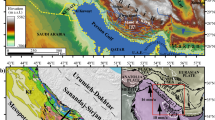
Abstract
The study of the spatial distribution of strain and stress accumulation in a continent-continent convergent system is significant for seismic hazard assessment. The Indian Plate is moving towards the north-east at a pace of 5cm/year, according to GPS velocity vectors. Since the Main Central Thrust (MCT) was active from 23 Ma to 12 Ma, when the Eurasian and Indian Plates collided for the first time, The Main Boundary Thrust (MBT) was formed by continuous collision to the south of the MCT, which continued until 3 Ma. The Main Frontal Thrust (MFT) is newly formed in the Himalayan Orogeny and is still tectonically active. This tectonically active area has been divided into four regions according to the computed ‘b’ value distribution. Regions 2 and 3 represent the inverse relationship between magnitude and frequency distribution. The magnitude range is greater than the frequency in Region 2, while the frequency distribution is greater than the magnitude in Region 3. In an overview of such alteration, two selected watersheds, namely Kameng from R-3 (Region 3) and Dibang from R-2 (Region 2), display the different values of the index of active tectonics (IAT), considering the sub-basins. Here parameters like the basin shape index (Bs), the compactness coefficient (Cc), the form ratio (Rf), the circularity ratio (Rc), the leminscate coefficient (k), the hypsometric integral (HI), the stream gradient index (SL), and the sinuosity index (SI) have been considered to compute the IAT. According to the overall average range of the IAT of the two watersheds, Kameng is more active (2.198) than Dibang (2.272). The VP and VS anomalies at 20 km, 40 km and 60 km indicate that the Kameng watershed is more active than Dibang as the higher range of VP and VS at a depth of 20 km lies near the foredeep section and it is also supported by the location of active sub-basins between the MBT (Main Boundary Thrust) and the MFT (Main Frontal Trust). The active crustal shortening across the southern part of the Kameng River, around the Main Frontal Thrust Décollement Zone, intensifies the plate movement by 10 mm/year along the section of R-3.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aier, I., Luirei, K., Bhakuni, S., Thong, G.T., and Kothyari, G.C., 2011, Geomorphic evolution of Medziphema intermontane basin and Quaternary deformation in the schuppen belt, Nagaland, NE India. Zeitschrift fur Geomorphologie, 55, 247. https://doi.org/10.1127/0372-8854/2011/0055-0048
Anand, A.K. and Pradhan, S.P., 2019, Assessment of active tectonics from geomorphic indices and morphometric parameters in part of Ganga basin. Journal of Mountain Science, 16, 1943–1961.
Angelier, J. and Baruah, S., 2009, Seismotectonics in Northeast India: a stress analysis of focal mechanism solutions of earthquakes and its kinematic implications. Geophysical Journal International, 178, 303–326.
Arora, B.R., Prajapati, S.K., and Reddy, C., 2014, Geophysical constraints on the seismotectonics of the Sikkim Himalaya. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 104, 2278–2287.
Ata, H.A., 2008, A test of the validity of morphometric analysis in determining tectonic activity from aster derived DEMS in the Jordan-Dead Sea transform zone. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Arkansas, Arkansas, 169 p.
Azor, A., Keller, E.A., and Yeats, R.S., 2002, Geomorphic indicators of active fold growth: South Mountain-Oak Ridge anticline, Ventura basin, southern California. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 114, 745–753.
Bahrami, S., 2013, Analyzing the drainage system anomaly of Zagros basins: implications for active tectonics. Tectonophysics, 608, 914–928.
Baruah, M.P., Bezbaruah, D., and Goswami, T., 2020, Active tectonics deduced from geomorphic indices and its implication on economic development of water resources in South-Eastern part of Mikir massif, Assam, India. Geology, Ecology, and Landscapes, 6, 99–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2020.1754705
Baruah, S. and Hazarika, D., 2008, A GIS based tectonic map of northeastern India. Current Science, 95, 176–177.
Bhakuni, S.S., Luirei, K., and Kothyari, G.C., 2013, Neotectonic fault in the middle part of Lesser Himalaya, Arunachal Pradesh: a study based on structural and morphotectonic analyses. Himalayan Geology, 34, 57–64.
Biswas, M., Gogoi, M.P., Mondal, B., Thota Sivasankar, T., Mukherjee, S., and Dasgupta, S., 2022, Geomorphic assessment of active tectonics in Jaisalmer basin (Western Rajasthan, India). Geocarto International. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2066726
Biswas, M. and Paul, A., 2021, Application of geomorphic indices to address the foreland Himalayan tectonics and landform deformation-Matiali-Chalsa-Baradighi recess, West Bengal, India. Quaternary International, 585, 3–14.
