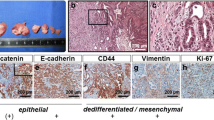
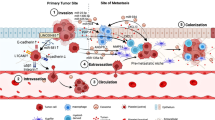
Abstract
Colon cancer frequently metastasizes to the liver but the genetic and phenotypic properties of specific cancer cells able to implant and grow in this organ have not yet been established. The contribution of the patient’s genetic, physiologic and pathologic backgrounds to the incidence and development of hepatic colon cancer metastases is also presently misunderstood. At a transcriptional level, hepatic metastasis development is in part associated with marked changes in gene expression of colon cancer cells that may originate in the primary tumor. Other changes occur in the liver and are regulated by hepatic cells, which represent the new microenvironment for metastatic colon cancer cells. However, hepatic parenchymal and non-parenchymal cell functions are also affected by both tumor-derived factors and systemic host factors, which suggests that the hepatic metastasis microenvironment is a functional linkage between the hepatic pathophysiology of the colon cancer patient and the biology of its cancer cells. Therefore, together with metastasis-related gene profiles suggesting the existence of liver metastasis potential in primary tumors, new biomarkers of the prometastatic microenvironment supported by the liver reaction to colon cancer factors may be helpful for the individual assessment of hepatic metastasis risk in colon cancer patients. In addition, knowledge on hepatic metastasis gene regulation by the hepatic microenvironment may open multiple opportunities for therapeutic intervention during colon cancer metastasis at both subclinical and advanced stages.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Egeblad M, Nakasone ES, Werb Z (2010) Tumors as organs: complex tissues that interface with the entire organism. Dev Cell 18:884–901
Witz IP, Levy-Nissenbaum O (2006) The tumor microenvironment in the post-PAGET era. Cancer Letters 246:1–10
Fidler IJ (2001) Seed and soil revisited: contribution of the organ microenvironment to cancer metastasis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 10:257–269
Paget S (1889) The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet 133:571–573
Wang HB, Dembo M, Hanks SK, Wang Y (2001) Focal adhesion kinase is involved in mechanosensing during fibroblast migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11295–11300
Schedin P, Keely PJ (2011) Mammary gland ECM remodeling, stiffness, and mechanosignaling in normal development and tumor progression. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a003228
Jessup JM, Laguinge L, Lin S et al (2004) Carcinoembryonic antigen induction of IL-10 and IL-6 inhibits hepatic ischemic/reperfusion injury to colorectal carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 111:332–337
Beacham DA, Cukierman E (2005) Stromagenesis: The changing face of fibroblastic microenvironments during tumor progression. Semin Cancer Biol 15:329–341
Baeriswyl V, Christofori G (2009) The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 19:329–337
Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye QH et al (2006) Prediction of venous metastases, recurrence, and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma based on a unique immune response signature of the liver microenvironment. Cancer Cell 10:99–111
Vidal-Vanaclocha F (2008) The prometastatic microenvironment of the liver. Cancer Microenvironment 1:113–129
Kaplan RN, Rafii S, Lyden D (2006) Preparing the “soil”: the premetastatic niche. Cancer Res 66:11089–11093
Vidal-Vanaclocha F (2011). The Tumor Microenvironment at Different Stages of Hepatic Metastasis P. Brodt (ed.), Liver Metastasis: Biology and Clinical Management, Cancer Metastasis – Biology and Treatment 16, doi:10.1007/978-94-007-0292-9_3, C_ Springer Science + Business Media B.V.
Herath NI, Boyd AW (2010) The role of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 126:2003–2011
Bellam N, Pasche B (2010) Tgf-beta signaling alterations and colon cancer. Cancer Treat Res 155:85–103
Jiang Y, Kimchi ET, Staveley-O'Carroll KF et al (2009) Assessment of K-ras mutation: a step toward personalized medicine for patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer 115:3609–3617
Vidal-Vanaclocha F. Architectural and Functional Aspects of the Liver with Implications for Cancer Metastasis. P. Brodt (ed.), Liver Metastasis: Biology and Clinical Management, Cancer Metastasis – Biology and Treatment 16, doi:10.1007/978-94-007-0292-9_2,C_ Springer Science + Business Media B.V. 2011.
