Abstract
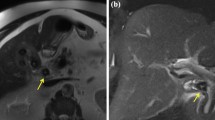
Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery is a rare complication of cholecystitis. 34 cases have been reported from 1976 to 2012, searched on MEDLINE and most of the cases have presented with gastrointestinal bleeding. We report the third case of an unruptured pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery associated with calculous cholecystitis. An 85-year-old female presented to the emergency unit with epigastric pain and jaundice. Laboratory data and contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) revealed calculous cholecystitis and Mirizzi syndrome accompanied by a pseudoaneurysm in the gallbladder. Color Doppler ultrasonography (US) clearly demonstrated the pulsatile pseudoaneurysm. After biliary drainage and antimicrobial therapy, selective hepatic angiography with the aim of providing transcatheter arterial embolization was performed but the pseudoaneurysm had already thrombosed spontaneously. Open cholecystectomy was successfully carried out. Histological specimens demonstrated the pseudoaneurysm with organized thrombus in the epithelial wall of the gallbladder thickened with severe fibrosis. It is suggested that cholecystitis with unusual symptoms such as gastrointestinal bleeding requires immediate enhanced CT and US with Doppler imaging in order not to overlook a rare but life-threatening pseudoaneurysm.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osada H, Ohno H, Watanabe W, Okada T, Nakada K, Honda H. Cystic artery bleeding due to blunt gallbladder injury: computed tomography findings and treatment with transcatheter arterial embolization. Jpn J Radiol. 2010;28(2):162–5.
Hanazaki K, Machida E, Sodeyama H, Asato S, Sode Y, Wakabayashi M, et al. Chronic cholecystitis following hemobilia due to traumatic intrahepatic injury. Surg Endosc. 1995;9(9):1004–7.
Moses V, Keshava SN, Wann VC, Joseph P, Sitaram V. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm after laparoscopic cholecystectomy presenting as haemobilia: a case report. Trop Gastroenterol. 2008;2:107–9.
Srinivasaiah N, Bhojak M, Jackson R, Woodcock S. Vascular emergencies in cholelithiasis and cholecystectomy: our experience with two cases and literature review. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2008;7(2):217–20.
Madanur MA, Battula N, Sethi H, Deshpande R, Heaton N, Rela N. Pseudoaneurysm following laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007;6(3):294–8.
Halbe S, Ahmed NI, Sundar K, Sathyakumar C. Pseudoaneurysm in gall bladder fossa following laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Indian J Gastroenterol. 1999;18(3):122.
Bergey E, Einstein DM, Herts BR. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm as a complication of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Abdom Imaging. 1995;1:75–7.
Hakami M, Beheshti Gh, Amirkhan A. Hemobilia caused by rupture of cystic artery aneurysm. Am J Proctol. 1976;27:56–7.
Berland LL, Doust BD, Foley WD. Acute hemorrhage into the gallbladder diagnosed by computed tomography and ultrasonography. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1980;4:260–2.
Reddy SC. Pseudoaneurysm of cystic artery with upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. South Med J. 1983;76:85–6.
Sasaki F, Koga S, Takeuchi A. A case of hemorrhage from hepatic pseudoaneurysm due to cholelithiasis into the gallbladder (in Japanese with English abstract). Rinsho Hoshasen. 1983;28:407–10.
Rhee JW, Bonnheim DC, Upson J. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm, NY State. J Med. 1987;87:47.
Wu TC, Liu TJ, Ho YJ. Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery with upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Acta Chir Scand. 1988;154:151–2.
Strickland SK, Khoury MB, Kiproff PM, Raves JJ. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm: a rare cause of hemobilia. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 1991;14:183–4.
Read A, Lannan M, Chou ST, Hennessy O. Bleeding cystic artery aneurysm: rare cause of hemobilia. Aust NZ J Surg. 1991;61:159–61.
Barba CA, Bret PM, Hinchey EJ. Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: a rare cause of hemobilia. Can J Surg. 1994;37:64–6.
Nakajima M, Hoshino H, Hayashi E, Nagano K, Nishimura D, Katada N, et al. Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery associated with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. J Gastroenterol. 1996;31:750–4.
Maw A, Mander BJ, Nandi SC, Taube M, Evans HJR. Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery. Eur J Surg. 1997;163:307–9.
