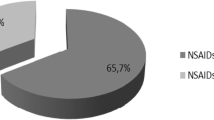
Abstract
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are among the most common class of drugs utilized for a variety of disorders, including headaches, pain states, fever, and other common conditions. In recent years, a link between NSAIDs and adverse effects has been identified, including renal, heart, and liver disease, bleeding, and increased mortality. NSAID-mediated renal disease is associated with interference with the cyclooxygenase enzyme. Literature evaluating NSAID renal effects has indicated that a number of factors are associated with acute and chronic kidney injury (AKI). Early diagnosis can identify changes in renal function and allow for cessation of NSAID use, limiting the risk for long-term chronic renal disease and in some cases reversal of renal injury. Alternative medications should be considered in those patients identified with morbidity linked to NSAID use. Nephrotoxicity is increased in the elderly population and in hypovolemia, high dose exposure, use of vasoconstrictors such as calcineurin inhibitors, and use of renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors or diuretics. Careful risk/benefit considerations from healthcare professionals can limit the incidence and degree of morbidity and mortality, including in NSAID-mediated renal disease. Selective NSAID cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors also possess risks and therefore clinicians should always recommend short-term courses of this class of drugs versus long-term dosing because of the risk of morbidity and mortality. Given that these drugs are available over the counter as well by prescribing, clinicians must communicate the risks and benefits of NSAIDs and provide sound recommendations to their patients regarding use short and long term.

Reprinted with permission from Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2021.02.013

Permission has been granted by the author. https://tmedweb.tulane.edu/pharmwiki/doku.php/nsaid_side_effects

