Abstract
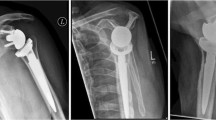
In reverse shoulder arthroplasty, an eccentric glenosphere has been developed with the aim of lowering the centre of rotation, in order to prevent inferior scapular notching as occurs with concentric designs. The objective of this retrospective study was to evaluate clinical and radiographic outcomes using the eccentric glenosphere and to determine whether this design might prevent inferior scapular notching. Between 2006 and 2010, 40 patients affected by cuff tear arthropathy underwent reverse shoulder arthroplasty with an eccentric 36-mm glenoid component. Patients with less than 2 years’ follow-up were excluded. The results for 25 patients with a minimum of 24 months’ follow-up are reported. Clinical and radiographic evaluation was performed preoperatively and at 1, 3, 6 months, 1 year and annually thereafter. All patients were evaluated with MRI or CT scan preoperatively and with X-ray examinations postoperatively to evaluate the presence of inferior scapular notching and to measure the prosthesis-scapular neck angle (PSNA), the peg-glenoid rim distance (PGRD) and the distance between the scapula neck and the glenosphere. At last follow-up (average 27.5 months, range 24–46), the Constant Score, the VAS score and range of motion had improved significantly. The average PSNA was 92° + 29°, the average PGRD was 21.2 mm + 9 mm and the average distance between the inferior bony glenoid rim and the inferior edge of the glenosphere was 4.3 mm + 0.8 mm. No inferior scapular notching and no implant-related complications were seen. The data suggest that use of an eccentric glenosphere lowers the centre of rotation, reducing the risk of inferior scapular notching.
Level of evidence IV.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anglin C, Wyss UP, Pichora DR (2000) Mechanical testing of shoulder prostheses and recommendations for glenoid design. J Should Elbow Surg 9(4):323–331
Arntz CT, Jackins S, Matsen FA 3rd (1993) Prosthetic replacement of the shoulder for the treatment of defects in the rotator cuff and the surface of the glenohumeral joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75(4):485–491
Boileau P, Watkinson DJ, Hatzidakis AM, Balg F (2005) Grammont reverse prosthesis: design, rationale, and biomechanics. J Should Elbow Surg 14(1 Suppl S):147S–161S. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.10.006
Boileau P, Watkinson D, Hatzidakis AM, Hovorka I (2006) Neer Award 2005: the Grammont reverse shoulder prosthesis: results in cuff tear arthritis, fracture sequelae, and revision arthroplasty. J Should Elbow Surg 15(5):527–540. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2006.01.003
Boileau P, Gonzalez JF, Chuinard C, Bicknell R, Walch G (2009) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty after failed rotator cuff surgery. J Should Elbow Surg 18(4):600–606. Epub 2009 May 29. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2009.03.011
Chebli C, Huber P, Watling J, Bertelsen A, Bicknell RT, Matsen F 3rd (2008) Factors affecting fixation of the glenoid component of a reverse total shoulder prosthesis. J Should Elbow Surg 17(2):323–327. Epub 2008 Feb 4. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.07.015
Chou J, Malak SF, Anderson IA, Astley T, Poon PC (2009) Biomechanical evaluation of different designs of glenospheres in the SMR reverse total shoulder prosthesis: range of motion and risk of scapular notching. J Should Elbow Surg 18(3):354–359. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2009.01.015
Codman EA (1934) The shoulder: rupture of the supraspinatus tendon and other lesions in or about the subacromial bursa. Thomas Todd Co., Boston
Constant CR, Murley AHG (1987) A clinical method of functional assessment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop 214:160–164
Cuff D, Pupello D, Virani N, Levy J, Frankle M (2008) Reverse shoulder arthroplasty for the treatment of rotator cuff deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(6):1244–1251. doi:10.2106/JBJS.G.00775
Edwards TB, Boulahia A, Kempf JF, Boileau P, Nemoz C, Walch G (2002) The influence of rotator cuff disease on the results of shoulder arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis: results of a multicenter study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:2240–2248
Edwards TB, Williams MD, Labriola JE, Elkousy HA, Gartsman GM, O’Connor DP (2009) Subscapularis insufficiency and the risk of shoulder dislocation after reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Should Elbow Surg 18(6):892–896. Epub 2009 Mar 17. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.12.013
Frankle M, Siegal S, Pupello D, Saleem A, Mighel M, Vasey M (2005) The reverse shoulder prosthesis for glenohumeral arthritis associated with severe rotator cuff deficiency: a minimum two-year follow-up study of sixty patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(8):1697–1705. doi:10.2106/JBJS.D.02813
Franklin JL, Barret WP, Jackins SE, Matsen FA 3rd (1988) Glenoid loosening in total shoulder arthroplasty. Association with rotator cuff deficiency. J Arthroplast 3(1):39–46
Gerber C, Pennington SD, Nyffeler RW (2009) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 17(5):284–295; Review
Goldberg SS, Bell JE, Kim HJ, Bak SF, Levine WN, Bigliani LU (2008) Hemiarthroplasty for rotator cuff-deficient shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(3):554–559
Guery J, Favard L, Sirveaux F, Oudet D, Mole D, Walch G (2006) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. Survivorship analysis of eighty replacements followed for five to ten years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88(8):1742–1747. doi:10.2106/JBJS.E.00851