Kaman L, Kumar S, Behera A, Katariya RN. Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: a rare cause of hemobilia. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93:1535–7.
England RE, Marsh PJ, Ashleigh R, Martin DF. Case report: pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: a rare cause of haemobilia. Clin Radiol. 1998;53:72–5.
Delgadillo X, Berney T, Perrot MD, Didier D, Morel P. Successful treatment of a pseudoaneruysm of the cystic artery with microcoil embolization. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1999;10:789–92.
Maeda A, Kunou T, Saeki S, Aono K, Murata T, Niinomi N. Pseudoaneusysm of the cystic artery with hemobilia treated by arterial embolization and elective cholecystectomy. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002;9:755–8.
Akatsu T, Hayashi S, Egawa T, Doi M, Nagashima A, Kitano M, et al. Hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm associated with cholecystitis that ruptured into the gallbladder. J Gastroenterol. 2004;39:900–3.
Morioka D, Ueda M, Baba N, Kubota K, Otsuka Y, Akiyama H, et al. Hemobilia caused by pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004;19:724–6.
Gutiérrez G, Ramia JM, Villar J, Garrote D, Ferron A, Ruiz E. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm from an evolved acute calculous cholecystitis. Am J Surg. 2004;187:519–20.
Sibulesky L, Ridlen M, Pricolo VE. Hemobilia due to cystic artery pseudoaneurysm. Am J Surg. 2006;191:797–8.
Pérez-Castrillon JL, Mendo M, Calero H. Hemorrhage into the gallbladder caused by pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery. Endoscopy. 2006;38:E50.
Lee JW, Kim MY, Kim YJ, Suh CH. CT of acute lower GI bleeding in chronic cholecystitis: concomitant pseudoaneruysm of cystic artery and cholecystocolonic fistula. Clin Radiol. 2006;61:634–6.
Akatsu T, Tanabe M, Shimizu T, Handa K, Kawachi S, Aiura K, et al. Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery secondary to cholecystitis as a cause of hemobilia: report of a case. Surg Today. 2007;37:412–7.
Ghoz A, Kheir E, Kotru A, Halazun K, Kessel D, Patel JJ, et al. Hemoperitoneum secondary to rupture of cystic artery pseudoaneurysm. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2007;6(3):321–3.
Saluja SS, Ray S, Gulati MS, Pal S, Sahni P, Chattopadhyay TK. Acute cholecystitis with massive upper gastrointestinal bleed: a case report and review of the literature. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007;7:12.
Machida H, Ueno E, Shiozawa S, Fujimura M, Tsuchiya A, Kim DH, et al. Unruptured pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery with acute calculous cholecystitis incidentally detected by computed tomography. Radiat Med. 2008;26:384–7.
Shimada K, Sakamoto Y, Esaki M, Kosuge T. Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery associated with xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Dig Surg. 2008;25:8–9.
Mullen R, Suttie SA, Bhat R, Evgenikos N, Yalamarthi S, McBride KD. Microcoil embolisation of mycotic cystic artery pseudoaneurysm: a viable option in high-risk patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2009;32:1275–9.
Sousa HT, Amaro P, Brito J, Almeida J, Silva MR, Romãozinho JM. Hemobilia due to pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 2009;33:80–7.
Lin YH, Lee RC, Hsia CY, Chen HC, Chiang JH, Tseng HS, et al. Right hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm ruptured into the gallbladder demonstrated by magnetic resonance angiography. J Chin Med Assoc. 2010;73:331–3.
Ahmed I, Tanveer UH, Sajjad Z, Bunazza B, Azeem UD, Basit S. Cystic artery pseudo-aneurysm: a complication of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Br J Radiol. 2010;83:e165–7.
Hague J, Brennand D, Raja J, Amin Z. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm in hemorrhagic acute cholecystitis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010;33:1287–90.
Disclosures
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human/animal rights: All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008(5).
Informed consent: Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suzuki, S., Saito, Y., Nakamura, K. et al. Unruptured cystic artery pseudoaneurysm accompanied by Mirizzi syndrome: a report of a case . Clin J Gastroenterol 6, 490–495 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-013-0434-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12328-013-0434-6