Abstract
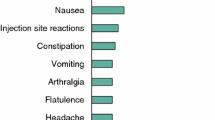
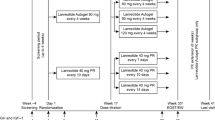
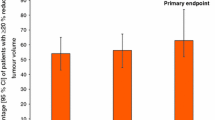
Lanreotide is an eight-amino acid peptide, which is an analog of the native somatostatin peptide, physiological inhibitor of growth hormone (GH). The drug shows high binding affinity for somatostatin receptors, SSTR2 and SSTR5, which is the primary mechanism considered to be responsible for decreasing GH secretion and GH cell proliferation in acromegaly. Two different formulations of lanreotide are currently available: lanreotide slow release, which requires intramuscular injection every 7–14 days, and lanreotide autogel, which requires deep subcutaneous injection every 4–8 weeks. Several studies have been published to date on the use of lanreotide in acromegaly. Antisecretory efficacy has been reported in 35%–70% of cases; this huge variability is probably explained by different indications (eg, primary or adjunctive postsurgical treatment), or the fact that some studies were based on patients known to be responders to somatostatin analogs. As a primary treatment, antisecretory efficacy was very similar, confirming the possibility of lanreotide as an option in cases of unsuccessful surgery, contraindication, or surgery refusal. Lanreotide also has antitumoral effects as it induces a decrease in tumor volume of 〉25% in 30%–70% of patients. This could be beneficial before transsphenoidal surgery, as a pretreatment, to decrease tumor volume and ease surgery; however, to date, advantages in terms of final remission or uncured status remain a matter of debate. Side effects are rare; the most frequent being gastrointestinal discomfort and increased risk of gallstone formation, and glucose metabolism modifications. Comparison with the other somatostatin analog, octreotide, tends to show identical levels of efficacy between both drugs. Lanreotide thus seems to be an effective treatment in acromegaly. To date, however, lanreotide is still considered as only suspending GH secretion, thus requiring prolonged and costly treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melmed S, Colao A, Barkan A, et al. Guidelines for acromegaly management: an update. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1509–1517.
Chanson P, Salenave S. Acromegaly. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2008;3:17.
Dekkers OM, Biermasz NR, Pereira AM, Romijn JA, Vandenbroucke JP. Mortality in acromegaly: a metaanalysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:61–67.
Brazeau P, Guillemin R. Editorial: Somatostatin: newcomer from the hypothalamus. N Engl J Med. 1974;290:963–964.
Lamberts SW. The role of somatostatin in the regulation of anterior pituitary hormone secretion and the use of its analogs in the treatment of human pituitary tumors. Endocr Rev. 1988;9:417–436.
Saveanu A, Jaquet P, Brue T, Barlier A. Relevance of coexpression of somatostatin and dopamine D2 receptors in pituitary adenomas. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2008;286:206–213.
Hofland LJ, Lamberts SW. The pathophysiological consequences of somatostatin receptor internalization and resistance. Endocr Rev. 2003;24:28–47.
Oberg K, Kvols L, Caplin M, et al. Consensus report on the use of somatostatin analogs for the management of neuroendocrine tumors of the gastroenteropancreatic system. Ann Oncol. 2004;15:966–973.
Ciccarelli A, Daly A, Beckers A. Lanreotide Autogel for acromegaly: a new addition to the treatment armamentarium. Treat Endocrinol. 2004;3:77–81.
Danila DC, Haidar JN, Zhang X, Katznelson L, Culler MD, Klibanski A. Somatostatin receptor-specific analogs: effects on cell proliferation and growth hormone secretion in human somatotroph tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:2976–2981.
Molitch ME. Lanreotide Autogel in the management of acromegaly. Drugs. 2008;68:724.
Troconiz IF, Cendros JM, Peraire C, et al. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of lanreotide autogel((r)) in healthy subjects: evidence for injection interval of up to 2 months. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2009;48:51–62.
Cendros JM, Peraire C, Troconiz IF, Obach R. Pharmacokinetics and population pharmacodynamic analysis of lanreotide Autogel. Metabolism. 2005;54:1276–1281.