Barbera-Guillem E, Smith I, Weiss L (1993) Cancer-cell traffic in the liver. II. Arrest, transit and death of B16F10 and M5076 cells in the sinusoids. Int J Cancer 53:298–301
Friedman SL (2008) Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 134:1655–1669
Jungermann K (1986) Functional heterogeneity of periportal and perivenous hepatocytes. Enzyme 35:161–180
Parker GA, Picut CA (2005) Liver Immunobiology. Toxicol Pathol 33:52–62
McCuskey RS (1994) The hepatic microvascular system. In: Arias IM, Boyer JL, Fausto N et al (eds) The liver: biology and pathobiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 1089–1106
Oda M, Han JY, Yokomori H (2000) Local regulators of hepatic sinusoidal microcirculation: recent advances. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 23:85–94
Barberá-Guillem E, Rocha M, Alvarez A et al (1991) Differences in the lectin-binding patterns of the periportal and perivenous endothelial domains in the liver sinusoids. Hepatology 14:131–139
Scoazec JY, Feldmann G (1994) The cell adhesion molecules of hepatic sinusoidal endothelial cells. J Hepatol 20:296–300
Seternes T, Sorensen K, Smedsrod B (2002) Scavenger endothelial cells of vertebrates: a nonperipheral leukocyte system for high-capacity elimination of waste macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7594–7597
Seki E, Brenner DA (2008) Toll-like receptors and adaptor molecules in liver disease: update. Hepatology 48:322–335
Arteta B, Lasuen N, Lopategi A et al (2010) Colon carcinoma cell interaction with liver sinusoidal endothelium inhibits organ-specific anti-tumor immunity via IL-1-induced mannose receptor. Hepatology 51:2172–2182
Mendoza L, Carrascal T, de Luca M et al (2001) Hydrogen peroxide mediates vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression from IL-18-activated hepatic sinusoidal endothelium: implications for circulating cancer cell arrest in murine liver. Hepatology 34:298–310
Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Fantuzzi G, Mendoza L et al (2000) IL-18 regulates IL-1 beta-dependent hepatic melanoma metastasis via vascular adhesion molecule-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:734–739
Khatib AM, Auguste P, Fallavollita L et al (2005) Characterization of the host proinflammatory response to tumor cells during the initial stages of liver metastasis. Am J Pathol 167:749–759
Anasagasti MJ, Alvarez A, Martin JJ et al (1997) Sinusoidal endothelium release of hydrogen peroxide enhances very late antigen-4-mediated melanoma cell adherence and tumor cytotoxicity during interleukin-1 promotion of hepatic melanoma metastasis in mice. Hepatology 25:840–846
Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Amézaga C, Asumendi A et al (1994) Interleukin-1 receptor blockade reduces the number and size of murine B16 melanoma hepatic metastases. Cancer Res 54:2667–2672
Carrascal T, Mendoza L, Vacarcel M et al (2003) Interleukin-18 binding protein reduces B16 melanoma hepatic metastasis by neutralizing the adhesiveness and growth factors of sinusoidal endothelial cell. Cancer Res 63:491–497
Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Alvarez A, Asumendi A et al (1996) Interleukin 1 (IL-1)-dependent melanoma hepatic metastasis in vivo; increased endothelial adherence by IL-1-induced mannose receptors and growth factor production in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:198–205
Zubia A, Mendoza L, Vivanco S et al (2005) Application of stereocontrolled stepwise [3 + 2] Cycloadditions to the preparation of inhibitors of alpha(4)beta(1)-integrin-mediated hepatic melanoma metastasis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 44:2903–2907
