Abstract
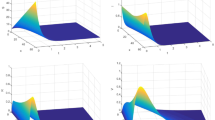
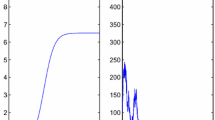
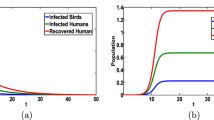
In order to reveal the transmission dynamics of Avian influenza and explore effective control measures, we develop a non-local delayed reaction-diffusion model of Avian influenza with vaccination and multiple transmission routes in the heterogeneous spatial environment, taking into account the incubation period of Avian influenza in humans and poultry. Firstly, the well-posedness of model is obtained which includes the existence, uniform boundedness and the existence of global attractor. Further, the basic reproduction number \({\mathcal {R}}_0 \) of this model is calculated by the definition of the spectral radius of the next generation operator, and its variational form is also derived. Further, the global dynamics of the model is established based on the biological significance of \({\mathcal {R}}_0 \). To be more precise, if \({\mathcal {R}}_0<1\), the disease-free steady state is globally asymptotically stable (i.e., the disease is extinct), while if \({\mathcal {R}}_0>1\), the disease is uniformly persistent and model admits at least one endemic steady state. In addition, by constructing suitable Lyapunov functionals, we achieve the global asymptotic stability of the disease-free and endemic steady states of this model in spatially homogeneous. Finally, some numerical simulations illustrate the main theoretical results, and discuss the sensitivity of \({\mathcal {R}}_0 \) on the model parameters and the influences of non-local delayed and diffusion rates on the transmission of Avian influenza. The theoretical results and numerical simulations show that prolonging the incubation period, controlling the movement of infected poultry, and regular disinfecting the environment are all effective ways to prevent Avian influenza outbreaks.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
https://www.chp.gov.hk/files/pdf/2022 avian influenza report vol18 wk46 chi.pdf
Iwami, S., Takeuchi, Y., Liu, X.: Avian-human influenza epidemic model. Math. Biosci. 207, 1–25 (2007)
Agusto, F., Gumel, A.: Theoretical assessment of avian influenza vaccine. Discret. Cont. Dyn. B 13, 1–25 (2010)
Feukouo Fossi, A., Lubuma, J., Tadmon, C., Tsanou, B.: Mathematical modeling and nonstandard finite difference scheme analysis for the environmental and spillover transmissions of Avian Influenza A model. Dyn. Syst. 36, 212–255 (2021)
Iwami, S., Takeuchi, Y., Korobeinikov, A., Liu, X.: Prevention of avian influenza epidemic: what policy should we choose? J. Theor. Biol. 252, 732–741 (2008)
Iwami, S., Takeuchi, Y., Liu, X., Nakaoka, S.: A geographical spread of vaccine-resistance in avian influenza epidemics. J. Theor. Biol. 259, 219–228 (2009)
Chen, Y., Wen, Y.: Global dynamic analysis of a H7N9 avian-human influenza model in an outbreak region. J. Theor. Biol. 367, 180–188 (2015)
Liu, Z., Fang, C.: A modeling study of human infections with avian influenza A H7N9 virus in mainland China. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 41, 73–78 (2015)
Guo, S., Wang, J., Ghost, M., Li, X.: Analysis of avian influenza A (H7N9) model based on the low pathogenicity in poultry. J. Biol. Syst. 25, 1–16 (2017)
Yu, X., Ma, Y.: An avian influenza model with nonlinear incidence and recovery rates in deterministic and stochastic environments. Nonlinear Dyn. 108, 4611–4628 (2022)
Geng, J., Wang, Y., Liu, Y., Yang, L., Yan, J.: Analysis of an avian influenza model with Allee effect and stochasticity. Int. J. Biomath. 16, 2250111 (2023)
Ali, A., Khan, S., Ali, I., Khan, F.: On dynamics of stochastic avian influenza model with asymptomatic carrier using spectral method. Math. Method Appl. Sci. 45, 8230–8246 (2022)
Dwivedi, A., Keval, R., Khajanchi, S.: Modeling optimal vaccination strategy for dengue epidemic model: a case study of India. Phys. Scripta 97, 085214 (2022)
Silver, S., van den Driessche, P., Khajanchi, S.: A dynamic multistate and control model of the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Public Health-UK, 1-14 (2023)
Kumar, R., Kumar, T., Khajanchi, S.: Modeling the influence of vaccination coverage on the dynamics of COVID-19 pandemic with the effect of environmental contamination. Math. Method Appl. Sci. 46, 12425–12453 (2023)
Khajanchi, S., Das, D., Kar, T.: Dynamics of tuberculosis transmission with exogenous reinfections and endogenous reactivation. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 497, 52–71 (2018)
Das, D., Khajanchi, S., Kar, T.K.: The impact of the media awareness and optimal strategy on the prevalence of tuberculosis. Appl. Math. Comput. 366, 124732 (2020)