Bronstein M, Musolino N, Jallad R, et al. Pharmacokinetic profile of lanreotide Autogel in patients with acromegaly after four deep subcutaneous injections of 60, 90 or 120 mg every 28 days. Clin Endocrinol. 2005;63:514–519.
Antonijoan RM, Barbanoj MJ, Cordero JA, et al. Pharmacokinetics of a new Autogel formulation of the somatostatin analogue lanreotide after a single subcutaneous dose in healthy volunteers. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2004;56:471–476.
Bevan JS, Newell-Price J, Wass JA, et al. Home administration of lanreotide Autogel by patients with acromegaly, or their partners, is safe and effective. Clin Endocrinol. 2008;68:343–349.
Maiza JC, Vezzosi D, Matta M, et al. Long-term (up to 18 years) effects on GH/IGF-1 hypersecretion and tumour size of primary somatostatin analogue (SSTa) therapy in patients with GH-secreting pituitary adenoma responsive to SSTa. Clin Endocrinol. 2007;67:282–289.
Colao A, Auriemma RS, Rebora A, et al. Significant tumour shrinkage after 12 months of Lanreotide Autogel-120 mg treatment given first-line in acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008 Dec 15 [Epub ahead of print]
Attanasio R, Lanzi R, Losa M, et al. Effects of lanreotide Autogel on growth hormone, insulinlike growth factor 1, and tumor size in acromegaly: a 1-year prospective multicenter study. Endocr Pract. 2008;14:846–855.
Chanson P, Borson-Chazot F, Kuhn JM, Blumberg J, Maisonobe P, Delemer B. Control of IGF-I levels with titrated dosing of lanreotide Autogel over 48 weeks in patients with acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol. 2008;69:299–305.
Lucas T, Astorga R. Efficacy of lanreotide Autogel administered every 4-8 weeks in patients with acromegaly previously responsive to lanreotide microparticles 30 mg: a phase III trial. Clin Endocrinol. 2006;65:320–326.
Caron P, Cogne M, Raingeard I, Bex-Bachellerie V, Kuhn JM. Effectiveness and tolerability of 3-year lanreotide Autogel treatment in patients with acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol. 2006;64:209–214.
Caron P, Bex M, Cullen DR, et al. One-year followup of patients with acromegaly treated with fixed or titrated doses of lanreotide Autogel. Clin Endocrinol. 2004;60:734–740.
Attanasio R, Baldelli R, Pivonello R, et al. Lanreotide 60 mg, a new long-acting formulation: effectiveness in the chronic treatment of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:5258–5265.
Ayuk J, Stewart SE, Stewart PM, Sheppard MC. Long-term safety and efficacy of depot long-acting somatostatin analogs for the treatment of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:4142–4146.
Ambrosio MR, Franceschetti P, Bondanelli M, et al. Efficacy and safety of the new 60-mg formulation of the long-acting somatostatin analog lanreotide in the treatment of acromegaly. Metabolism. 2002;51:387–393.
Amato G, Mazziotti G, Rotondi M, et al. Long-term effects of lanreotide SR and octreotide LAR on tumour shrinkage and GH hypersecretion in patients with previously untreated acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol. 2002;56:65–71.
Caron P, Beckers A, Cullen DR, et al. Efficacy of the new long-acting formulation of lanreotide (lanreotide Autogel) in the management of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87:99–104.
Cozzi R, Barausse M, Sberna M, et al. Lanreotide 60 mg, a longer-acting somatostatin analog: tumor shrinkage and hormonal normalization in acromegaly. Pituitary. 2000;3:231–238.
Attanasio R, Barausse M, Cozzi R. GH/IGF-I normalization and tumor shrinkage during long-term treatment of acromegaly by lanreotide. J Endocrinol Invest. 2001;24:209–216.
Baldelli R, Colao A, Razzore P, et al. Two-year follow-up of acromegalic patients treated with slow release lanreotide (30 mg). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2000;85:4099–4103.
