Abstract
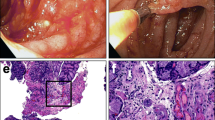
Thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA) is a life-threatening complication after transplantation including liver transplantation, and its typical clinical picture is characterized by hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction, neurological abnormalities, and fever. We report the case of a 56-year-old female with end-stage liver disease who underwent living donor liver transplantation (LDLT), and whose postoperative course was characterized by renal failure and progressive hyperbilirubinemia. Two weeks after LDLT, she started to show progressive thrombocytopenia, anemia, oliguria, and encephalopathy. From these clinical manifestations, she was diagnosed as having TMA and underwent plasma exchanges with continuous hemodialysis under temporary holding calcineurin inhibitors. The patient promptly responded to the treatment, with improved hematological, hepatic, and renal conditions, and was discharged from hospital a month later in a stable condition. We describe this case of TMA after LDLT with poor graft function and extensively review the disease in liver transplant recipients.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TMA:
-
Thrombotic microangiopathy
- LDLT:
-
Living donor liver transplantation
- AIH:
-
Autoimmune hepatitis
- PBC:
-
Primary biliary cirrhosis
- CNI:
-
Calcineurin inhibitor
- POD:
-
Postoperative day
- PE:
-
Plasma exchange
- CHDF:
-
Continuous hemodiafiltration
- ADAMTS13:
-
A disintegrin-like and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin type-1 motifs 13
- vWF:
-
von Willebrand factor
References
Ikegami T, Shimada M, Imura S, Arakawa Y, Nii A, Morine Y, et al. Current concept of small-for-size grafts in living donor liver transplantation. Surg Today. 2008;38:971–82.
Lee SG, Hwang S, Kim KH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, Ha TY, et al. Toward 300 liver transplants a year. Surg Today. 2009;39:367–73.
Moake JL. Thrombotic microangiopathies. N Engl J Med. 2002;22(347):589–600.
Ferrari S, Scheiflinger F, Rieger M, Mudde G, Wolf M, Coppo P, et al. Prognostic value of anti-ADAMTS 13 antibody features (Ig isotype, titer, and inhibitory effect) in a cohort of 35 adult French patients undergoing a first episode of thrombotic microangiopathy with undetectable ADAMTS 13 activity. Blood. 2007;109:2815–22.
Tamura S, Sugawara Y, Matsui Y, Kishi Y, Akamatsu N, Kaneko J, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy in living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2005;80:169–75.
Crawley JT, de Groot R, Xiang Y, Luken BM, Lane DA. Unraveling the scissile bond: how ADAMTS13 recognizes and cleaves von Willebrand factor. Blood. 2011;118:3212–21.
Kamioka I, Nozu K, Fujita T, Kaito H, Tanaka R, Yoshiya K, et al. Prognosis and pathological characteristics of five children with non-Shiga toxin-mediated hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Int. 2007;49:196–201.
Trimarchi HM, Truong LD, Brennan S, Gonzalez JM, Suki WN. FK506-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: report of two cases and review of the literature. Transplantation. 1999;67:539–44.
Ponticelli C, Banfi G. Thrombotic microangiopathy after kidney transplantation. Transpl Int. 2006;19:789–94.
Ikegami T, Imai D, Wang H, Yoshizumi T, Yamashita YI, Ninomiya M, et al. D-MELD as a predictor of early graft mortality in adult-to-adult living-donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2013 [Epub ahead of print].
Ikegami T, Shirabe K, Yoshizumi T, Aishima S, Taketomi YA, Soejima Y, et al. Primary graft dysfunction after living donor liver transplantation is characterized by delayed functional hyperbilirubinemia. Am J Transplant. 2012;12:1886.
Nakazawa Y, Hashikura Y, Urata K, Ikegami T, Terada M, Yagi H, et al. Von Willebrand factor-cleaving protease activity in thrombotic microangiopathy after living donor liver transplantation: a case report. Liver Transpl. 2003;9:1328–33.
Uemura M, Tatsumi K, Matsumoto M, Fujimoto M, Matsuyama T, Ishikawa M, et al. Localization of ADAMTS13 to the stellate cells of human liver. Blood. 2005;106:922–4.
Kobayashi T, Wada H, Usui M, Sakurai H, Matsumoto T, Nobori T, et al. Decreased ADAMTS13 levels in patients after living donor liver transplantation. Thromb Res. 2009;124:541.
Kuriyama N, Isaji S, Hamada T, Kishiwada M, Ohsawa I, Usui M, et al. The cryoprotective effects of addition of activated protein C into preservation solution on small-for-size grafts in rats. Liver Transpl. 2010;16:1–11.
Shindoh J, Sugawara Y, Akamatsu N, Kaneko J, Tamura S, Yamashiki N, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy after living-donor liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2012;12:728–36.
Disclosures
Conflict of Interest:
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human/Animal Rights:
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5).
Informed Consent:
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuda, D., Toshima, T., Ikegami, T. et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy caused by severe graft dysfunction after living donor liver transplantation: report of a case. Clin J Gastroenterol 7, 159–163 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-013-0446-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-013-0446-2