Biswas, M., Puniya, M.K., Gogoi, M.P., Dasgupta, S., Mukherjee, S., and Kar, N.R., 2022, Morphotectonic analysis of petroliferous Barmer rift basin (Rajasthan, India). Journal of Earth System Science, 131, 140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-022-01871-8
Brunnschweiler, R., 1966, On the geology of the Indoburman ranges (Arakan Coast and Yoma, Chin Hills, Naga Hills). Journal of the Geological Society of Australia, 13, 137–194.
Bull, W.B. and McFadden, L.D., 2020, Tectonic geomorphology north and south of the Garlock Fault, California. In: Doehring, D.O. (ed.), Geomorphology in Arid Regions. Routledge, London, p. 115–138. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780429299230-5
Burgess, W.P., Yin, A., Mo, C.S., Shen, Z.-K., and Kelty, T.K., 2012, Holocene shortening across the Main Frontal Thrust zone in the eastern Himalaya. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 357, 152–167.
Chandra, U., 1978, Seismicity, earthquake mechanisms and tectonics along the Himalayan mountain range and vicinity. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 16, 109–131.
Chatterjee, R., Nath, S., and Kumar, S.G., 2019, Morphotectonic analysis of the Himalayan frontal Region of Northwest Himalaya in the light of geomorphic signatures of active tectonics. In: Navalgund, R.R., Senthil Kumar, A., and Nandy, S. (eds.), Remote Sensing of Northwest Himalayan Ecosystems. Springer, Singapore, p. 17–35.
Chattopadhyay, B., Venkataramana, P., Roy, D., Bhattacharya, S., and Ghosh, S., 1983, Geology of Naga Hills Ophiolites. In: Ghose, N. C., Chatterjee, N., and Fareeduddin. (eds.), A Petrographic Atlas of Ophiolite — An Example from the Eastern India-Asia Collision Zone. Springer, New Delhi, p. 25–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-81-322-1569-1_3
Chen, Y.W., Shyu, J.B.H., and Chang, C.P., 2015, Neotectonic characteristics along the eastern flank of the Central Range in the active Taiwan orogen inferred from fluvial channel morphology. Tectonics, 34, 2249–2270.
Chirouze, F., Huyghe, P., van der Beek, P., Chauvel, C., Chakraborty, T., Dupont-Nivet, G., and Bernet, M., 2013, Tectonics, exhumation, and drainage evolution of the eastern Himalaya since 13 Ma from detrital geochemistry and thermochronology, Kameng River Section, Arunachal Pradesh. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 125, 523–538. https://doi.org/10.1130/B30697.1
Chorley, R.J., 2019, The drainage basin as the fundamental geomorphic unit. In: Chorley, R.J. (ed.), Water, Earth, and Man: A Synthesis of Hydrology, Geomorphology, and Socio-Economic Geography. Routledge, London, p. 37–59.
Choudhury, S. and Datta, A., 1973, Bouguer gravity and its geologic evaluation in the western part of the Bengal Basin and adjoining area, India. Geophysics, 38, 691–700. https://doi.org/10.1190/L1440368
Clark, M., Schoenbohm, L., Royden, L., Whipple, K., Burchfiel, B., Zhang, X., Tang, W., Wang, E., and Chen, L., 2004, Surface uplift, tectonics, and erosion of eastern Tibet from large-scale drainage patterns. Tectonics, 23, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002TC00140
Cox, R.T., 1994, Analysis of drainage-basin symmetry as a rapid technique to identify areas of possible Quaternary tilt-block tectonics: an example from the Mississippi Embayment. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 106, 571–581.
Dasgupta, S., Biswas, M., Mukherjee, S., and Chatterjee, R., 2022, Structural evolution and sediment depositional system along the transform margin-Palar-Pennar basin, Indian east coast. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 211, 110–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2022.110155
Diehl, T., Singer, J., Hetényi, G., Grujic, D., Clinton, J., Giardini, D., Kissling, E., and Group, G.W., 2017, Seismotectonics of Bhutan: evidence for segmentation of the eastern Himalayas and link to foreland deformation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 471, 54–64.
Dubey, R., Dar, J.A., and Kothyari, G.C., 2017, Evaluation of relative tectonic perturbations of the Kashmir Basin, Northwest Himalaya, India: an integrated morphological approach. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 148, 153–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.08.032
Dumka, R.K., Kotlia, B.S., Kothyari, G.C., Paikrey, J., and Dimri, S., 2018, Detection of high and moderate crustal strain zones in Uttarakhand Himalaya, India. Acta Geodaetica et Geophysica, 53, 503–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-018-0226-z
Flügel, T.J., Eckardt, F.D., and Cotterill, F.P.D., 2015, The present day drainage patterns of the Congo River System and their Neogene evolution. In: de Wit, M.J., Guillocheau, F., and de Wit, M.C.J. (eds.), Geology and Resource Potential of the Congo Basin. Springer, Berlin, p. 315–337.
