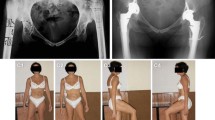
Abstract
Total hip replacement in developmental dysplasia of the hip grade IV of Crowe’s classification presents some difficulties. In this study, we present our results of the treatment for this pathology, also describing the surgical techniques used and the complication we had. In this paper, 18 total hip replacements in developmental dysplasia of the hip Crowe IV were studied clinically and radiologically before and after surgery, with a mean follow-up of 4.2 years (min: 1 year). The average Harris Hip Score improved from 52 to 89. The average leg lengthening was 36 mm. When a subtrochanteric shortening osteotomy was performed, the healing occurred in all cases, in an average time of 5.3 months. At now, the implant survivorship is 100 % (no revision required). The techniques and principles described in this paper allow to achieve good results in this surgery. An accurate preoperative evaluation and the availability of specific materials are also important steps. The subtrochanteric shortening is a safe procedure to avoid neurovascular injuries.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crowe JF, Massi I, Ranawat CJ (1979) Total hip replacement in congenital dislocation and dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 61-A:15–23
Dudkiewicz I, Salai M, Ganel A, Blankstein A, Chechik A (2002) Total hip arthroplasty in patients younger than 30 years of age following developmental dysplasia of hip (DDH) in infancy. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122(3):139–142
Stringa G et al (1995) Total hip replacement with bone grafting using the removed femoral head in severe acetabular dysplasia. Int Orthop 19(2):72–76
Eggli S, Hankemayer S, Muller ME (1999) Nerve palsy after leg lengthening in total replacement arthroplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 81-B:843–845
Inao S, Gotoh E, Ando M (1994) Total hip replacement using femoral neck bone to graft the dysplastic acetabulum. Follow-up study of 18 patients with old congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 76(5):735–739
Sankar WN, Neubuerger CO, Moseley CF (2009) Femoral anteversion in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 29(8):885–888
Delaunay S, Dussault RG, Kaplan PA, Alford BA (1997) Radiographic measurements of dysplastic adult hips. Skeletal Radiol 26(2):75–81
Wu X, Li SH, Lou LM, Cai ZD (2012) The techniques of soft tissue release and true socket reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. Int Orthop 36(9):1795–1801
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 51-A:737–755
Pierchon et al (1993) Evaluation radiologique du centre de rotation de la hanche. Revue de chirurgie ortopédique 79:281–284
Hartofilakidis G, Stamos K, Karachalios T, Ioannidis TT, Zacharakis N (1996) Congenital hip disease in adults. Classification of acetabular deficiencies and operative treatment with acetabuloplasty combined with total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 78(5):683–692
Dorr LD, Tawakkol S, Moorthy M, Long W, Wan Z (1999) Medial protrusio technique for placement of a porous-coated, hemispherical acetabular component without cement in a total hip arthroplasty in patients who have acetabular dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81(1):83–92
Campbell’s Operative Orthopedics S. Terry Canale Vol. I. 2003
Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH (1972) Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement: incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am 55-A:1629–1635
Bicanic G, Delimar D, Delimar M, Pecina M (2009) Influence of the acetabular cup position on hip load during arthroplasty in hip dysplasia. Int Orthop 33(2):397–402 (Epub 2008 Nov 18)
Eskelinen A, Helenius I, Remes V, Ylinen P, Tallroth K, Paavilainen T (2006) Cementless total hip arthroplasty in patients with high congenital hip dislocation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(1):80–91
Nagoya S, Kaya M, Sasaki M, Tateda K, Kosukegawa I, Yamashita T (2009) Cementless total hip replacement with subtrchanteric femoral shortening for severe developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 91-B:1142–1147
Linde F, Jensen J (1988) Socket loosening in arthroplasty for congenital dislocation of the hip. Acta Orthop Scand 59:254–257
Bernasek TL, Haidukewych GJ, Gustke KA, Hill O, Levering M (2007) Total hip arthroplasty requiring subtrochanteric osteotomy for developmental hip dysplasia: 5- to 14-year results. J Arthroplasty 22(6):145–150
Edwards BN, Tullos HS, Noble PC (1987) Contributory factors and etiology of sciatic nerve palsy in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop 218:136–141
Krych AJ, Howard JL, Trousdale RT, Cabanela ME, Berry DJ (2009) Total hip arthroplasty with shortening subtrochanteric osteotomy in Crowe type-IV developmental dysplasia. J Bone Joint Surg Am 91(9):2213–2221
Sener N, Tozun R, Asik M (2002) Femoral shortening and cemetless arthroplasty in high congenital dislocation of the hip. J Arthroplasty 17:41–48
Makita H, Inaba Y, Hirakawa K, Saito T (2007) Results on total hip arthroplasties with femoral shortening for Crowe’s group IV dislocated hips. J Arthroplasty 22:32–38
Masonis JL, Patel JV, Miu A, Bourne RB, McCalden R, MacDonald SJ, Rorabeck CH (2003) Subtrochanteric shortening and derotational osteotomy in primary total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe hip dysplasia: 5-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty 18(3):68–73
Bruce WJM, Rizkallah SM, Kwon Y-M, Goldberg JA, Walsh WR (2000) A new technique of subtrochanteric shortening in total hip arthroplasty: surgical technique and results of 9 cases. J Arthroplasty 15(5):617–626
Myung-Sik P, Kyu-Hyung K, Woo-Cheol J (2007) Transverse subtrochanteric shortening osteotomy in primary total hip arthroplasty for patients with severe hip developmental dysplasia. J Arthroplasty 22(7):1031–1036
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imarisio, D., Trecci, A., Sabatini, L. et al. Cementless total hip replacement for severe developmental dysplasia of the hip: our experience in Crowe’s group IV. Musculoskelet Surg 97, 25–30 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-012-0227-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-012-0227-y