Abstract
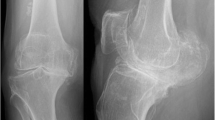
In total knee replacement (TKR), regarding tibial component positioning, almost all implants offer both an intramedullary and an extramedullary alignment guide, leaving it up to the surgeon which guide to use. However, early failure in TKR can be caused by incorrect positioning or orientation with poor limb alignment. Recently computer-based alignment systems have been developed to help the surgeon to overcome these complications. The Authors retrospectively analysed their experience using a computer-based CT-free alignment system. They assessed the radiological alignment of the tibial components in 38 computer-assisted TKR 6 months after surgery. The frontal tibial component angle (FTC) and the sagittal orientation of the tibial component (slope) were evaluated 6 months after the operation. The results were compared to those achieved with traditional alignment systems. The surgical time was statistically longer in the computer-assisted group but in this group all the tibial components were aligned within 4° of all the ideal measurements in both frontal and sagittal planes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aglietti P, Buzzi R (1988) Posteriorly stabilized total condylar knee replacement: three to eight years follow-up of knees. J Bone Joint Surg Br 70:211–216
Insall JN, Scott W, Ranawat CS (1979) The total condylar knee prosthesis. A report of two hundred and twenty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 61:173–177
Lotke PA, Ecker ML (1977) Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 59:77–82
Wasielewski RC, Galante JO, Leighty R et al (1994) Wear patterns on retrieved polyethylene tibial inserts and their relationship to technical considerations during total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:31–36
Ecker MI, Lotke PA, Windor RE, Cello JP (1997) Long term results after total condylar knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 216:151–157
Oswald MH, Jakob RP, Schneider E, Hoogewoud HM (1993) Radiological analysis of normal axial alignment of femur and tibia in view of total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 8:419–423
Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating EM, Meding JB (1994) Postoperative alignment of total knee replacement: its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res 299:153–158
Nabeyama R, Matsuda S, Miura H et al (2004) The accuracy of image-guided knee replacement based on computed tomography. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:366–372
Saragaglia D, Picard F, Chaussard R (2001) Computer assisted knee arthroplasty: comparison with a conventional procedure. Results of 50 cases in a prospective randomised study. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 87:18–23
Confalonieri N, Saragaglia D, Picard F et al (2000) Computerised OrthoPilot system in arthroprosthesis surgery of the knee. J Orthopaed Traumatol 2:91–98
Maestro A, Harwin S, Sandoval MG et al (1998) Influence of intramedullary versus extramedullary alignment guides on final total knee arthroplasty component position: a radiographic analysis. J Arthroplasty 13:552–556
Stulberg SD, Loan P, Sarin V (2002) Computer-assisted navigation in total knee replacement: results of an initial experience in thirty-five patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84[Suppl 2]:90–94
Stulberg SD (2003) How accurate is current TKR instrumentation? Clin Orthop Relat Res 416:177–183
Garg A, Walker PS (1990) Prediction of total knee motion using a three-dimensional computer graphics model. J Biomech 23:45–50
Brys DA, Lombardi AV Jr, Mallory Th, Vaughan BK (1991) A comparison of intramedullary and extramedullary alignment systems for tibial component placement in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 263:175–181
Reed MR, Bliss W, Sher L et al (2002) Extramedullary or intramedullary tibial alignment guides: a randomised prospective trial of radiological alignment. J Bone Joint Surg Br 84:858–862
Chauban SK, Scott RG, Breidahl W, Beaver RJ (2004) Computer assisted knee arthroplasty versus conventional jig-based technique: a randomised, prospective trial. J Bone Joint Surg Br 86:372–376
Confalonieri N, Saragaglia D, Picard F et al (2000) Il sistema computerizzato Orthopilot negli interventi di artroprotesi di ginocchio. Giorn Ital Ortop Traumat 26[Suppl 1]:5415–5422
Jenny JY, Boeri C (2001) Computer-assisted implantation of total knee prostheses: a case control comparative study with classical instrumentation. Comput Aided Surg 6:217–223
Sparmann M, Wolke B, Czupalla H et al (2003) Positioning of total knee arthroplasty with and without navigation support. A prospective randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 85:830–834
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manzotti, A., Pullen, C. & Confalonieri, N. Computer-assisted alignment system for tibial component placement in total knee replacement: a radiological study. Chir Organi Mov 91, 7–11 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-007-0002-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12306-007-0002-7