Chanson P, Leselbaum A, Blumberg J, Schaison G. Efficacy and tolerability of the long-acting somatostatin analog lanreotide in acromegaly. A 12-month multicenter study of 58 acromegalic patients. French Multicenter Study Group on Lanreotide in Acromegaly. Pituitary. 2000;2:269–276.
Verhelst JA, Pedroncelli AM, Abs R, et al. Slowrelease lanreotide in the treatment of acromegaly: a study in 66 patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2000;143:577–584.
Colao A, Marzullo P, Ferone D, et al. Effectiveness and tolerability of slow release lanreotide treatment in active acromegaly. J Endocrinol Invest. 1999;22:40–47.
Caron P, Morange-Ramos I, Cogne M, Jaquet P. Three year follow-up of acromegalic patients treated with intramuscular slow-release lanreotide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997.82:18–22.
Giusti M, Gussoni G, Cuttica CM, Giordano G. Effectiveness and tolerability of slow release lanreotide treatment in active acromegaly: six-month report on an Italian multicenter study. Italian Multicenter Slow Release Lanreotide Study Group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996;81:2089–2097.
Morange I, De Boisvilliers F, Chanson P, et al. Slow release lanreotide treatment in acromegalic patients previously normalized by octreotide. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;79:145–151.
Colao A, Pivonello R, Auriemma RS, et al. Predictors of tumor shrinkage after primary therapy with somatostatin analogs in acromegaly: a prospective study in 99 patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:2112–2118.
Melmed S, Sternberg R, Cook D, et al. A critical analysis of pituitary tumor shrinkage during primary medical therapy in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4405–4410.
Mazziotti G, Giustina A. Effects of lanreotide SR and Autogel on tumor mass in patients with acromegaly: a systematic review. Pituitary. 2009 Feb 3 [Epub ahead of print].
Murray RD, Melmed S. A critical analysis of clinically available somatostatin analog formulations for therapy of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2957–2968.
Freda PU, Katznelson L, van der Lely AJ, Reyes CM, Zhao S, Rabinowitz D. Long-acting somatostatin analog therapy of acromegaly: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4465–4473.
Ezzat S, Snyder PJ, Young WF, et al. Octreotide treatment of acromegaly. A randomized, multicenter study. Ann Intern Med. 1992.117:711–718.
Lucas T, Astorga R, Catala M. Preoperative lanreotide treatment for GH-secreting pituitary adenomas: effect on tumour volume and predictive factors of significant tumour shrinkage. Clin Endocrinol. 2003;58:471–481.
Cannavo S, Squadrito S, Curto L, Almoto B, Trimarchi F. Effectiveness of slow-release lanreotide in previously operated and untreated patients with GH-secreting pituitary macroadenoma. Horm Metab Res. 2001;33:618–624.
Nemergut EC, Dumont AS, Barry UT, Laws ER. Perioperative management of patients undergoing transsphenoidal pituitary surgery. Anesth Analg. 2005;101:1170–1181.
Carlsen SM, Lund-Johansen M, Schreiner T, et al. Preoperative octreotide treatment in newly diagnosed acromegalic patients with macroadenomas increases cure short-term postoperative rates: a prospective, randomized trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:2984–2990.
Baldelli R, Ferretti E, Jaffrain-Rea ML, et al. Cardiac effects of slow-release lanreotide, a slow-release somatostatin analog, in acromegalic patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999.84:527–532.
Hradec J, Kral J, Janota T, et al. Regression of acromegalic left ventricular hypertrophy after lanreotide (a slow-release somatostatin analog). Am J Cardiol. 1999;83:1506–1509.
Lombardi G, Colao A, Marzullo P, Biondi B, Palmieri E, Fazio S. Improvement of left ventricular hypertrophy and arrhythmias after lanreotideinduced GH and IGF-I decrease in acromegaly. A prospective multi-center study. J Endocrinol Invest. 2002;25:971–976.
Maison P, Tropeano AI, Macquin-Mavier I, Giustina A, Chanson P. Impact of somatostatin analogs on the heart in acromegaly: a metaanalysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:1743–1747.
