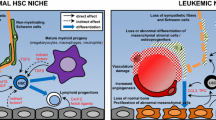
Abstract
The origin and propagation of normal and leukemic hematopoietic cells critically depend on their interplays with the hematopoietic microenvironment (or so-called niche), which represent important biological models for understanding organogenesis and tumorigenesis. Nevertheless, the anatomic and functional characterizations of the niche cells for normal hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) have proved a formidable task. It is uncertain whether the combinational effects of a few sets of molecular niche elements, behind the long-sought cellular architectures with preferred anatomic locations, actually meets the functional definition of HSC niche. Moreover, even much less is known about the niche components for numerous types of leukemia-stem cells (LSCs) that originate via discrete cellular and molecular transforming mechanisms. However, one interesting scenario is emerging, i.e., the leukemia cells can positively remodel the hematopoietic microenvironment favorable for their competition over the normal hematopoiesis that co-exists within the same eco-system. This property probably represents a previously unappreciated essential trait of a functional LSC. Obviously, the further exploration into how the hematopoietic microenvironment interplay with normal or malignant hematopoiesis will shed light onto the designing of novel types of niche-targeting therapies for leukemia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schofield R (1978) The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells 4:7–25
Roobrouck VD, Vanuytsel K, Verfaillie CM (2011) Concise review: culture mediated changes in fate and/or potency of stem cells. Stem Cells 29:583–589, doi: 10.1002/stem.603
Chow A, Lucas D, Hidalgo A, Mendez-Ferrer S, Hashimoto D, Scheiermann C, Battista M, Leboeuf M, Prophete C, van Rooijen N et al (2011) Bone marrow CD169+ macrophages promote the retention of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in the mesenchymal stem cell niche. J Exp Med 208:261–271
Christopher MJ, Rao M, Liu F, Woloszynek JR, Link DC (2011) Expression of the G-CSF receptor in monocytic cells is sufficient to mediate hematopoietic progenitor mobilization by G-CSF in mice. J Exp Med 208:251–260
Winkler IG, Sims NA, Pettit AR, Barbier V, Nowlan B, Helwani F, Poulton IJ, van Rooijen N, Alexander KA, Raggatt LJ et al (2010) Bone marrow macrophages maintain hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niches and their depletion mobilizes HSCs. Blood 116:4815–4828
Fujisaki J, Wu J, Carlson AL, Silberstein L, Putheti P, Larocca R, Gao W, Saito TI, Lo Celso C, Tsuyuzaki H et al (2011) In vivo imaging of Treg cells providing immune privilege to the haematopoietic stem-cell niche. Nature 474:216–219
Mondal BC, Mukherjee T, Mandal L, Evans CJ, Sinenko SA, Martinez-Agosto JA, Banerjee U (2011) Interaction between differentiating cell- and niche-derived signals in hematopoietic progenitor maintenance. Cell 147:1589–1600
Taichman RS, Emerson SG (1994) Human osteoblasts support hematopoiesis through the production of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med 179:1677–1682
Zhu J, Emerson SG (2004) A new bone to pick: osteoblasts and the haematopoietic stem-cell niche. Bioessays 26:595–599
Gong JK (1978) Endosteal marrow: a rich source of hematopoietic stem cells. Science 199:1443–1445
Taichman RS, Reilly MJ, Emerson SG (1996) Human osteoblasts support human hematopoietic progenitor cells in vitro bone marrow cultures. Blood 87:518–524
Calvi LM, Adams GB, Weibrecht KW, Weber JM, Olson DP, Knight MC, Martin RP, Schipani E, Divieti P, Bringhurst FR et al (2003) Osteoblastic cells regulate the haematopoietic stem cell niche. Nature 425:841–846