Gutiérrez S, Levy JC, Frankle MA, Cuff D, Keller TS, Pupello DR, Lee WE 3rd (2008) Evaluation of abduction range of motion and avoidance of inferior scapular impingement in a reverse shoulder model. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 17(4):608–615. Epub 2008 Mar 6 doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.11.010
Grammont PM, Baulot E (1993) Delta shoulder prosthesis for rotator cuff rupture. Orthopedics 16:65–68
Harman M, Frankle M, Vasey M, Banks S (2005) Initial glenoid component fixation in “reverse” total shoulder arthroplasty: a biomechanical evaluation. J Should Elbow Surg 14(1 Suppl S):162S–167S. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.09.030
Jasty M, Bragdon C, Burke D, O’Connor D, Lowenstein J, Harris WH (1997) In vivo skeletal responses to porous-surfaced implants subjected to small induced motions. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79(5):707–714
Jasty M, Bragdon CR, Zalenski E, O’Connors D, Page A, Harris WH (1997) Enhanced stability of uncemented canine femoral components by bone ingrowth into the porous coatings. JArthroplast 12:106–113
Kelly JD 2nd, Humphrey CS, Norris TR (2008) Optimizing glenosphere position and fixation in reverse shoulder arthroplasty, part one: the twelve-mm rule. J Should Elbow Surg 17(4):589–594. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.08.013
Kenmore PI, MacCartee C, Viket B (1974) A simple shoulder replacement. J Biomed Mater Res 5:329–330
Krueger F (1951) A vitallium replica arthroplasty on the shoulder; a case report of aseptic necrosis of the proximal end of the humerus. Surgery 30(6):1005–1011
Lévigne C, Boileau P, Favard L, Garaud P, Molé D, Sirveaux F, Walch G (2008) Scapular notching in reverse shoulder arthroplasty. J Should Elbow Surg. 17(6):925–935. Epub 2008 Jun 16. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2008.02.010
Middernacht B, De Roo PJ, Van Maele G, De Wilde LF (2008) Consequences of scapular anatomy for reversed total shoulder arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(6):1410–1418. Epub 2008 Mar 6. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0187-6
Neer CS II, Watson KC, Stanton FJ (1982) Recent experience in total shoulder replacement. JBJS 64A:319–337
Neer CS, Craig EV, Fukuda H (1983) Cuff-tear arthropathy. J Bone Joint Surg 65-A: 1232–1244
Nyffeler RW, Werner CM, Gerber C (2005) Biomechanical relevance of glenoid component positioning in the reverse Delta III total shoulder prosthesis. J Should Elbow Surg 14(5):524–528. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2004.09.010
Pilliar RM, Lee JM, Maniatopoulos C (1986) Observations on the effect of movement on bone ingrowth into porous-surfaced implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res 208:108–113
Poon PC, Chou J, Young D, Malak SF, Anderson IA (2010) Biomechanical evaluation of different designs of glenospheres in the smr reverse shoulder prosthesis: micromotion of the baseplate and risk of loosening. Should Elbow 2:94–99. doi:10.1111/j.1758-5740.2010.00059.x
Rockwood CA Jr (2007) The reverse total shoulder prosthesis. The new kid on the block. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(2):233–235. doi:10.2106/jbjs.F.01394
Sanchez-Sotelo J, Cofield RH, Rowland CM (2001) Shoulder hemiarthroplasty for glenohumeral arthritis associated with severe rotator cuff deficiency. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A(12):1814–1822
Simovitch RW, Zumstein MA, Lohri E, Helmy N, Gerber C (2007) Predictors of scapular notching in patients managed with the Delta III reverse total shoulder replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(3):588–600. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00226
Smith R (1853) Observations upon chronic rheumatic arthritis of the shoulder (part I). Dublin Q J Med Sci 15:1–16
Smith R (1853) Observations upon chronic rheumatic arthritis of the soulder (part II). Dublin Q J Med Sci 15:343–425
Wall B, Nové-Josserand L, O’Connor DP, Edwards TB, Walch G (2007) Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: a review of results according to etiology. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89(7):1476–1485. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00666
Wierks C, Richard L, Skolasky ScD, Jong Hun Ji MD, Edward G, McFarland MD (2009) Reverse total shoulder replacement intraoperative and early postoperative complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:225–234. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0406-1
Werner CM, Steinmann PA, Gilbart M, Gerber C (2005) Treatment of painful pseudoparesis due to irreparable rotator cuff dysfunction with the Delta III reverse-ball-and-socket total shoulder prosthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(7):1476–1486. doi:10.2106/JBJS.D.02342
Young SW, Everts NM, Ball CM, Astley TM, Poon PC (2009) The SMR reverse shoulder prosthesis in the treatment of cuff-deficient shoulder conditions. J Should Elbow Surg 18(4):622–626. Epub 2009 Apr 11. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2009.01.017
Zuckerman JD, Scott AJ, Gallagher MA (2000) Hemiarthroplasty for cuff tear arthropathy. J Should Elbow Surg. 9(3):169–172
Acknowledgments
A heartfelt thanks to Professor Alfredo Carfagni for his significant contribution to my personal, cultural and professional growth. Dott. Carlo Felice de Biase.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Biase, C.F., Delcogliano, M., Borroni, M. et al. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty: radiological and clinical result using an eccentric glenosphere. Musculoskelet Surg 96 (Suppl 1), 27–34 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-012-0193-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-012-0193-4