Abstract
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an increasingly recognized immune-mediated condition that results in inflammation, stricturing and mass formation. It causes a wide spectrum of disease and clinical presentations depending on the organ system involved. Isolated esophageal IgG4-RD is rare and diagnosis can be difficult. It is highly responsive to corticosteroids, and early identification and instigation of management is key.
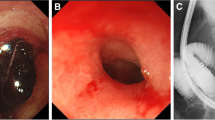
We describe the case of a 47-year-old man who presented with a food bolus obstruction on a background of progressive dysphagia and weight loss. Imaging and gastroscopy demonstrated diffuse esophageal thickening with a benign appearing stricture. Following non-specific histologic findings on biopsy and a non-diagnostic endoscopic ultrasound guided fine needle aspiration, he underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery with esophageal core biopsy. This confirmed the diagnosis of IgG4-RD. Initial treatment was with corticosteroids. However, due to recurrence of symptoms upon weaning of corticosteroids, azathioprine maintenance therapy was instituted. Azathioprine has previously been used in systemic cases of IgG4-RD but has not been reported for isolated esophageal disease.
This case highlights the difficulties in the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal IgG4-RD and the need to consider it as a differential diagnosis when histology reveals esophagitis with lymphoplasmacytic infiltration.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IgG4:
-
Immunoglobulin G4
- IgG4-RD:
-
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease
- HPF:
-
High-power field
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- EUS:
-
Endoscopic ultrasound
References
Wallace ZS, Naden RP, Chari S, et al. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism classification criteria for IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72:7–19.
Krishnamurthy P, Moukhachen H, Kaplan R. Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease mimicking esophageal cancer with pulmonary metastases. Chest. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.11028.
Padniewski JJ, Thottam G, Nasr R. IgG4 sclerosing disease of the esophagus: a case-based review. Rheumatol Int. 2020;40:1733–7.
Obiorah I, Hussain A, Palese C, et al. IgG4-related disease involving the esophagus: a clinicopathological study. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30:1–7.
Jang SW, Jeon MH, Shin HD. IgG4-related disease with esophageal involvement. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2019;13:369–75.
Sah RP, Chari ST. Serologic issues in IgG4-related systemic disease and autoimmune pancreatitis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23:108–13.
Hara A, Watanabe T, Minaga K, et al. Biomarkers in autoimmune pancreatitis and immunoglobulin G4-related disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27:2257–69.
Yokode M, Shiokawa M, Kodama Y. Review of diagnostic biomarkers in autoimmune pancreatitis: where are we now? Diagnostics. 2021;11:770.
Shiokawa M, Kodama Y, Kuriyama K, et al. Pathogenicity of IgG in patients with IgG-related disease. Gut. 2016;65:1322–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HP, SF and JAH were involved in conceptualization, data curation and manuscript writing and critical appraisal. PM assisted in the diagnosis and provided representative histology slides. PM, AM and ML provided professional comments and critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures followed have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Written, informed consent was given by the patient for the publication of this case report.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poole, H., Fehily, S., McKelvie, P. et al. Isolated esophageal IgG4-related disease presenting with progressive dysphagia and weight loss in a middle-aged man. Clin J Gastroenterol 15, 526–530 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-022-01623-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-022-01623-7