Zhang J, Niu C, Ye L, Huang H, He X, Tong WG, Ross J, Haug J, Johnson T, Feng JQ et al (2003) Identification of the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size. Nature 425:836–841
Kiel MJ, Radice GL, Morrison SJ (2007) Lack of evidence that hematopoietic stem cells depend on N-cadherin-mediated adhesion to osteoblasts for their maintenance. Cell Stem Cell 1:204–217
Ding L, Saunders TL, Enikolopov G, Morrison SJ (2012) Endothelial and perivascular cells maintain haematopoietic stem cells. Nature 481:457–462
Arai F, Hirao A, Ohmura M, Sato H, Matsuoka S, Takubo K, Ito K, Koh GY, Suda T (2004) Tie2/angiopoietin-1 signaling regulates hematopoietic stem cell quiescence in the bone marrow niche. Cell 118:149–161
Raaijmakers MH, Mukherjee S, Guo S, Zhang S, Kobayashi T, Schoonmaker JA, Ebert BL, Al-Shahrour F, Hasserjian RP, Scadden EO et al (2010) Bone progenitor dysfunction induces myelodysplasia and secondary leukaemia. Nature 464:852–857
Xie Y, Yin T, Wiegraebe W, He XC, Miller D, Stark D, Perko K, Alexander R, Schwartz J, Grindley JC et al (2009) Detection of functional haematopoietic stem cell niche using real-time imaging. Nature 457:97–101
Lane SW, De Vita S, Alexander KA, Karaman R, Milsom MD, Dorrance AM, Purdon A, Louis L, Bouxsein ML, Williams DA (2012) Rac signaling in osteoblastic cells is required for normal bone development but is dispensable for hematopoietic development. Blood 119:736–744
Sacchetti B, Funari A, Michienzi S, Di Cesare S, Piersanti S, Saggio I, Tagliafico E, Ferrari S, Robey PG, Riminucci M et al (2007) Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment. Cell 131:324–336
Koc ON, Gerson SL, Cooper BW, Dyhouse SM, Haynesworth SE, Caplan AI, Lazarus HM (2000) Rapid hematopoietic recovery after coinfusion of autologous-blood stem cells and culture-expanded marrow mesenchymal stem cells in advanced breast cancer patients receiving high-dose chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 18:307–316
Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Noda M, Nagasawa T (2006) Maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool by CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling in bone marrow stromal cell niches. Immunity 25:977–988
Omatsu Y, Sugiyama T, Kohara H, Kondoh G, Fujii N, Kohno K, Nagasawa T (2010) The essential functions of adipo-osteogenic progenitors as the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell niche. Immunity 33:387–399
Mendez-Ferrer S, Michurina TV, Ferraro F, Mazloom AR, Macarthur BD, Lira SA, Scadden DT, Ma'ayan A, Enikolopov GN, Frenette PS (2010) Mesenchymal and haematopoietic stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche. Nature 466:829–834
Kiel MJ, Yilmaz OH, Iwashita T, Terhorst C, Morrison SJ (2005) SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell 121:1109–1121
Bertrand JY, Traver D (2009) Hematopoietic cell development in the zebrafish embryo. Curr Opin Hematol 16:243–248
Chan CK, Chen CC, Luppen CA, Kim JB, DeBoer AT, Wei K, Helms JA, Kuo CJ, Kraft DL, Weissman IL (2009) Endochondral ossification is required for haematopoietic stem-cell niche formation. Nature 457:490–494
Hooper AT, Butler JM, Nolan DJ, Kranz A, Iida K, Kobayashi M, Kopp HG, Shido K, Petit I, Yanger K et al (2009) Engraftment and reconstitution of hematopoiesis is dependent on VEGFR2-mediated regeneration of sinusoidal endothelial cells. Cell Stem Cell 4:263–274
Butler JM, Nolan DJ, Vertes EL, Varnum-Finney B, Kobayashi H, Hooper AT, Seandel M, Shido K, White IA, Kobayashi M et al (2010) Endothelial cells are essential for the self-renewal and repopulation of Notch-dependent hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 6:251–264
