Abstract
Introduction
The aim of this study was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics (PK) of single and multiple doses of oral lafutidine tablets and the effect of food on the PK properties in healthy Chinese subjects. The tolerability and the effect of gender on the PK properties were also evaluated to acquire more PK information.
Methods
Three PK studies were conducted in 12 healthy Chinese subjects (6 male, 6 female). Study 1 was a single-dose, three-period, three-dose level (10, 20, and 40 mg), three-sequence cross-over study under fasting conditions. Study 2 was a repeat-dose study (10 mg twice daily over 6 days; all 12 subjects). Study 3 was a two-period, two-sequence cross-over single-dose (10 mg) food interaction study. All randomizations (study 1, study 3) were done to ascertain 1:1 gender ratio per sequence. A validated liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) method was used to determine plasma lafutidine concentrations. PK parameters were calculated by the non-compartmental method.
Results
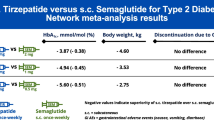
The area under the time–concentration curve (AUC) and maximum plasma concentration (C max) of lafutidine tablets were dose-independent in the single-dose study among these healthy volunteers. The PK parameters of the multiple-dose study were inconsistent with the single study. After administration of a single dose of 10 mg under either fed or fasting conditions, we found that food may not affect the degree of absorption of the lafutidine tablets, but it may slow down the absorption rate. This is shown by the fact that the AUC showed no significant difference while the peak time was significantly delayed under fed conditions.
Conclusion
The PK of lafutidine showed dose proportionality. There was no significant accumulation of lafutidine tablets with multiple dosing. Food did not affect the degree of lafutidine absorption, but it did reduce the rate of absorption. Further study is needed regarding the effect of gender on lafutidine. Lafutidine was well tolerated within the dose range 10–40 mg, and no serious adverse events were observed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen Wei-Dong, Liang Yan, et al. Simple, sensitive and rapid LC–ESI–MS method for the quantitation of lafutidine in human plasma—application to pharmacokinetic studies. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2006;41:256–60.
Onodera S, Shibata M, Tanaka M, Inaba N, Yamaura T, Ohnishi H. Gastroprotective activity of FRG-8813, a novel histamine H2-receptor antagonist, in rats. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1995;68:161–73.
Ren Q, Ma B, Yang K, Yan X. Lafutidine-based triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication. Hepatogastroenterology. 2010;57:102–3.
Shibata M, Yamaura T, Inaba N, Onodera S, Chida Y, Ohnishi H. Gastric anti-secretory effect of FRG-8813, a new histamine H2 receptor antagonist, in rats and dogs. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1993;235:245.
Yamaura T, Shibata M, Inaba N, Onodera S, Chida Y, Ohnishi H. Effects of FRG-8813, a new-type histamine H2 receptor antagonist, on various experimental gastric and duodenal lesions in rats. Nippon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1992;99:401.
Lili Wu, Zhang Zunjian, et al. Determination of lafutidine in human plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: application to a bioequivalence study. J Mass Spectrom. 2005;40:1637–43.
Saegusa Y, Ichikawa T, Iwai T, et al. Effects of acid antisecretory drugs on mucus barrier of the rat against 5-fluorouracil-induced gastrointestinal mucositis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008;43:531–7.
Kim EH, et al. Efficacy of lafutidine versus famotidine in patients with reflux esophagitis: a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority phase III trial. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60:1724–1732.
Namikawa T, et al. Feasibility study of supportive care using lafutidine, a histamine H2 receptor antagonist, to prevent gastrointestinal toxicity during chemotherapy for gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014;34(12):7297–301.
Yamamoto H, et al. Changes in the mucus barrier during cisplatin-induced intestinal mucositis in rats. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:276186.
Nagano H, Sanai H, Muraoka M, Takagi K. Efficacy of lafutidine, a histamine H2-receptor antagonist, for taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with gynecological malignancies. Gynecol Oncol. 2012;127(1):172–4.
Ikawa K, Shimatani T, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of lafutidine after postprandial oral administration in healthy subjects: comparison with famotidine. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007;30(5):1003–6.
Dewan B, Chimata R, et al. An open-label, randomized, cross-over bioequivalence study of lafutidine 10 mg under fasting condition. World J Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 2010;1(5):112–8.
Haruki S, Matsumoto H, Kodama K, Tanabe M, Takayanagi H, Cyong J, et al. Pharmacokinetic studies of lafutidime (FRG–8813) in man. Jpn Pharmacol Ther. 1995;23:3049–59.
Chinese Pharmacological Society. http://www.cnphars.org/. Accessed 6 May 2007.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the subjects who participated in the study. No funding or sponsorship was received for this study or publication of this article. The article processing charges for this publication were funded by the authors. All named authors meet the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) criteria for authorship for this manuscript, take responsibility for the integrity of the work as a whole, and have given final approval for the version to be published. All authors were responsible for the study conception and design, data acquisition and analysis, and writing and revising of the manuscript.
Disclosures
Shihong Li, Mingzhen Xu, Huqun Li, Juan Du, and Weiyong Li have no conflicts of interest to disclose regarding the content of this article.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964, as revised in 2013. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Enhanced content
To view enhanced content for this article go to http://www.medengine.com/Redeem/E2E4F06032D6C585.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Xu, M., Li, H. et al. Pharmacokinetic Properties of Oral Lafutidine Tablets and the Effect of Food on its Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Chinese Subjects. Adv Ther 33, 1704–1714 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-016-0383-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-016-0383-9