Abstract
Introduction
It is hypothesized that health and patient-reported outcomes in asthma are positively influenced by the level of patient satisfaction with their inhaler device. This paper uses data from a real-world observational study to investigate the extent of the relationship between inhaler satisfaction and patient compliance, and the influence this has on health and patient-reported outcomes.
Methods
Data were drawn from the Adelphi Respiratory Disease Specific Programme® (Adelphi, Macclesfield, UK), a cross-sectional study of consulting patients in five European countries undertaken between June and September 2009. A range of clinical and patient-reported outcomes were observed allowing analysis of these and their relationship with patient-reported inhaler satisfaction and patient compliance.
Results
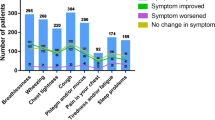
The analysis demonstrates that for the majority of patients the higher the level of satisfaction that the patient reports for their device the more likely the patient is observed to be compliant and to experience better outcomes including quality of life (as measured by EuroQol 5 Dimensions [EQ-5D] utility score, P<0.001), fewer exacerbations (P<0.001), fewer hospital visits (P=0.011), fewer healthcare visits (P=0.001), fewer primary care physician visits (P=0.001), and fewer sleep disturbances (P<0.001).
Conclusion
The level of patient satisfaction with their inhaler device is observed to have a positive influence on the treatment goals for asthma through its association with improved compliance.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
References
Braman S. The global burden of asthma. Chest. 2006;130:4S–12S.
Masoli M, Fabian D, Holt S, et al. Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) program: the global burden of asthma: executive summary of the GINA Dissemination Committee Report. Allergy. 2004;59: 469–478.
Rabe KF, Vermeire PA, Soriano JB, et al. Clinical management of asthma in 1999: the Asthma Insight and Reality in Europe (AIRE) study. Eur Resp J. 2000;16:802–807.
GlaxoSmithKline. Asthma in America: a landmark survey. Available at: www.asthmainamerica.com. Accessed March 25, 2010.
Adachi M, Morikawa A, Ishihara K. Asthma insights and reality in Japan (AIRJ). Arerugi. 2002;51: 411–420
Lai CK, De Guia TS, Kim YY, et al. Asthma control in the Asia-Pacific region: the Asthma Insights and Reality in Asia-Pacific Study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003;111:263–268.
Global Initiative for Asthma. GINA report, Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention 2009. Available at: www.ginasthma.org. Accessed: November 24, 2010.
Horne R. Compliance, adherence and concordance. Implications for asthma treatment. Chest. 2006;130(Suppl. 1):65S–72S.
Ward M, Reynolds C. Patient empowerment: the key to compliance in asthma. Nursing Times. 2000;96:8.
Anderson P, Benford M, Harris N, et al. Realworld physician and patient behaviour across countries: disease-specific programmes — a means to understand. Curr Med Res Opin. 2008;24: 3063–3072.
Higgins V, Kay S, Small M. Physician and patient survey of allergic rhinitis: methodology. Allergy. 2007;62:6–8.
Small M, Vickers A, Anderson P, Kay S. The patient-physician partnership in asthma: real-world observations associated with clinical and patientreported outcomes. Adv Ther. 2010;27:511–599.
European Pharmaceutical Market Research Association Code of Conduct for International Healthcare Market Research. Available at: www.ephmra.org/professional-standards.aspx. Accessed September 10, 2010.
Ley P, Llewellyn S. Improving patients’ understanding, recall, satisfaction and compliance. In: Broome, A, Llewellyn S, eds. Health Psychology: Process and Applications. 2nd edition. London: Chapman and Hall; 1995:75–98.
Jenkins CD, Stanton BA, Niemcryk SJ, Rose RM. A scale for the estimation of sleep problems in clinical research. J Clin Epidemiol. 1988;41:313–321.
Wood S. Generalized Additive Models: an Introduction with R. Boca Raton, FL: Chapman and Hall/CRC; 2006.
Grömping U. Relative importance for linear regression in R: the package relaimpo. J Stat Soft. 2006;17:1–27.
Nunnally J, Bernstein I. Psychometric Theory. 3rd Edition. New York: McGraw Hill; 1994.
Cochrane GM. Compliance in asthma: a European perspective. Eur Respir J. 1995;5:116–119.
Bourbeau J, Bartlett S J. Patient adherence in COPD. Thorax. 2008;63:831–838.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Small, M., Anderson, P., Vickers, A. et al. Importance of inhaler-device satisfaction in asthma treatment: Real-world observations of physician-observed compliance and clinical/patient-reported outcomes. Adv Therapy 28, 202–212 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-010-0108-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-010-0108-4