Kobayashi H, Butler JM, O'Donnell R, Kobayashi M, Ding BS, Bonner B, Chiu VK, Nolan DJ, Shido K, Benjamin L et al (2010) Angiocrine factors from Akt-activated endothelial cells balance self-renewal and differentiation of haematopoietic stem cells. Nat Cell Biol 12:1046–1056
Yamazaki S, Ema H, Karlsson G, Yamaguchi T, Miyoshi H, Shioda S, Taketo MM, Karlsson S, Iwama A, Nakauchi H (2011) Nonmyelinating Schwann cells maintain hematopoietic stem cell hibernation in the bone marrow niche. Cell 147:1146–1158
Johns JL & Christopher MM (2012) Extramedullary Hematopoiesis: a new Look at the Underlying Stem Cell Niche, Theories of Development, and Occurrence in Animals. Vet Pathol
Mendt M & Cardier JE (2012) Stromal-Derived Factor-1 and Its Receptor, CXCR4, Are Constitutively Expressed by Mouse Liver Sinusoidal Endothelial Cells: Implications for the Regulation of Hematopoietic Cell Migration to the Liver During Extramedullary Hematopoiesis. Stem Cells Dev
Parmar K, Mauch P, Vergilio JA, Sackstein R, Down JD (2007) Distribution of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow according to regional hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:5431–5436
Simsek T, Kocabas F, Zheng J, Deberardinis RJ, Mahmoud AI, Olson EN, Schneider JW, Zhang CC, Sadek HA (2010) The distinct metabolic profile of hematopoietic stem cells reflects their location in a hypoxic niche. Cell Stem Cell 7:380–390
Jang YY, Sharkis SJ (2007) A low level of reactive oxygen species selects for primitive hematopoietic stem cells that may reside in the low-oxygenic niche. Blood 110:3056–3063
Winkler IG, Barbier V, Wadley R, Zannettino AC, Williams S, Levesque JP (2010) Positioning of bone marrow hematopoietic and stromal cells relative to blood flow in vivo: serially reconstituting hematopoietic stem cells reside in distinct nonperfused niches. Blood 116:375–385
Levesque JP, Winkler IG, Hendy J, Williams B, Helwani F, Barbier V, Nowlan B, Nilsson SK (2007) Hematopoietic progenitor cell mobilization results in hypoxia with increased hypoxia-inducible transcription factor-1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor A in bone marrow. Stem Cells 25:1954–1965
Kubota Y, Takubo K, Suda T (2008) Bone marrow long label-retaining cells reside in the sinusoidal hypoxic niche. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 366:335–339
Takubo K, Goda N, Yamada W, Iriuchishima H, Ikeda E, Kubota Y, Shima H, Johnson RS, Hirao A, Suematsu M et al (2010) Regulation of the HIF-1alpha level is essential for hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 7:391–402
Rehn M, Olsson A, Reckzeh K, Diffner E, Carmeliet P, Landberg G, Cammenga J (2011) Hypoxic induction of vascular endothelial growth factor regulates murine hematopoietic stem cell function in the low-oxygenic niche. Blood 118:1534–1543
Greenbaum AM, Revollo LD, Woloszynek JR, Civitelli R & Link DC (2012) N-cadherin in osteolineage cells is not required for maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood
Kiel MJ, Acar M, Radice GL, Morrison SJ (2009) Hematopoietic stem cells do not depend on N-cadherin to regulate their maintenance. Cell Stem Cell 4:170–179
Hosokawa K, Arai F, Yoshihara H, Iwasaki H, Hembree M, Yin T, Nakamura Y, Gomei Y, Takubo K, Shiama H et al (2010) Cadherin-based adhesion is a potential target for niche manipulation to protect hematopoietic stem cells in adult bone marrow. Cell Stem Cell 6:194–198
Wei J, Wunderlich M, Fox C, Alvarez S, Cigudosa JC, Wilhelm JS, Zheng Y, Cancelas JA, Gu Y, Jansen M et al (2008) Microenvironment determines lineage fate in a human model of MLL-AF9 leukemia. Cancer Cell 13:483–495
