Abstract
Introduction
Patients with diabetes complicated by hypertension and microalbuminuria have elevated cardiovascular risk, and controlling blood pressure in these patients is an urgent clinical priority. The present study aimed to examine the effects of a fixed-dose combination of antihypertensives on blood pressure and microalbuminuria.
Methods
Patients with type 2 diabetes, mild-to-moderate hypertension (diastolic blood pressure 85–105 mmHg, systolic blood pressure <160 mmHg, and 24-hour mean systolic blood pressure >130 mmHg), and microalbuminuria were randomized to 1 year of doubleblind treatment with fixed-dose manidipine/delapril (n=54) or losartan/hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) (n=56).
Results
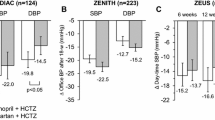
Blood pressure was significantly reduced at 1 year in both groups (−22.2/−14.6 mmHg and −19.5/−14.3 mmHg, for systolic and diastolic blood pressure respectively, P<0.001 for each), with no significant between-group difference. Reductions in microalbuminuria occurred in both groups, with mean changes at 1 year of −3.9 mg/mmol creatinine (95% CI −5.3, −2.5) for manidipine/delapril (P<0.001 vs. baseline) and −2.7 mg/mmol creatinine (95% CI −4.0, −1.3) for losartan/HCTZ (P<0.001 vs. baseline and P=0.199 between groups). Glycemia over the 1-year study was largely unaffected; the blood glucose concentration was reduced from baseline with manidipine/delapril, although not statistically significant (mean change −0.2 mmol/L, P=0.064). Both treatments were well tolerated, with discontinuation for adverse events for one (1.9%) patient in the manidipine/delapril group and two (3.6%) in the losartan/HCTZ group.
Conclusions
A fixed-dose manidipine/delapril combination represents a useful addition to the treatment options available to control hypertension complicated by diabetes and microalbuminuria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton JD, Wentworth D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care. 1993;16:434–444.
Klausen KP, Parving HH, Scharling H, Jensen JS. The association between metabolic syndrome, microalbuminuria and impaired renal function in the general population: impact on cardiovascular disease and mortality. J Intern Med. 2007;262:470–478.
Mogensen CE. Microalbuminuria predicts clinical proteinuria and early mortality in maturity-onset diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1984;310:356–360.
Pontremoli R, Leoncini G, Viazzi F, et al. Role of microalbuminuria in the assessment of cardiovascular risk in essential hypertension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(suppl. 1):S39–S41.
Jensen JS, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Strandgaard S, Schroll M, Borch-Johnsen K. Arterial hypertension, microalbuminuria, and risk of ischemic heart disease. Hypertension. 2000;35:898–903.
Borch-Johnsen K, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Strandgaard S, Schroll M, Jensen JS. Urinary albumin excretion: an independent predictor of ischemic heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1999;19:1992–1997.
Donnelly R, Yeung JM, Manning G. Microalbuminuria: a common, independent cardiovascular risk factor, especially but not exclusively in type 2 diabetes. J Hypertens. 2003;21(suppl. 1):S7–S12.
Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, Bilous RW, Cull CA, Holman RR. Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS 64). Kidney Int. 2003;63:225–232.
Ryden L, Standl E, Bartnik M, et al. The Task Force on Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Guidelines on diabetes, pre-diabetes and cardiovascular diseases: executive summary. Eur Heart J. 2007;28:88–136.
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, et al. 2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: the Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). J Hypertens. 2007;25:1105–1187.
American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes — 2007. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(suppl. 1):S4–S41.
Wenzel RR. Renal protection in hypertensive patients: selection of antihypertensive therapy. Drugs. 2005;65(suppl. 2):29–39.
McCormack PL, Keating GM. Delapril/manidipine. Drugs. 2006;66:961–969.
Roca-Cusachs A, Schmieder RE, Triposkiadis F, et al. Efficacy of manidipine/delapril versus losartan/HCTZ fixed combinations in patients with hypertension and diabetes. J Hypertens. 2008;26:813–816.
Mugellini A, Dobovisek J, Planinc D, Cremonesi G, Fogari R. Efficacy and safety of delapril plus manidipine compared with enalapril plus hydrochlorothiazide in mild to moderate essential hypertension: results of a randomized trial. Clin Ther. 2004;26:1419–1426.