Non-commercial uses of the work are permitted without any further permission from Dove Medical Press Limited, provided the work is properly attributed. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/259722202_Risk_of_stroke_associated_with_nonsteroidal_anti-inflammatory_drugs
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klomjit N, Ungprasert P. Acute kidney injury associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Intern Med. 2022;101:21–8.
Cui Y, Yang Y, Lei W, Lang X, Chen J. The clinicopathological features of drug-induced acute kidney injury—a single-center retrospective analysis. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(5):400.
Keen MU, Aeddula NR. Analgesic nephropathy. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls; 2022. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541101/. Accessed 31 Jul 2022.
Prieto-García L, Pericacho M, Sancho-Martínez SM, et al. Mechanisms of triple whammy acute kidney injury. Pharmacol Ther. 2016;167:132–45.
Zhang X, Donnan PT, Bell S, Guthrie B. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug induced acute kidney injury in the community dwelling general population and people with chronic kidney disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18(1):256.
Klomjit N, Ungprasert P. Acute kidney injury associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Intern Med. 2022;101:21–8.
Baker M, Perazella MA. NSAIDs in CKD: are they safe? Am J Kidney Dis. 2020;76(4):546–57.
Drożdżal S, Lechowicz K, Szostak B, et al. Kidney damage from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs—Myth or truth? Review of selected literature. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2021;9(4):e00817.
Giovanni G, Giovanni P. Do non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and COX-2 selective inhibitors have different renal effects? J Nephrol. 2002;15(5):480–8.
Brater DC. Anti-inflammatory agents and renal function. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2002;32(3 Suppl 1):33–42.
Keen MU, Aeddula NR. Analgesic nephropathy. Treasure Island: StatPearls; 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541101/. Accessed 10 Aug 2022.
Lucas GNC, Leitão ACC, Alencar RL, Xavier RMF, Daher EDF, da Silva GB. Pathophysiological aspects of nephropathy caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Braz J Nephrol. 2018;21(41):124–30.
Dixit M, Doan T, Kirschner R, Dixit N. Significant acute kidney injury due to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: inpatient setting. Pharmaceuticals. 2010;3(4):1279–85.
Levey AS, James MT. Acute kidney injury. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(9):ITC66.
Jacob J, Dannenhoffer J, Rutter A. Acute kidney injury. Prim Care. 2020;47(4):571–84.
Ungprasert P, Cheungpasitporn W, Crowson CS, Matteson EL. Individual non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Intern Med. 2015;26(4):285–91.
Does sulindac affect renal function less than other NSAIDs? https://www.practicalpainmanagement.com/treatments/pharmacological/non-opioids/does-sulindac-affect-renal-function-less-other-nsaids. Accessed 30 Aug 2022.
Pfizer. Ketorolac Tromethamine Injection, USP. 2017 p. 1–40. https://www.pfizer.ca/sites/default/files/201712/2017.12.01_Ketorolac_PM_E_209949.pdf.
Sawyer GA, Anderson BC, Raukar NP, Fadale PD. Intramuscular ketorolac injections in the athlete. Sports Health. 2012;4(4):319–27.
Hayashi K, Miki K, Kajiyama H, Ikemoto T, Yukioka M. Impact of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration for 12 months on renal function. Front Pain Res. 2021;26(2): 644391.
Yu C, Guo D, Yao C, et al. Clinical characteristics of hospitalized patients with drug-induced acute kidney injury and associated risk factors: a case-control study. BioMed Res Int. 2020;15(2020):1–8.
Murray MD, Brater DC. Effects of NSAIDs on the kidney. Prog Drug Res. 1997;49:155–71.
Thongprayoon C, Hansrivijit P, Kovvuru K, et al. Diagnostics, risk factors, treatment and outcomes of acute kidney injury in a new paradigm. J Clin Med. 2020;9(4):1104.
Koza Y. Acute kidney injury: current concepts and new insights. J Inj Violence Res. 2016;5:58.
Blairon L, Abbasi M, Beukinga I, Melot C, Libertalis M. Improving NSAIDs prescription in emergency services unit by a point-of-care-based renal function evaluation. J Emerg Med. 2020;58(3):481–6.
Peerapornratana S, Manrique-Caballero CL, Gómez H, Kellum JA. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019;96(5):1083–99.
Benoit SW, Devarajan P. Acute kidney injury: emerging pharmacotherapies in current clinical trials. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018;33(5):779–87.
Lim CC, Tan NC, Teo EPS, et al. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of acute kidney injury and hyperkalemia in older adults: a retrospective cohort study and external validation of a clinical risk model. Drugs Aging. 2022;39(1):75–82.
Wan EYF, Yu EYT, Chan L, et al. Comparative risks of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021;16(6):898–907.
Lin SX, Phillips T, Culliford D, et al. Characterising risk of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-related acute kidney injury: a retrospective cohort study. BJGP Open. 6(1):BJGPO.2021.0208.
Gong J, Ma L, Li M, et al. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs associated acute kidney injury in hospitalized children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2022;31(2):117–27.
Jeon N, Park H, Segal R, Brumback B, Winterstein AG. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-associated acute kidney injury: does short-term NSAID use pose a risk in hospitalized patients? Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;77(9):1409–17.
Nelson DA, Marks ES, Deuster PA, O’Connor FG, Kurina LM. Association of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug prescriptions with kidney disease among active young and middle-aged adults. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(2):e187896.
Gameiro J, Fonseca JA, Outerelo C, Lopes JA. Acute kidney injury: from diagnosis to prevention and treatment strategies. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1704.
Lucas GNC, Leitão ACC, Alencar RL, Xavier RMF, Daher EDF, Silva Junior da GB. Pathophysiological aspects of nephropathy caused by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Bras Nefrol Orgao. 2019;41(1):124–30.
Misurac JM, Knoderer CA, Leiser JD, Nailescu C, Wilson AC, Andreoli SP. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are an important cause of acute kidney injury in children. J Pediatr. 2013;162(6):1153–9 (1159.e1).
Xu Y, Zou P, Cao X. Advances in pharmacotherapy for acute kidney injury. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2022;23(6):713–26.
Acknowledgements
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article.
Author Contributions
John M. LaForge, BS, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Kelsey Urso, CRC, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Juan Martin Day, BS, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Cade W. Bourgeois, BS, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Maggie M. Ross, BS, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Shahab Ahmadzadeh, MD, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Sahar Shekoohi, PhD, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Elyse M. Cornett, PhD, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Adam M. Kaye, PharmD, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis. Alan David Kaye MD, PhD, Study concept and design, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of the manuscript, critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content, statistical analysis.
Disclosures
All authors have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethical Guidelines
This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LaForge, J.M., Urso, K., Day, J.M. et al. Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Clinical Implications, Renal Impairment Risks, and AKI. Adv Ther 40, 2082–2096 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-023-02481-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-023-02481-6