Ishikawa F, Yoshida S, Saito Y, Hijikata A, Kitamura H, Tanaka S, Nakamura R, Tanaka T, Tomiyama H, Saito N et al (2007) Chemotherapy-resistant human AML stem cells home to and engraft within the bone-marrow endosteal region. Nat Biotechnol 25:1315–1321
Lane SW, Wang YJ, Lo Celso C, Ragu C, Bullinger L, Sykes SM, Ferraro F, Shterental S, Lin CP, Gilliland DG et al (2011) Differential niche and Wnt requirements during acute myeloid leukemia progression. Blood 118:2849–2856
Kojima K, McQueen T, Chen Y, Jacamo R, Konopleva M, Shinojima N, Shpall E, Huang X, Andreeff M (2011) p53 activation of mesenchymal stromal cells partially abrogates microenvironment-mediated resistance to FLT3 inhibition in AML through HIF-1alpha-mediated down-regulation of CXCL12. Blood 118:4431–4439
Zeng Z, Shi YX, Samudio IJ, Wang RY, Ling X, Frolova O, Levis M, Rubin JB, Negrin RR, Estey EH et al (2009) Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML. Blood 113:6215–6224
Olsnes AM, Hatfield KJ, Bruserud O (2009) The chemokine system and its contribution to leukemogenesis and treatment responsiveness in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. J Buon 14(Suppl 1):S131–140
Nervi B, Ramirez P, Rettig MP, Uy GL, Holt MS, Ritchey JK, Prior JL, Piwnica-Worms D, Bridger G, Ley TJ et al (2009) Chemosensitization of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) following mobilization by the CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100. Blood 113:6206–6214
Tavor S, Eisenbach M, Jacob-Hirsch J, Golan T, Petit I, Benzion K, Kay S, Baron S, Amariglio N, Deutsch V et al (2008) The CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 impairs survival of human AML cells and induces their differentiation. Leukemia 22:2151–5158
Li H, Guo L, Jie S, Liu W, Zhu J, Du W, Fan L, Wang X, Fu B, Huang S (2008) Berberine inhibits SDF-1-induced AML cells and leukemic stem cells migration via regulation of SDF-1 level in bone marrow stromal cells. Biomed Pharmacother 62:573–578
Spoo AC, Lubbert M, Wierda WG, Burger JA (2007) CXCR4 is a prognostic marker in acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 109:786–791
Becker PS, Kopecky KJ, Wilks AN, Chien S, Harlan JM, Willman CL, Petersdorf SH, Stirewalt DL, Papayannopoulou T, Appelbaum FR (2009) Very late antigen-4 function of myeloblasts correlates with improved overall survival for patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 113:866–874
Bradstock KF, Gottlieb DJ (1995) Interaction of acute leukemia cells with the bone marrow microenvironment: implications for control of minimal residual disease. Leuk Lymphoma 18:1–16
Matsunaga T, Takemoto N, Sato T, Takimoto R, Tanaka I, Fujimi A, Akiyama T, Kuroda H, Kawano Y, Kobune M et al (2003) Interaction between leukemic-cell VLA-4 and stromal fibronectin is a decisive factor for minimal residual disease of acute myelogenous leukemia. Nat Med 9:1158–1165
Jin L, Hope KJ, Zhai Q, Smadja-Joffe F, Dick JE (2006) Targeting of CD44 eradicates human acute myeloid leukemic stem cells. Nat Med 12:1167–1174
Charrad RS, Li Y, Delpech B, Balitrand N, Clay D, Jasmin C, Chomienne C, Smadja-Joffe F (1999) Ligation of the CD44 adhesion molecule reverses blockage of differentiation in human acute myeloid leukemia. Nat Med 5:669–676
Sipkins DA, Wei X, Wu JW, Runnels JM, Cote D, Means TK, Luster AD, Scadden DT, Lin CP (2005) In vivo imaging of specialized bone marrow endothelial microdomains for tumour engraftment. Nature 435:969–973
Nwabo Kamdje AH, Mosna F, Bifari F, Lisi V, Bassi G, Malpeli G, Ricciardi M, Perbellini O, Scupoli MT, Pizzolo G et al (2011) Notch-3 and Notch-4 signaling rescue from apoptosis human B-ALL cells in contact with human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood 118:380–389