Das, D., Khajanchi, S., Kar, T.: Transmission dynamics of tuberculosis with multiple re-infections. Chaos Soliton Fractals 130, 109450 (2020)
Khajanchi, S., Bera, S., Roy, T.: Mathematical analysis of the global dynamics of a HTLV-I infection model, considering the role of cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. Math. Comput. Simulat. 180, 354–378 (2021)
Bera, S., Khajanchi, S., Roy, T.: Stability analysis of fuzzy HTLV-I infection model: a dynamic approach. J. Appl. Math. Comput. 69, 171–199 (2023)
Liu, S., Ruan, S., Zhang, X.: On avian influenza epidemic models with time delay. Theory Biosci. 134, 75–82 (2015)
Kang, T., Zhang, Q., Rong, L.: A delayed avian influenza model with avian slaughter: stability analysis and optimal control. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 529, 121544 (2019)
Ding, C., Liu, W., Sun, Y., Zhu, Y.: A delayed Schistosomiasis transmission model and its dynamics. Chaos Soliton Fractals 118, 18–34 (2019)
Song, P., Xiao, Y.: Analysis of an epidemic system with two response delays in media impact function. Bull. Math. Biol. 81, 1–31 (2019)
Wang, N., Qi, L., Bessane, M., Hao, M.: Global Hopf bifurcation of a two-delay epidemic model with media coverage and asymptomatic infection. J. Differ. Equ. 369, 1–40 (2023)
Zhang, Z., Kundu, S., Tripathi, J., Bugalia, S.: Stability and Hopf bifurcation analysis of an SVEIR epidemic model with vaccination and multiple time delays. Chaos Soliton Fractals 131, 109483 (2020)
Zheng, T., Nie, L., Teng, Z., Luo, Y.: Competitive exclusion in a multi-strain malaria transmission model with incubation period. Chaos Soliton Fractals 131, 109545 (2020)
Zhang, T., Li, Z., Ma, L., Song, X.: Threshold dynamics in a clonorchiasis model with time delays. Appl. Math. Model. 102, 351–370 (2022)
Wang, N., Qi, L., Bessane, M., Hao, M.: Global Hopf bifurcation of a two-delay epidemic model with media coverage and asymptomatic infection. J. Differ. Equ. 369, 1–40 (2023)
Bera, S., Khajanchi, S., Roy, T.: Dynamics of an HTLV-I infection model with delayed CTLs immune response. Appl. Math. Comput. 430, 127206 (2022)
Allen, L., Bolker, B., Lou, Y., Nevai, A.: Asymptotic profiles of the steady states for an SIS epidemic reaction-diffusion model. Discret. Cont. Dyn. A 21, 1–20 (2008)
Cai, Y., Wang, K., Wang, W.: Global transmission dynamics of a Zika virus model. Appl. Math. Lett. 92, 190–195 (2019)
Cui, R., Lam, K., Lou, Y.: Dynamics and asymptotic profiles of steady states of an epidemic model in advective environments. J. Differ. Equ. 263, 2343–2373 (2017)
Wang, J., Cui, R.: Analysis of a diffusive host-pathogen model with standard incidence and distinct dispersal rates. Adv. Nonlinear Anal. 10, 922–951 (2021)
Zhang, C., Gao, J., Sun, H., Wang, J.: Dynamics of a reaction-diffusion SVIR model in a spatial heterogeneous environment. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 533, 1220490 (2019)
Luo, Y., Tang, S., Teng, Z., Zhang, L.: Global dynamics in a reaction-diffusion multi-group SIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 50, 365–385 (2019)
Wu, Y., Zou, X.: Dynamics and profiles of a diffusive host-pathogen system with distinct dispersal rates. J. Differ. Equ. 264, 4989–5024 (2018)
Xu, Z., Xu, Y., Huang, Y.: Stability and traveling waves of a vaccination model with nonlinear incidence. Comput. Math. Appl. 75, 561–581 (2018)
Yang, Y., Zhang, S.: Dynamics of a diffusive vaccination model with nonlinear incidence. Comput. Math. Appl. 75, 4355–4360 (2018)
Peng, R.: Asymptotic profiles of the positive steady state for an SIS epidemic reaction-diffusion model. J. Differ. Equ. 247, 1096–1119 (2009)
Yang, Y., Zou, L., Zhou, J., Hsu, C.: Dynamics of a waterborne pathogen model with spatial heterogeneity and general incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 53, 103065 (2020)
Zheng, T., Nie, L., Zhu, H., Luo, Y., Teng, Z.: Role of seasonality and spatial heterogeneous in the transmission dynamics of avian influenza. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 67, 103567 (2022)
Wang, W., Zhao, X.: A nonlocal and time-delayed reaction-diffusion model of dengue transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 71, 147–168 (2011)
Xu, Z., Zhao, Y.: A diffusive dengue disease model with nonlocal delayed transmission. Appl. Math. Comput. 270, 808–829 (2015)
Ruan, S.: Spatial-temporal dynamics in nonlocal epidemiological models. In: Mathematics for Life Science and Medicine. Springer, Berlin, 97-122 (2007)
Qu, H., Jiang, T., Wang, J., Zhao, J.: Dynamical analysis of a diffusive malaria model with fixed latent period in the human and vector populations. Int. J. Biomath. 16, 2250069 (2023)
Lin, H., Wang, F.: On a reaction-diffusion system modeling the dengue transmission with nonlocal infections and crowding effects. Appl. Math. Comput. 248, 184–194 (2014)