Fausto N (2004) Liver regeneration and repair: hepatocytes, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Hepatology 39:1477–1487
Smedsrød B, Le Couteur D, Ikejima K et al (2009) Hepatic sinusoidal cells in health and disease: update from the 14th International Symposium. Liver Int 29:490–501
Malik R, Selden C, Hodgson H (2002) The role of non-parenchymal cells in liver growth. Sem Cell Dev Biol 13:425–431
Ramadori G, Saile B (2004) Portal tract fibrogenesis in the liver. Lab Invest 84:153–159
Olaso E, Santisteban A, Bidaurrazaga J et al (1997) Tumor-dependent activation of rodent hepatic stellate cells during experimental melanoma metastasis. Hepatology 26:634–642
Olaso E, Salado C, Egilegor E et al (2003) Proangiogenic role of tumor-activated hepatic stellate cells in experimental melanoma metastasis. Hepatology 37:674–685
Libbrecht L, Cassiman D, Desmet V et al (2002) The correlation between portal myofibroblasts and development of intrahepatic bile ducts and arterial branches in human liver. Liver 22:252–258
Asai K, Tamakawa S, Yamamoto M et al (2006) Activated hepatic stellate cells overexpress p75NTR after partial hepatectomy and undergo apoptosis on nerve growth factor stimulation. Liver Int 26:595–603
Li Z, Diehl AM (2003) Innate immunity in the liver. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 19:565–571
Parker GA, Picut CA (2003) Liver Immunobiology. Toxicol Pathol 33:52–62
Starzl TE, Murase N, Abu-Elmagd K et al (2003) Tolerogenic immunosuppression for organ transplantation. Lancet 361:1502–1510
Safadi R, Alvarez CE, Ohta M et al (2005) Enhanced oral tolerance in transgenic mice with hepatocyte secretion of IL-10. J Immunol 175:3577–3583
Kern M, Popov A, Kurts C et al (2010) Taking off the brakes: T cell immunity in the liver. Trends Immunol 31:311–317
Frevert U, Engelmann S, Zougbédé S et al (2005) Intravital Observation of Plasmodium berghei Sporozoite Infection of the Liver. PLoS Biol 3:1034–1046
Anttila VJ, Elonen E, Nordling S et al (1997) Hepatosplenic candidiasis in patients with acute leukemia: incidence and prognostic implications. Clin Infect Dis 24:375–380
Beaskoetxea J, Telleria N, Del Villar A et al (2006) Identification of microenvironmentally-regulated genes of colon carcinoma cells from human hepatic metastasis. Proc Amer Assoc Cancer Res 47:4298
Murthy SM, Goldschmidt RA, Rao LN et al (1989) The influence of surgical trauma on experimental metastasis. Cancer 64:2035–2044
Murthy MS, Scanlon EF, Jelachich ML et al (1995) Growth and metastasis of human breast cancers in athymic nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis 13:3–15
Bogden AE, Moreau J-P, Eden PA (1997) Proliferative response of human animal tumors to surgical wounding of normal tissues: Onset, duration and inhibition. Br J Cancer 75:1021–1027
Hofer SO, Shrayer D, Reichner JS et al (1998) Wound-induced tumor progression: A probable role in recurrence after tumor resection. Arch Surg 133:383–389
Nordlinger B, Guiguet M, Vaillant JC et al (1996) Surgical resection of colorectal carcinoma metastases to the liver: a prognostic scoring system to improve case selection, based on 1568 patients. Cancer 77:1254–1262
Jaeck D, Bachellier P, Guiguet M et al (1997) Long-term survival following resection of colorectal hepatic metastases. Br J Surg 84:977–980
Makuuchi M, Le Thai B, Takayasu K et al (1990) Preoperative portal embolizationto increase safety of major hepatectomy for hilar bile duct carcinoma: a preliminary report. Surgery 107:521–527