Ayala F, Dewar R, Kieran M, Kalluri R (2009) Contribution of bone microenvironment to leukemogenesis and leukemia progression. Leukemia 23:2233–2241
Blau O, Baldus CD, Hofmann WK, Thiel G, Nolte F, Burmeister T, Turkmen S, Benlasfer O, Schumann E, Sindram A et al (2011) Mesenchymal stromal cells of myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia patients have distinct genetic abnormalities compared with leukemic blasts. Blood 118:5583–5592
Hu X, Shen H, Tian C, Yu H, Zheng G, XuFeng R, Ju Z, Xu J, Wang J, Cheng T (2009) Kinetics of normal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in a Notch1-induced leukemia model. Blood 114:3783–3792
Zhang B, Ho YW, Huang Q, Maeda T, Lin A, Lee SU, Hair A, Holyoake TL, Huettner C, Bhatia R (2012) Altered microenvironmental regulation of leukemic and normal stem cells in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Cell 21:577–592
Colmone A, Amorim M, Pontier AL, Wang S, Jablonski E, Sipkins DA (2008) Leukemic cells create bone marrow niches that disrupt the behavior of normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. Science 322:1861–1865
Despeaux M, Labat E, Gadelorge M, Prade N, Bertrand J, Demur C, Recher C, Bonnevialle P, Payrastre B, Bourin P et al (2011) Critical features of FAK-expressing AML bone marrow microenvironment through leukemia stem cell hijacking of mesenchymal stromal cells. Leukemia 25:1789–1793
Frisch BJ, Ashton JM, Xing L, Becker MW, Jordan CT, Calvi LM (2012) Functional inhibition of osteoblastic cells in an in vivo mouse model of myeloid leukemia. Blood 119:540–550
Zhu J, Garrett R, Jung Y, Zhang Y, Kim N, Wang J, Joe GJ, Hexner E, Choi Y, Taichman RS et al (2007) Osteoblasts support B-lymphocyte commitment and differentiation from hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 109:3706–3712
Hosokawa K, Arai F, Yoshihara H, Iwasaki H, Nakamura Y, Gomei Y, Suda T (2010) Knockdown of N-cadherin suppresses the long-term engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 116:554–563
Nygren MK, Dosen-Dahl G, Stubberud H, Walchli S, Munthe E, Rian E (2009) beta-catenin is involved in N-cadherin-dependent adhesion, but not in canonical Wnt signaling in E2A-PBX1-positive B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Exp Hematol 37:225–233
Zhang B, Groffen J, Heisterkamp N (2007) Increased resistance to a farnesyltransferase inhibitor by N-cadherin expression in Bcr/Abl-P190 lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia 21:1189–1197
Zhang T, Liu S, Yang P, Han C, Wang J, Liu J, Han Y, Yu Y, Cao X (2009) Fibronectin maintains survival of mouse natural killer (NK) cells via CD11b/Src/beta-catenin pathway. Blood 114:4081–4088
Umemoto T, Yamato M, Ishihara J, Shiratsuchi Y, Utsumi M, Morita Y, Tsukui H, Terasawa M, Shibata T, Nishida K et al (2012) Integrin-alphavbeta3 regulates thrombopoietin-mediated maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 119:83–94
Maillard I, Koch U, Dumortier A, Shestova O, Xu L, Sai H, Pross SE, Aster JC, Bhandoola A, Radtke F et al (2008) Canonical notch signaling is dispensable for the maintenance of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2:356–366
Mercher T, Cornejo MG, Sears C, Kindler T, Moore SA, Maillard I, Pear WS, Aster JC, Gilliland DG (2008) Notch signaling specifies megakaryocyte development from hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 3:314–326
Duncan AW, Rattis FM, DiMascio LN, Congdon KL, Pazianos G, Zhao C, Yoon K, Cook JM, Willert K, Gaiano N et al (2005) Integration of Notch and Wnt signaling in hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Nat Immunol 6:314–322
Varnum-Finney B, Halasz LM, Sun M, Gridley T, Radtke F, Bernstein ID (2011) Notch2 governs the rate of generation of mouse long—and short-term repopulating stem cells. J Clin Invest 121:1207–1216