Wu, P., Zhao, H.: Dynamical analysis of a nonlocal delayed and diffusive HIV latent infection model with spatial heterogeneity. J. Franklin Inst. I(358), 5552–5587 (2021)
Sun, G., Zhang, H., Chang, L., Jin, Z., Wang, H., Ruan, S.: On the dynamics of a diffusive foot-and-mouth disease model with nonlocal infections. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 82, 1587–1610 (2022)
Shu, H., Ma, Z., Wang, H.: Diffusive host-pathogen model revisited: Nonlocal infections, incubation period and spatial heterogeneity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 516, 126477 (2022)
Li, F., Zhao, X.: Global dynamics of a nonlocal periodic reaction-diffusion model of bluetongue disease. J. Differ. Equ. 272, 127–163 (2021)
Zhang, L., Wang, S.: A time-periodic and reaction-diffusion Dengue fever model with extrinsic incubation period and crowding effects. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 51, 102988 (2020)
Luo, Y., Teng, Z., Zhao, X.: Transmission dynamics of a general temporal-spatial vector-host epidemic model with an application to the dengue fever in Guangdong, China. Discret. Cont. Dyn. B 28, 134–169 (2023)
Metz, J., Diekmann, O.: The dynamics of physiologically structured populations. Springer, New York (1986)
Guo, Z., Wang, F., Zou, X.: Threshold dynamics of an infective disease model with a fixed latent period and non-local infections. J. Math. Biol. 65, 1387–1410 (2012)
Smith, H.: Monotone dynamical systems: an introduction to the theory of competitive and cooperative systems. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1995)
Martin, R., Smith, H.: Abstract functional differential equations and reaction-diffusion systems. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 321, 1–44 (1990)
Wu, J.: Theory and applications of partial functional differential equations. Springer, New York (1996)
Hale, J.: Asymptotic behavior of dissipative systems. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1988)
Gourley, S., Kuang, Y.: A delay reaction-diffusion model of the spread of bacterio-phage infection. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 65, 550–566 (2004)
Wang, W., Zhao, X.: A nonlocal and time-delayed reaction-diffusion model of dengue transmission. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 71, 147–168 (2011)
Thieme, H.: Spectral bound and reproduction number for infinite-dimensional population structure and time heterogeneity. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 70, 188–211 (2009)
Thieme, H., Zhao, X.: A non-local delayed and diffusive predator-prey model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2, 145–160 (2001)
Wang, J., Wang, J.: Analysis of a reaction-diffusion cholera model with distinct dispersal rates in the human population. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ. 33, 549–575 (2021)
Protter, M., Weinberger, H.: Maximum principles in differential equations. Springer, New York (1984)
Thieme, H.: Convergence results and a Poincare-Bendixson trichotomy for asymptotically autonomous differential equations. J. Math. Biol. 30, 755–763 (1992)
Smith, H., Zhao, X.: Robust persistence for semidynamical systems. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 47, 6169–6179 (2001)
Magal, P., Zhao, X.: Global attractors and steady states for uniformly persistent dynamical systems. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 37, 251–275 (2005)
It\(\acute{o}\), S.: Diffusion equations, translations of mathematical monographs. American Mathematical Society, Providence (1992)
Wang, W., Zhao, X.: Basic reproduction numbers for reaction-diffusion epidemic models. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 11, 1652–1673 (2012)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and the editors for their valuable suggestions for the improvement of the paper.
Funding
This research is partially supported by the Tianshan Talent Training Program (Grant No. 2022TSYCCX0015), the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (Grant No. 2021D01E12), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 12361103).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.Li and L.Nie wrote the main manuscript text. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Nie, L. Global Dynamics Analysis of Non-Local Delayed Reaction-Diffusion Avian Influenza Model with Vaccination and Multiple Transmission Routes in the Spatial Heterogeneous Environment. Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst. 23, 198 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12346-024-01057-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12346-024-01057-1