Elias D, Roche A, Vavasseur D et al (1992) Induction of hypertrophy of a small left hepatic lobe by preoperative right portal embolization, preceding extended right hepatectomy. Ann Chir 46:404–410
Azoulay D, Castaing D, Smail A et al (2000) Resection of non resectable liver metastases from colorectal cancer after percutaneous PVE. Ann Surg 231:480–486
Liu H, Zhu S (2009) Present status and future perspectives of preoperative portal vein embolization. Am J Surgery 197:686–690
Elias D, de Baere T, Roche A et al (1999) During liver regeneration following right portal embolization the growth rate of liver metastases is more rapid than that of the liver parenchyma. Br J Surg 86:784–788
Higgins GM, Anderson RM (1931) Experimental pathology of the liver. I. Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Arch Pathol 12:186–202
Ichihashi H, Mabuchi H, Suenaga M et al (1984) Liver regeneration andtumor growth in the rat after partial hepatectomy. Jpn J Surg 14:510–514
Morimoto H, Nio Y, Imai S et al (1992) Hepatectomy accelerates the growthof transplanted liver tumor in mice. Cancer Detec Prev 16:137–147
Panis Y, Ribeiro J, Chretien Y et al (1992) Dormant liver metastases: an experimental study. Br J Surg 79:221–223
Gutman M, Singh RK, Price JE et al (1994) Accelerated growth of human colon cancer cells in nude mice undergoing liver regeneration. Invasion Metastasis 14:362–371
Asaga T, Suzuki K, Umeda M et al (1991) The enhancement of tumor growth after partial hepatectomy and the effect of sera obtained from hepatectomized rats on tumor cell growth. Jpn J Surg 21:669–675
Kokudo N, Tada K, Seki M et al (2001) Proliferative activity of intrahepatic colorectal metastases after preoperative hemihepatic portal vein embolization. Hepatology 34:267–272
Takahara T, Xue F, Mazzone M et al (2008) Metron factor-1 prevents liver injury without promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Hepatology 47:2010–2025
Gervaz P, Pak-art R, Nivatvongs S et al (2003) Colorectal adenocarcinoma in cirrhotic patients. J Am Coll Surg 196:874–879
Melato M, Laurino L, Mucli E et al (1989) Relationship between cirrhosis, liver cancer, and hepatic metastases. An autopsy study. Cancer 64:455–459
Pereira-Lima JE, Lichtenfels E, Barbosa FS et al (2003) Prevalence study of metastases in cirrhotic livers. Hepatogastroenterology 50:1490–1495
Seymour K, Charnley RM (1999) Evidence that metastasis is less common in cirrhotic than normal liver: a systematic review of post-mortem case-control studies. Br J Surg 86:1237–1242
Uetsuji S, Yamamura M, Yamamichi K et al (1992) Absence of colorectal cancer metastasis to the cirrhotic liver. Am J Surg 164:176–177
Song E, Chen J, Ouyang N et al (2001) Kupffer cells of cirrhotic rat livers sensitize colon cancer cells to Fas-mediated apoptosis. Br J Cancer 84:1265–1271
Vanbockrijck M, Kloppel G (1992) Incidence and morphology of liver metastasis from extrahepatic malignancies to cirrhotic livers. Zentralbl Pathol 138:91–96
Qi K, Qiu H, Sun D et al (2004) Impact of cirrhosis on the development of experimental hepatic metastases by B16F1 melanoma cells in C57BL/6 mice. Hepatology 40:1144–1150
Olaso E, Ikeda K, Eng FJ et al (2001) DDR2 receptor promotes MMP-2-mediated proliferation and invasion by hepatic stellate cells. J Clin Invest 108:1369–1378
Badiola I, Olaso E, Crende O, et al (2011). Discoidin domain receptor 2 deficiency predisposes hepatic tissue to colon carcinoma metastasis. Gut, in press.