Aerbajinai W, Zhu J, Kumkhaek C, Chin K, Rodgers GP (2009) SCF induces gamma-globin gene expression by regulating downstream transcription factor COUP-TFII. Blood 114:187–194
Simon C, Dondi E, Chaix A, de Sepulveda P, Kubiseski TJ, Varin-Blank N, Velazquez L (2008) Lnk adaptor protein down-regulates specific Kit-induced signaling pathways in primary mast cells. Blood 112:4039–4047
Calderon L, Boehm T (2012) Synergistic, context-dependent, and hierarchical functions of epithelial components in thymic microenvironments. Cell 149:159–172
Wunderlich M, Chou FS, Link KA, Mizukawa B, Perry RL, Carroll M, Mulloy JC (2011) AML xenograft efficiency is significantly improved in NOD/SCID-IL2RG mice constitutively expressing human SCF, GM-CSF and IL-3. Leukemia 24:1785–1788
Avecilla ST, Hattori K, Heissig B, Tejada R, Liao F, Shido K, Jin DK, Dias S, Zhang F, Hartman TE et al (2004) Chemokine-mediated interaction of hematopoietic progenitors with the bone marrow vascular niche is required for thrombopoiesis. Nat Med 10:64–71
Hatfield K, Oyan AM, Ersvaer E, Kalland KH, Lassalle P, Gjertsen BT, Bruserud O (2009) Primary human acute myeloid leukaemia cells increase the proliferation of microvascular endothelial cells through the release of soluble mediators. Br J Haematol 144:53–68
Nakajima H, Ito M, Smookler DS, Shibata F, Fukuchi Y, Morikawa Y, Ikeda Y, Arai F, Suda T, Khokha R et al (2010) TIMP-3 recruits quiescent hematopoietic stem cells into active cell cycle and expands multipotent progenitor pool. Blood 116:4474–4482
Corazza F, Hermans C, D'Hondt S, Ferster A, Kentos A, Benoit Y, Sariban E (2006) Circulating thrombopoietin as an in vivo growth factor for blast cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 107:2525–2530
Kirito K, Fox N, Komatsu N, Kaushansky K (2005) Thrombopoietin enhances expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in primitive hematopoietic cells through induction of HIF-1alpha. Blood 105:4258–4263
Kirito K, Fox N, Kaushansky K (2003) Thrombopoietin stimulates Hoxb4 expression: an explanation for the favorable effects of TPO on hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 102:3172–3178
Luis TC, Naber BA, Roozen PP, Brugman MH, de Haas EF, Ghazvini M, Fibbe WE, van Dongen JJ, Fodde R, Staal FJ (2011) Canonical wnt signaling regulates hematopoiesis in a dosage-dependent fashion. Cell Stem Cell 9:345–356
Malhotra S, Kincade PW (2009) Wnt-related molecules and signaling pathway equilibrium in hematopoiesis. Cell Stem Cell 4:27–36
Fleming HE, Janzen V, Lo Celso C, Guo J, Leahy KM, Kronenberg HM, Scadden DT (2008) Wnt signaling in the niche enforces hematopoietic stem cell quiescence and is necessary to preserve self-renewal in vivo. Cell Stem Cell 2:274–283
Wang Y, Krivtsov AV, Sinha AU, North TE, Goessling W, Feng Z, Zon LI, Armstrong SA (2010) The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway is required for the development of leukemia stem cells in AML. Science 327:1650–1653
Jeannet G, Scheller M, Scarpellino L, Duboux S, Gardiol N, Back J, Kuttler F, Malanchi I, Birchmeier W, Leutz A et al (2008) Long-term, multilineage hematopoiesis occurs in the combined absence of beta-catenin and gamma-catenin. Blood 111:142–149
Kim DH, Lee NY, Lee MH, Sohn SK, Do YR, Park JY (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene (VEGFA) polymorphism can predict the prognosis in acute myeloid leukaemia patients. Br J Haematol 140:71–79
Gao J, Graves S, Koch U, Liu S, Jankovic V, Buonamici S, El Andaloussi A, Nimer SD, Kee BL, Taichman R et al (2009) Hedgehog signaling is dispensable for adult hematopoietic stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell 4:548–558
