SPECT MPI to coronary angiography. J Nucl Cardiol 2011;18:595-604.
Fiechter M, Ghadri JR, Kuest SM, Pazhenkottil AP, Wolfrum M, Nkoulou RN, et al. Nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging with a novel cadmium-zinc-telluride detector SPECT/CT device: First validation versus invasive coronary angiography. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011;38:2025-30.
Gimelli A, Bottai M, Genovesi D, Giorgetti A, Di Martino F, Marzullo P. High diagnostic accuracy of low-dose gated-SPECT with solid-state ultrafast detectors: Preliminary clinical results. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2011. Sept 2 [Epub ahead of print].
Hansen CL, Goldstein RA, Berman DS, Churchwell KB, Cooke CD, Corbett JR, et al. Myocardial perfusion and function single photon emission computed tomography. J Nucl Cardiol 2006;13:e97-120.
Henzlova MJ, Cerqueira MD, Hansen CL, Taillefer R, Yao SS. ASNC Imaging Guidelines for nuclear cardiology procedures: Stress protocols and tracers. J Nucl Cardiol 2009;16:331.
Henzlova MJ, Cerqueira MD, Mahmarian JJ, Yao SS. Stress protocols and tracers. J Nucl Cardiol 2006;13:e80-90.
Hendel RC, Berman DS, Di Carli MF, Heidenreich PA, Henkin RE, Pellikka PA, et al. ACCF/ASNC/ACR/AHA/ASE/SCCT/SCMR/SNM 2009 appropriate use criteria for cardiac radionuclide imaging: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriate Use Criteria Task Force, the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology, the American College of Radiology, the American Heart Association, the American Society of Echocardiography, the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography, the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, and the Society of Nuclear Medicine. Circulation 2009;119:e561-87.
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Laskey WK, et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart: A statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. J Nucl Cardiol 2002;9:240-5.
Fazel R, Krumholz HM, Wang Y, Ross JS, Chen J, Ting HH, et al. Exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation from medical imaging procedures. N Engl J Med 2009;361:849-57.
Berrington de Gonzalez A, Kim KP, Smith-Bindman R, McAreavey D. Myocardial perfusion scans: Projected population cancer risks from current levels of use in the United States. Circulation 2010;122:2403-10.
Cerqueira MD, Allman KC, Ficaro EP, Hansen CL, Nichols KJ, Thompson RC, et al. ASNC Information Statement: Recommendations for reducing radiation exposure in myocardial perfusion imaging 2010. http://www.asnc.org/imageuploads/RadiationReduction060110.pdf.
Borges-Neto S, Pagnanelli RA, Shaw LK, Honeycutt E, Shwartz SC, Adams GL, et al. Clinical results of a novel wide beam reconstruction method for shortening scan time of Tc-99m cardiac SPECT perfusion studies. J Nucl Cardiol 2007;14:555-65.
Depuey EG, Bommireddipalli S, Clark J, Leykekhman A, Thompson LB, Friedman M. A comparison of the image quality of full-time myocardial perfusion SPECT vs wide beam reconstruction half-time and half-dose SPECT. J Nucl Cardiol 2011;18:273-80.
Herzog BA, Husmann L, Buechel RR, Pazhenkottil AP, Burger IA, Valenta I, et al. Rapid cardiac hybrid imaging with minimized radiation dose for accurate non-invasive assessment of ischemic coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiol 2010;153:10-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duvall, W.L., Sweeny, J.M., Croft, L.B. et al. Reduced stress dose with rapid acquisition CZT SPECT MPI in a non-obese clinical population: Comparison to coronary angiography. J. Nucl. Cardiol. 19, 19–27 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-011-9480-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12350-011-9480-y