Ertorer ME, Bakiner O, Anaforoglu I, Bozkirli E, Tutuncu NB, Demirag NG. Lanreotide autogel and insulin sensitivity markers: report of 5 acromegalic patients and literature review. Neuroendocrinol Lett. 2007;28:727–733.
Steffin B, Gutt B, Bidlingmaier M, Dieterle C, Oltmann F, Schopohl J. Effects of the long-acting somatostatin analogue Lanreotide Autogel on glucose tolerance and insulin resistance in acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006;155:73–78.
Baldelli R, Battista C, Leonetti F, et al. Glucose homeostasis in acromegaly: effects of long-acting somatostatin analogues treatment. Clin Endocrinol. 2003;59:492–499.
Mazziotti G, Floriani I, Bonadonna S, Torri V, Chanson P, Giustina A. Effects of somatostatin analogs on glucose homeostasis: a meta-analysis of acromegaly studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009;94:1500–1508.
Paisley AN, Roberts ME, Trainer PJ. Withdrawal of somatostatin analogue therapy in patients with acromegaly is associated with an increased risk of acute biliary problems. Clin Endocrinol. 2007;66:723–726.
Turner HE, Lindsell DR, Vadivale A, Thillainayagam AV, Wass JA. Differing effects on gall-bladder motility of lanreotide SR and octreotide LAR for treatment of acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol. 1999;141:590–594.
Ronchi CL, Boschetti M, Degli Uberti EC, et al. Efficacy of a slow-release formulation of lanreotide (Autogel) 120 mg) in patients with acromegaly previously treated with octreotide long acting release (LAR): an open, multicentre longitudinal study. Clin Endocrinol. 2007;67:512–519.
Alexopoulou O, Abrams P, Verhelst J, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of lanreotide Autogel therapy in acromegalic patients previously treated with octreotide LAR. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;151:317–324.
van Thiel SW, Romijn JA, Biermasz NR, et al. Octreotide long-acting repeatable and lanreotide Autogel are equally effective in controlling growth hormone secretion in acromegalic patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;150:489–495.
Ashwell SG, Bevan JS, Edwards OM, et al. The efficacy and safety of lanreotide Autogel in patients with acromegaly previously treated with octreotide LAR. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004;150:473–480.
Andries M, Glintborg D, Kvistborg A, Hagen C, Andersen M. A 12-month randomized crossover study on the effects of lanreotide Autogel and octreotide long-acting repeatable on GH and IGF-l in patients with acromegaly. Clin Endocrinol. 2008;68:473–480.
Castinetti F, Morange I, Dubois N, et al. Does firstline surgery still have its place in the treatment of acromegaly? Ann Endocrinol. 2009;70:107–112.
Bates PR, Carson MN, Trainer PJ, Wass JA. Wide variation in surgical outcomes for acromegaly in the UK. Clin Endocrinol. 2008;68:136–142.
Castinetti F, Taieb D, Kuhn JM, et al. Outcome of gamma knife radiosurgery in 82 patients with acromegaly: correlation with initial hypersecretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:4483–4488.
Castinetti F, Morange I, Dufour H, Regis J, Brue T. Radiotherapy and radiosurgery in acromegaly. Pituitary. 2009;12:3–10.
Cozzi R, Attanasio R, Lodrini S, Lasio G. Cabergoline addition to depot somatostatin analogues in resistant acromegalic patients: efficacy and lack of predictive value of prolactin status. Clin Endocrinol. 2004;61:209–215.
Neggers SJ, van Aken MO, Janssen JA, Feelders RA, de Herder WW, van der Lely AJ. Long-term efficacy and safety of combined treatment of somatostatin analogs and pegvisomant in acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4598–4601.
Neggers S, de Herder W, Janssen J, Feelders R, Van der Lely A. Combined treatment for acromegaly with long-acting somatostatin analogues and pegvisomant: long-term safety up to 4.5 years (median 2.2 yrs) of follow-up in 86 patients. Eur J Endocrinol. 2009;160:529–533.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castinetti, F., Saveanu, A., Morange, I. et al. Lanreotide for the treatment of acromegaly. Adv Therapy 26, 600–612 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-009-0035-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-009-0035-4