Merchant A, Joseph G, Wang Q, Brennan S, Matsui W (2010) Gli1 regulates the proliferation and differentiation of HSCs and myeloid progenitors. Blood 115:2391–2396
Trowbridge JJ, Scott MP, Bhatia M (2006) Hedgehog modulates cell cycle regulators in stem cells to control hematopoietic regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14134–14139
Hofmann I, Stover EH, Cullen DE, Mao J, Morgan KJ, Lee BH, Kharas MG, Miller PG, Cornejo MG, Okabe R et al (2009) Hedgehog signaling is dispensable for adult murine hematopoietic stem cell function and hematopoiesis. Cell Stem Cell 4:559–567
Dierks C, Beigi R, Guo GR, Zirlik K, Stegert MR, Manley P, Trussell C, Schmitt-Graeff A, Landwerlin K, Veelken H et al (2008) Expansion of Bcr-Abl-positive leukemic stem cells is dependent on Hedgehog pathway activation. Cancer Cell 14:238–249
Zhao C, Chen A, Jamieson CH, Fereshteh M, Abrahamsson A, Blum J, Kwon HY, Kim J, Chute JP, Rizzieri D et al (2009) Hedgehog signalling is essential for maintenance of cancer stem cells in myeloid leukaemia. Nature 458:776–779
Lin TL, Wang QH, Brown P, Peacock C, Merchant AA, Brennan S, Jones E, McGovern K, Watkins DN, Sakamoto KM et al (2012) Self-renewal of acute lymphocytic leukemia cells is limited by the Hedgehog pathway inhibitors cyclopamine and IPI-926. PLoS One 5:e15262
Challen GA, Boles NC, Chambers SM, Goodell MA (2010) Distinct hematopoietic stem cell subtypes are differentially regulated by TGF-beta1. Cell Stem Cell 6:265–278
Ficara F, Murphy MJ, Lin M, Cleary ML (2008) Pbx1 regulates self-renewal of long-term hematopoietic stem cells by maintaining their quiescence. Cell Stem Cell 2:484–496
Larsson J, Blank U, Helgadottir H, Bjornsson JM, Ehinger M, Goumans MJ, Fan X, Leveen P, Karlsson S (2003) TGF-beta signaling-deficient hematopoietic stem cells have normal self-renewal and regenerative ability in vivo despite increased proliferative capacity in vitro. Blood 102:3129–3135
Ledran MH, Krassowska A, Armstrong L, Dimmick I, Renstrom J, Lang R, Yung S, Santibanez-Coref M, Dzierzak E, Stojkovic M et al (2008) Efficient hematopoietic differentiation of human embryonic stem cells on stromal cells derived from hematopoietic niches. Cell Stem Cell 3:85–98
Yamazaki S, Iwama A, Takayanagi S, Eto K, Ema H, Nakauchi H (2009) TGF-beta as a candidate bone marrow niche signal to induce hematopoietic stem cell hibernation. Blood 113:1250–1256
North TE, Goessling W, Walkley CR, Lengerke C, Kopani KR, Lord AM, Weber GJ, Bowman TV, Jang IH, Grosser T et al (2007) Prostaglandin E2 regulates vertebrate haematopoietic stem cell homeostasis. Nature 447:1007–1011
Frisch BJ, Porter RL, Gigliotti BJ, Olm-Shipman AJ, Weber JM, O'Keefe RJ, Jordan CT, Calvi LM (2009) In vivo prostaglandin E2 treatment alters the bone marrow microenvironment and preferentially expands short-term hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 114:4054–4063
Hoggatt J, Singh P, Sampath J, Pelus LM (2009) Prostaglandin E2 enhances hematopoietic stem cell homing, survival, and proliferation. Blood 113:5444–5455
Rocca B, Morosetti R, Habib A, Maggiano N, Zassadowski F, Ciabattoni G, Chomienne C, Papp B, Ranelletti FO (2004) Cyclooxygenase-1, but not-2, is upregulated in NB4 leukemic cells and human primary promyelocytic blasts during differentiation. Leukemia 18:1373–1379
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (81090412) to Jiang Zhu.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Mm., Zhu, J. The Regulation of Normal and Leukemic Hematopoietic Stem Cells by Niches. Cancer Microenvironment 5, 295–305 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-012-0114-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-012-0114-y