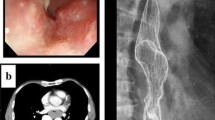
Abstract
Serum tumor markers in patients with cancer assist with establishing diagnosis, estimating prognosis, monitoring treatment, and detecting tumor recurrence. Changes in the p53 tumor suppressor gene are the most common genetic abnormalities in many different human malignancies. Several studies have demonstrated that serum p53 antibodies (S-p53Ab) comprise an early marker of malignant disease, a marker for treatment effects and a prognostic factor for patients with several types of tumors. We recently reported that S-p53Ab is useful for patients with gastric cancer. We describe a rare situation in which unusually high serum p53 antibodies helped to detect recurrent gastric cancer in the small intestine after gastrectomy. Further studies are required to gain a more precise understanding of the clinical impact of S-p53Ab titer monitoring in gastric cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
Shah SP, Roth A, Goya R, et al. The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature. 2012;486(7403):395–9.
Yachida S, White CM, Naito Y, et al. Clinical significance of the genetic landscape of pancreatic cancer and implications for identification of potential long-term survivors. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18(22):6339–47.
Kunizaki M, Sawai T, Takeshita H, et al. Clinical value of serum p53 antibody in the diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016;36(8):4171–5.
Shimada H, Ochiai T, Nomura F. Titration of serum p53 antibodies in 1085 patients with various types of malignant tumors. Cancer. 2013;97(3):682–9.
Ochiai H, Ohishi T, Osumi K, et al. Reevaluation of serum p53 antibody as a tumor marker in colorectal cancer patients. Surg Today. 2012;42:164–8.
Wu CW, Lin YY, Chen GD, et al. Serum anti-p53 antibodies in gastric adenocarcinoma patients are associated with poor prognosis, lymph node metastasis and poorly differentiated nuclear grade. Br J Cancer. 1999;80:483–8.
Shimada H, Shiratori T, Takeda A, et al. Preoperative changes of serum p53 antibody titer is a predictor for survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg. 2009;33:272–7.
Murayama K, Nanami T, Suzuki T, et al. Negative conversion of high serum p53 antibody titers in a patient with gastric cancer at 31 months after surgery. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2017;10(4):357–60. doi:10.1007/s12328-017-0749-9.
Kunizaki M, Fukuda A, Wakata K, et al. Clinical significance of serum p53 antibody in the early detection and poor prognosis of gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(4):1979–84.
Suzuki T, Shimada H, Ushigome M, et al. Three-year monitoring of serum p53 antibody during chemotherapy and surgery for stage IV rectal cancer. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2016;9:55–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human/animal rights
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients to be included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunizaki, M., Hamasaki, K., Wakata, K. et al. Unusually high levels of serum p53 antibody in recurrent gastric cancer. Clin J Gastroenterol 10, 503–507 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-017-0780-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-017-0780-x