Gogoi, M.P., Gogoi, B., and Mukherjee, S., 2022, Tectonic instability of the petroliferous upper Assam valley (NE India): a geomorphic approach. Journal of Earth System Science, 131, 1–18.
Gravelius, H., 1914, Flusskunde. GJ göschen, Berlin, 179 p.
Gutenberg, B. and Richter, C.F., 1944, Frequency of earthquakes in California. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 34, 185–188.
Hack, J.T., 1973, Stream-profile analysis and stream-gradient index. Journal of Research of the U.S. Geological Survey, 1, 421–429.
Hare, P.W. and Gardner, T.W., 1985, Geomorphic indicators of vertical neotectonism along converging plate margins, Nicoya Peninsula, Costa Rica. Tectonic Geomorphology, 4, 75–104.
Hassen, M.B., Deffontaines, B., and Turki, M.M., 2014, Recent tectonic activity of the Gafsa fault through morphometric analysis: southern Atlas of Tunisia. Quaternary International, 338, 99–112.
Hazarika, P., Kumar, M.R., Srijayanthi, G., Raju, P.S., Rao, N.P., and Srinagesh, D., 2010, Transverse tectonics in the Sikkim Himalaya: evidence from seismicity and focal-mechanism data. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 100, 1816–1822.
Heidbach, O., Rajabi, M., Cui, X., Fuchs, K., Müller, B., Reinecker, J., Reiter, K., Tingay, M., Wenzel, F., and Xie, F., 2018, The world stress map database release 2016: crustal stress pattern across scales. Tectonophysics, 744, 484–498.
Horton, R.E., 1945, Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 56, 275–370.
Hysa, A. and Baskaya, F.A.T., 2019, A GIS based method for indexing the broad-leaved forest surfaces by their wildfire ignition probability and wildfire spreading capacity. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment, 5, 71–84.
Imoto, M., 1991, Changes in the magnitude—Frequency b-value prior to large (M ≥ 6.0) earthquakes in Japan. Tectonophysics, 193, 311–325.
Jade, S., Mukul, M., Gaur, V., Kumar, K., Shrungeshwar, T., Satyal, G., Dumka, R.K., Jagannathan, S., Ananda, M., and Kumar, P.D., 2014, Contemporary deformation in the Kashmir-Himachal, Garhwal and Kumaon Himalaya: significant insights from 1995–2008 GPS time series. Journal of Geodesy, 88, 539–557. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001900-14-0702-3
Jade, S., Shrungeshwara, T., Kumar, K., Choudhury, P., Dumka, R.K., and Bhu, H., 2017, India plate angular velocity and contemporary deformation rates from continuous GPS measurements from 1996 to 2015. Scientific Reports, 7, 11439. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11697-w
Jain, A., Dasgupta, S., Bhargava, O., Israil, M., Patel, R., Mukul, M., Parcha, S., Adlakha, V., Agarwal, K., and Singh, P., 2016, Tectonics and evolution of the Himalaya. Proceedings of the Indian National Science Academy, 82, 581–604.
Joshi, N., Kothyari, G.C., and Pant, C.C., 2020, Drainage conformation and transient response of river system in thrust segmentation of Northwest Himachal Himalaya, India. Quaternary International, 575–576, 37–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2020.05.024
Kannan, R., Venkateswaran, S., Prabhu, M.V., and Sankar, K., 2018, Drainage morphometric analysis of the Nagavathi watershed, Cauvery river basin in Dharmapuri district, Tamil Nadu, India using SRTM data and GIS. Data in Brief, 19, 2420–2426.
Kar, N.R., Mani, D.R.K., Mukherjee, S., Dasgupta, S., Puniya, M.K., and Biswas, M., 2022, Source rock properties and kerogen decomposition kinetics of Eocene shales from petroliferous Barmer basin, western Rajasthan, India. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering. Earth ArXiv (Preprint). https://doi.org/10.31223/X5F05B
Kayal, J. and De, R., 1991, Microseismicity and tectonics in northeast India. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 81, 131–138.
Kent, W.N., Hickman, R.G., and Dasgupta, U., 2002, Application of a ramp/flat-fault model to interpretation of the Naga thrust and possible implications for petroleum exploration along the Naga thrust front. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 86, 2023–2045.