Zhang LJ, Zheng WD, Chen YX et al (2007) Antifibrotic effects of interleukin-10 on experimental hepatic fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology 54:2092–2098
Jessup JM, Samara R, Battle P et al (2004) Carcinoembryonic antigen promotes tumor cell survival in liver through an IL-10-dependent pathway. Clin Exp Metastasis 21:709–717
Zhang B, Halder SK, Kashikar ND et al (2010) Antimetastatic role of Smad4 signaling in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 138:969–980
Nadal C, Maurel J, Gascon P (2007) Is there a genetic signature for liver metastasis in colorectal cancer? World J Gastroenterol 13:5832–5844
Kwon HC, Kim SH, Roh MS et al (2004) Gene expression profiling in lymph node-positive and lymph node-negative colorectal cancer. Dis Colon Rectum 47:141–152
Ki DH, Jeung HC, Park CH et al (2007) Whole genome analysis for liver metastasis gene signatures in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer 121:2005–2012
Bertucci F, Salas S, Eysteries S et al (2004) Gene expression profi ling of colon cancer by DNA microarrays and correlation with histoclinical parameters. Oncogene 23:1377–1391
Koehler A, Bataille F, Schmid C et al (2004) Gene expression profiling of colorectal cancer and metastases divides tumours according to their clinicopathological stage. J Pathol 204:65–74
Agrawal D, Chen T, Irby R et al (2002) Osteopontin identified as lead marker of colon cancer progression, using pooled sample expression profiling. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:513–521
D’Arrigo A, Belluco C, Ambrosi A et al (2005) Metastatic transcriptional pattern revealed by gene expression profiling in primary colorectal carcinoma. Int J Cancer 115:256–262
Yamasaki M, Takemasa I, Komori T et al (2007) The gene expression profile represents the molecular nature of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol 30:129–138
Fritzmann J, Morkel M, Besser D et al (2009) A colorectal cancer expression profile that includes transforming growth factor beta inhibitor BAMBI predicts metastatic potential. Gastroenterology 137:165–175
Del Villar A, Telleria N, Beaskoetxea J, et al (2008). Differential contribution of hepatocytes and hepatic myofibroblasts to the microenvironmental regulation of hepatic metastasis genes from colon carcinoma patients. Proc Amer Assoc Cancer Res 48:
Beaskoetxea J, Telleria N, del Villar A, et al (2009). Exposure of colon carcinoma cells to hepatic microenvironment and of hepatic cells to tumor factors promotes gene expression mimic contributing to organ tropism and metastasis development. Proc Amer Assoc Cancer Res 49:
Arumugam T, Simeone DM, Schmidt AM, Logsdon CD (2004) S100P stimulates cell proliferation and survival via receptor for activated glycation end products (RAGE). J Biol Chem 279:5059–5065
Fuentes MK, Nigavekar SS, Arumugam T et al (2007) RAGE activation by S100P in colon cancer stimulates growth, migration, and cell signaling pathways. Dis Colon Rectum 50:1230–1240
Jiang L, Lai YK, Zhang J et al (2011) Targeting S100P inhibits colon cancer growth and metastasis by lentivirus-mediated RNA interference and proteomic analysis. Mol Med. doi:10.2119/molmed.2011.00008
Gout S, Huot J (2008) Role of Cancer Microenvironment in Metastasis: Focus on Colon Cancer. CAMI 1:69–83
Richert L, Alexandre E, Lloyd T et al (2004) Tissue collection, transport and isolation procedures required to optimise human hepatocyte isolation from waste liver surgical resections. A multi-laboratory study. Liver Int 24:371–378
Kim CH, Kim J, Kahng H, Choi EC (2007) Change of E-cadherin by hepatocyte growth factor and effects on the prognosis of hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol 14:1565–1574
Agrawal D, Chen T, Irby R et al (2002) Osteopontin identified as lead marker of colon cancer progression, using pooled sample expression profiling. J Natl Cancer Inst 94:513–521
