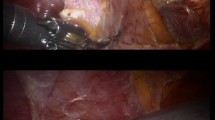
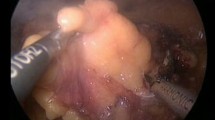
Abstract
Objective
To report on the pioneering clinical experiences of six cases of extraperitoneal laparoscopic kidney transplantation in China.
Methods
For the first time in clinical practice, a customised, controllable double-circulation cooling device was used to protect the transplanted kidney. Of the six patients, two underwent an allograft renal transplantation because they had been diagnosed with uraemia and were on maintenance haemodialysis. The other four patients underwent kidney autotransplantation because of a central renal tumour.
Results
The extraperitoneal laparoscopic kidney transplantations were successfully completed between 2017 and 2018. The operative time for the two patients undergoing the allograft transplantation was 3–3.5 h. The time for venous anastomosis was approximately 53–65 min, and the time for arterial anastomosis was approximately 25–30 min. The creatinine level was 90–80 μmol/L after surgery. The operative time of the four patients who underwent autotransplantation was 9.4–17.5 h. The times of venous and arterial anastomosis were 58–90 min and 35–48 min, respectively. The follow-up B-mode ultrasound after surgery showed good blood supply in the spared nephron. A renal graft was removed from one patient 6 months after surgery because of renal atrophy and dysfunction caused by poor blood supply. Five patients (two undergoing allografting and three undergoing autografting) completed the 12-month follow-up, and their renal graft function was good.
Conclusions
Extraperitoneal laparoscopic kidney transplantation, either allograft or autologous transplantation, is a safe and feasible procedure with a good chance of survival for the transplanted kidney. A customised cooling device is effective and practical during laparoscopic kidney transplantation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Musquera M, Peri L, Ajami T, et al. Robot-assisted kidney transplantation: update from the European Robotic Urology Section (ERUS) series. BJU Int. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/bju.15199.
Prudhomme T, Beauval JB, Lesourd M, et al. Robotic-assisted kidney transplantation in obese recipients compared to non-obese recipients: the European experience. World J Urol. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-020-03309-6.
Pein U, Girndt M, Markau S, et al. Minimally invasive robotic versus conventional open living donor kidney transplantation. World J Urol. 2020;38(3):795–802.
Modi P, Pal B, Kumar S, et al. Laparoscopic transplantation following transvaginal insertion of the kidney: description of technique and outcome. Am J Transplant. 2015;15(7):1915–22.
Rosales A, Salvador JT, Urdaneta G, et al. Laparoscopic kidney transplantation. Eur Urol. 2010;57(1):164–7.
Boggi U, Vistoli F, Signori S, et al. Robotic renal transplantation: first European case. Transpl Int. 2011;24(2):213–8.
Stiegler P, Schemmer P. Robot-assisted transplant surgery—vision or reality? A comprehensive review. Visc Med. 2018;34:24–30.
Breda A, Territo A, Gausa L, et al. Robot-assisted kidney transplantation: the European experience. Eur Urol. 2018;73(2):273–81.
Wagenaar S, Nederhoed JH, Hoksbergen AWJ, Bonjer HJ, Wisselink W, van Ramshorst GH. Minimally invasive, laparoscopic, and robotic-assisted techniques versus open techniques for kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review. Eur Urol. 2017;72(2):205–17.
Wang X, Zu Q, Zhu Q, et al. Surgical outcomes of robotic-assisted kidney transplantation in end-stage renal disease treatment (1 case report). J Min Invasive Urol. 2018;3(7):159–62.
Han X, Shan H, Zhao Y, et al. Laparoscopic kidney transplantation: a case report. Shandong Med J. 2018;46(58):63–5.
Siena G, Campi R, Decaestecker K, et al. Robot-assisted kidney transplantation with regional hypothermia using grafts with multiple vessels after extracorporeal vascular reconstruction: results from the European Association of Urology Robotic Urology Section Working Group. Eur Urol Focus. 2018;4(2):175–84.
Han X, Zhang B, Yan W, et al. Feasibility of laparoscopic orthotopic kidney transplantation: initial research with a pig model. Ann Transplant. 2013;18:342–8.
Michiels C, Rouffilange J, Comat V, et al. Total preperitoneal robot-assisted kidney transplantation. J Endourol Case Rep. 2017;3(1):169–72.
He B, Musk GC, Mou L, Waneck GL, Delriviere L. Laparoscopic surgery for kidney orthotopic transplant in the pig model. JSLS. 2013;17(1):126–31.
Boggi U, Signori S, Vistoli F, et al. Current perspectives on laparoscopic robot-assisted pancreas and pancreas-kidney transplantation. Rev Diabet Stud. 2011;8(1):28–34.
Meier RPH, Piller V, Hagen ME, et al. Intra-abdominal cooling system limits ischemia-reperfusion injury during robot-assisted renal transplantation. Am J Transpl. 2018;18:53–62.
Territo A, Mottrie A, Abaza R, et al. Robotic kidney transplantation: current status and future perspectives. Minerva Urol Nefrol. 2017;69(1):5–13.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the hard and dedicated work of all the staff that implemented the intervention and evaluation components of the study. We thank the participants of the study.
Funding
No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article. The Rapid Service Fee was funded by the authors.
Authorship
All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this article, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given their approval for this version to be published.
Disclosures
The authors (Xuhui Zhu, Yongwei Zhao, Xiuwu Han, Yansheng Li, Peng Zhang, Siyuan Wang, Gao Li, Chunhong Xiang) have nothing to disclose.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital (2017-ke-191). This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki.
Written informed consent document was obtained from all participants.
Among the six kidney transplant patients, four were patients with autologous kidney transplant, which did not involve ethical issues of transplantation. The other two cases were kidney transplants, both obtained through legal organ donation channels at local hospitals (Department of Urology, Beijing Chao-yang Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China), with the donors' knowledge and consent.
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article. We declared that materials described in the manuscript, including all relevant raw data, will be freely available to any scientist wishing to use them for non-commercial purposes, without breaching participant confidentiality.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, X., Zhao, Y., Han, X. et al. Extraperitoneal Laparoscopic Kidney Transplantation: Preliminary Clinical Experiences from China. Adv Ther 38, 1677–1689 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01639-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-021-01639-4