Mugellini A, Preti P, Zoppi A, et al. Effect of delapril-manidipine combination vs irbesartanhydrochlorothiazide combination on fibrinolytic function in hypertensive patients with type II diabetes mellitus. J Hum Hypertens. 2004;18:687–691.
Wright JT Jr., Bakris G, Greene T, et al. Effect of blood pressure lowering and antihypertensive drug class on progression of hypertensive kidney disease: results from the AASK trial. JAMA. 2002;288:2421–2431.
Fogari R, Corradi L, Zoppi A, et al. Addition of manidipine improves the antiproteinuric effect of candesartan in hypertensive patients with type II diabetes and microalbuminuria. Am J Hypertens. 2007;20:1092–1096.
Martinez-Martin FJ, Saiz-Satjes M. Add-on manidipine versus amlodipine in diabetic patients with hypertension and microalbuminuria: the AMANDHA study. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2008;6:1347–1355.
Schmieder RE, Schrader J, Zidek W, et al. Low grade albuminuria and cardiovascular risk. Clin Res Cardiol. 2007;96:247–257.
Viberti G, Wheeldon NM. MicroAlbuminuria Reduction with VALsartan (MARVAL) Study Investigators. Microalbuminuria reduction with valsartan in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a blood pressure independent effect. Circulation. 2002;106:672–678.
Delles C, Klingbeil AU, Schneider MP, Handrock R, Weidinger G, Schmieder RE. Direct comparison of the effects of valsartan and amlodipine on renal hemodynamics in human essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 2003;16:1030–1035.
Fioretto P, Bruseghin M, Berto I, Gallina P, Manzato E, Mussap M. Renal protection in diabetes: role of glycemic control. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17(suppl. 2):S86–S89.
Bosch J, Yusuf S, et al. DREAM Trial Investigators. Effect of ramipril on the incidence of diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:1551–1562.
Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Mancia G, et al. Effects of valsartan compared to amlodipine on preventing type 2 diabetes in high-risk hypertensive patients: the VALUE trial. J Hypertens. 2006;24:1405–1412.
Yusuf S, Gerstein H, Hoogwerf B, et al. Ramipril and the development of diabetes. JAMA. 2001;286:1882–1885.
Fogari R, Zoppi A, Corradi L, Lazzari P, Mugellini A, Lusardi P. Comparative effects of lisinopril and losartan on insulin sensitivity in the treatment of non diabetic hypertensive patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1998;46:467–471.
Yavuz D, Koc M, Toprak A, et al. Effects of ACE inhibition and AT1-receptor antagonism on endothelial function and insulin sensitivity in essential hypertensive patients. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2003;4:197–203.
Nielsen S, Schmitz A, Knudsen RE, Dollerup J, Mogensen CE. Enalapril versus bendroflumethiazide in type 2 diabetes complicated by hypertension. Q J Med. 1994;87:747–754.
Officers and Coordinators for the ALLHAT Collaborative Research Group. Major outcomes in high-risk hypertensive patients randomized to angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or calcium channel blocker vs diuretic. The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA. 2002;288:2981–2997.
Verdecchia P, Angeli F, Reboldi GP, Gattobigio R. New-onset diabetes in treated hypertensive patients. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2005;7:174–179.
Zillich AJ, Garg J, Basu S, Bakris GL, Carter BL. Thiazide diuretics, potassium, and the development of diabetes: a quantitative review. Hypertension. 2006;48:219–224.
Bakris G, Molitch M, Hewkin A, et al. Differences in glucose tolerance between fixed-dose antihypertensive drug combinations in people with metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2592–2597.
Cooper-Dehoff R, Cohen JD, Bakris GL, et al. Predictors of development of diabetes mellitus in patients with coronary artery disease taking antihypertensive medications (findings from the INternational VErapamil SR-Trandolapril STudy [INVEST]). Am J Cardiol. 2006;98:890–894.
Pepine CJ, Handberg EM, Cooper-DeHoff RM, et al. A calcium antagonist vs a non-calcium antagonist hypertension treatment strategy for patients with coronary artery disease. The International Verapamil-Trandolapril Study (INVEST): a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003;290:2805–2816.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohlmann, O., Roca-Cusachs, A., Laurent, S. et al. Fixed-dose manidipine/delapril versus losartan/hydrochlorothiazide in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes and microalbuminuria. Adv Therapy 26, 313–324 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-009-0015-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-009-0015-8