Pan HW, Ou YH, Peng SY et al (2003) Overexpression of osteopontin is associated with intrahepatic metastasis, early recurrence, and poorer prognosis of surgically resected hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 98:119–127
Reiniger IW, Wolf A, Welge-Lussen U et al (2007) Osteopontin as a serologic marker for metastatic uveal melanoma: results of a pilot study. Am J Ophthalmol 143:705–707
Wai PY, Mi Z, Guo H et al (2005) Osteopontin silencing by small interfering RNA suppresses in vitro and in vivo CT26 murine colon adenocarcinoma metastasis. Carcinogenesis 26:741–751
Ma C, Rong Y, Radiloff DR et al (2008) Extracellular matrix protein betaig-h3/TGFBI promotes metastasis of colon cancer by enhancing cell extravasation. Genes Dev 22:308–321
Raffel J, Bhattacharyya AK, Gallegos A et al (2003) Increased expression of thioredoxin-1 in human colorectal cancer is associated with decreased patient survival. J Lab Clin Med 142:46–51
Noike T, Miwa S, Soeda J et al (2008) Increased expression of thioredoxin-1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and redox factor-1 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with liver metastasis from colorectal cancer. Hum Pathol 39:201–208
Komatsu K, Murata K, Kameyama M et al (2002) Expression of S100A6 and S100A4 in matched samples of human colorectal mucosa, primary colorectal adenocarcinomas and liver metastases. Oncology 63:192–200
Wilson JM, Coletta PL, Cuthbert RJ et al (2005) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor promotes intestinal tumorigenesis. Gastroenterology 129:1485–1503
Lee H, Rhee H, Kang HJ et al (2008) Macrophage migration inhibitory factor may be used as an early diagnostic marker in colorectal carcinomas. Am J Clin Pathol 129:772–779
Li M, Lin YM, Hasegawa S et al (2004) Genes associated with liver metastasis of colon cancer, identified by genome-wide cDNA microarray. Int J Oncol 24:305–312
Okado-Matsumoto A, Matsumoto A, Fujii J, Taniguchi N (2000) Peroxiredoxin IV is a secretable protein with heparin-binding properties under reduced conditions. J Biochem 127:493–501
Tsao TY, Tsai CS, Tung JN et al (2009) Function of CSE1L/CAS in the secretion of HT-29 human colorectal cells and its expression in human colon. Mol Cell Biochem 327:163–170
Stella Tsai CS, Chen HC et al (2010) Serum cellular apoptosis susceptibility protein is a potential prognostic marker for metastatic colorectal cancer. Am J Pathol 176:1619–1628
Quaresima B, Crugliano T, Gaspari M et al (2008) A proteomics approach to identify changes in protein profiles in serum of Familial Adenomatous Polyposis patients. Cancer Lett 272:40–52
Li ZG, Zhao L, Liu L, Ding YQ (2007) Monitoring changes of serum protein markers in metastatic colorectal carcinoma model. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 36:48–52
Maeda S, Hikiba Y, Sakamoto K et al (2009) Ikappa B kinasebeta/nuclear factor-kappaB activation controls the development of liver metastasis by way of interleukin-6 expression. Hepatology 50:1851–1860
Matsui H, Hikichi Y, Tsuji I et al (2003) LIGHT, a member of the tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily, prevents tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated human primary hepatocyte apoptosis, but not Fas-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277:50054–50061
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by grants from the Spanish Carlos III Health Institute, Madrid (ADE09/90041), the Spanish Ministry of Innovation and Science (SAF2009-12376), and the Burdinola Professorship on Molecular Medicine to F. Vidal-Vanaclocha.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vidal-Vanaclocha, F. The Liver Prometastatic Reaction of Cancer Patients: Implications for Microenvironment-Dependent Colon Cancer Gene Regulation. Cancer Microenvironment 4, 163–180 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-011-0084-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-011-0084-5