Abstract
Purpose
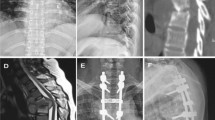
The present study evaluated the clinical and radiological outcomes in patients with tuberculosis of the thoracic and thoracolumbar spine, treated by an operative technique in which anterior debridement with posterior instrumentation and global fusion was performed through a single-stage posterior approach.
Methods
Ninty-seven patients with spinal tuberculosis, between T1 and L1, in whom anterior debridement, bone grafting, with posterior instrumentation and fusion was performed through a single-stage posterior approach, with a minimum follow-up of 2 years, formed the basis of this study. During each follow-up, neurological recovery was assessed using modified American Spinal Injury Association grading, healing of the disease was assessed by appearance of sclerosis and interbody fusion and the degree of kyphotic deformity was analysed using the modified Konstam’s angle.
Result
Two hundred and twenty-six lesions were found in the radiographs of 97 patients with 28.9% of them having multiple lesions. The mean ± SD preoperative, post-operative, and 2-year follow-up kyphotic angle were 49.5 ± 18.4°, 22.6 ± 7.1° and 24.5 ± 7.6°, respectively, and showed significant kyphosis correction (P < 0.01). Sclerosis was seen as early as 3 months in 82(84.5%) patients whereas interbody fusion started appearing at the end of 6 months in 38.14% of patients and peaked at 1 year. All patients recovered neurologically, with no significant loss of kyphosis correction, at final follow-up.
Conclusion
The surgical technique described in this study had favourable clinical and radiological outcomes. Early surgery helps in having a definitive diagnosis and detects the presence of drug-resistant strains.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tuli SM (2013) Historical aspects of Pott’s disease (spinal tuberculosis) management. Eur Spine J 22(4):529–538
Jain AK (2010) Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(7):905–913
Medical Research Council Working Party on Tuberculosis of the Spine (1998) A 15-year assessment of controlled trials of the management of tuberculosis of the spine in Korea and Hong Kong. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80(3):456–462
Luk KD (1999) Tuberculosis of the spine in the new millennium. Eur Spine J 8(5):338–345
Mohanty SP, Bhat S, Nair NS (2011) An analysis of clinicoradiological and histopathological correlation in tuberculosis of spine. J Indian Med Assoc 109:161–165
Oga M, Arizono T, Takasita M, Sugioka Y (1993) Evaluation of the risk of instrumentation as a foreign body in spinal tuberculosis. Clinical and biologic study. Spine 18:1890–1894
Chen WH, Jiang LS, Dai LY (2011) Influence of bacteria on spinal implant-centered infection: an in vitro and in vivo experimental comparison between Staphylococcus aureus and mycobacterium tuberculosis. Spine 36:103–108
Gokce A, Ozturkmen Y, Mutlu S, Gokay NS, Tonbul M, Caniklioglu M (2012) The role of debridement and reconstruction of sagittal balance in tuberculous spondylitis. Indian J Orthop 46:145
Benli I, Acaroğlu E, Akalin S, Kiş M, Duman E, Ün A (2003) Anterior radical debridement and anterior instrumentation in tuberculosis spondylitis. Eur Spine J 12:224–234
Özdemir HM, Us AK, Ögün T (2003) The role of anterior spinal instrumentation and allograft fibula for the treatment of pott disease. Spine 28(5):474–479
Sundararaj GD, Behera S, Ravi V, Venkatesh K, Cherian VM, Lee V (2003) Role of posterior stabilisation in the management of tuberculosis of the dorsal and lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85:100–106
Güven O, Kumano K, Yalçin S, Karahan M, Tsuji S (1994) A single stage posterior approach and rigid fixation for preventing kyphosis in the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Spine 19(9):1039–1043
Lee SH, Sung JK, Park YM (2006) Single-stage transpedicular decompression and posterior instrumentation in treatment of thoracic and thoracolumbar spinal tuberculosis: a retrospective case series. Clin Spine Surg 19(8):595–602
Moon MS, Woo YK, Lee KS, Ha KY, Kim SS, Sun DH (1995) Posterior instrumentation and anterior interbody fusion for tuberculous kyphosis of dorsal and lumbar spines. Spine 17:1910–1916
Chen WJ, Wu CC, Jung CH, Chen LH, Niu CC, Lai PL (2002) Combined anterior and posterior surgeries in the treatment of spinal tuberculous spondylitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res 398:50–59
Maynard FM, Bracken MB, Creasey GJ, Ditunno JF, Donovan WH, Ducker TB, Garber SL, Marino RJ, Stover SL, Tator CH, Waters RL (1997) International standards for neurological and functional classification of spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 35(5):266–274
Konstam PG, Blesovsky A (1962) The ambulant treatment of spinal tuberculosis. Br J Surg 50:26–38
Upadhyay SS, Saji MJ, Sell P, Sell B, Yau AC (1994) Longitudinal changes in spinal deformity after anterior spinal surgery for tuberculosis of the spine in adults. A comparative analysis between radical and debridement surgery. Spine 19(5):542–549
Rajasekaran S, Shanmugasundaram TK (1987) Prediction of the angle of gibbus deformity in tuberculosis of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 69:503–509
Hodgson AR, Stock FE (1956) Anterior spinal fusion: a preliminary communication on the radical treatment of Pott’s disease and Pott’s paraplegia. Br J Surg 44:266–275
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Institutional ethical clearance was obtained before starting the study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, S.P., Pai Kanhangad, M., Yogesh Kumar, B. et al. Single-stage anterior debridement, posterior instrumentation and global fusion in thoracic and thoracolumbar tubercular spondylodiscitis. Musculoskelet Surg 103, 243–249 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-018-0581-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-018-0581-5