Khattri, K. and Tyagi, A., 1983, The transverse tectonic features in the Himalaya. Tectonophysics, 96, 19–29.
Khayingshing, L., Bhakuni, S.S., Pradeep, S., and Suresh, N., 2012, Late Pleistocene-Holocene tectonic activities in the frontal part of NE Himalaya between Siang and Dibang river valleys, Arunachal Pradesh, India. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, 56, 477–493.
Kothyari, G.C., 2014, Morphometric analysis of tectonically active Pindar and Saryu River basins: central Kumaun Himalaya. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, 59, 421–442. https://doi.org/10.1127/zfg/2014/0162
Kothyari, G.C. and Luirei, K., 2016, Late Quaternary tectonic landforms and fluvial aggradation in the Saryu River valley: central Kumaun Himalaya. Geomorphology, 268, 159–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2016.06.010
Kothyari, G.C., Rastogi, B., Morthekai, P., and Dumka, R.K., 2016, Landform development in a zone of active Gedi Fault, Eastern Kachchh rift basin, India. Tectonophysics, 670, 115–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.12.027
Kothyari, G.C., Rastogi, B., Morthekai, P., Dumka, R.K., and Kandregula, R.S., 2016, Active segmentation assessment of the tectonically active South Wagad fault in Kachchh, western Peninsular India. Geomorphology, 253, 491–507. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.10.029
Kothyari, G.C., Shirvalkar, P., Kandregula, R.S., Rawat, Y., Dumka, R.K., and Joshi, N., 2019, Holocene tectonic activity along Kachchh Mainland Fault: impact on late mature Harappan civilization, Kachchh, western India. Quaternary International, 507, 274–287.
Kothyari, G.C., Singh, A.P., Mishra, S., Kandregula, R.S., Chaudhary, I., and Chauhan, G., 2018, Evolution of drainage in response to brittle-ductile dynamics and surface processes in Kachchh Rift Basin, western India. In: Sharkov, E.V. (ed.), Tectonics — Problems of Regional Settings. IntechOpen, p. 131–158. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.73653
Krishnan, M.S., 1960, Geology of India and Burma (4th edition). Higginbothams, Madras, 604 p.
Kumar, A., Mitra, S., and Suresh, G., 2015, Seismotectonics of the eastern Himalayan and Indo-Burman plate boundary systems. Tectonics, 34, 2279–2295.
Kumar, S. and Sharma, N., 2019, The seismicity of central and northeast Himalayan region. Contributions to Geophysics and Geodesy, 49, 265–281. https://doi.org/10.2478/congeo-2019-0014
Lahiri, S.K. and Sinha, R., 2012, Tectonic controls on the morphodynamics of the Brahmaputra River system in the upper Assam valley, India. Geomorphology, 169, 74–85.
Litchfield, N.J., Campbell, J.K., and Nicol, A., 2003, Recognition of active reverse faults and folds in North Canterbury, New Zealand, using structural mapping and geomorphic analysis. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 46, 563–579.
Luirei, K., Kothyari, G.C., Dumka, R.K., and Bhakuni, S.S., 2022, Assessment of the tectonically induced Quaternary landforms and active deformation in the area between Main Boundary Thrust and Himalayan Frontal Thrust, south of the Siang Antiform, Arunachal Himalaya, India. Geological Journal, 57, 557–574. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.4256
Luirei, K., Lokho, K., and Kothyari, G.C., 2018, Neotectonic activity along the Churachandpur-Mao Fault in and around Karong, Manipur, India: based on morphotectonics and morphometric analyses. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3902-y
Luirei, K., Lokho, K., Longkumer, L., Kothyari, G.C., Rai, R., Rawat, I.S., and Nakhro, D., 2021, Morphotectonic evolution of the Quaternary landforms in the Yangui River basin in the Indo-Myanmar Range. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 218, 104877. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2021.104877
Mahmood, S.A. and Gloaguen, R., 2012, Appraisal of active tectonics in Hindu Kush: insights from DEM derived geomorphic indices and drainage analysis. Geoscience Frontiers, 3, 407–428.
Main, I. and Meredith, P., 1989, Classification of earthquake precursors from a fracture mechanics model. Tectonophysics, 167, 273–283.
Malik, M.S. and Shukla, J., 2018, A GIS-based morphometric analysis of Kandaihimmat watershed, Hoshangabad district, MP India. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 47, 1980–1985.
McArthur, D.S. and Ehrlich, R., 1977, An efficiency evaluation of four drainage basin shape ratios. The Professional Geographer, 29, 290–295.
Miller, V.C., 1953, A quantitative geomorphic study of drainage basin characteristics in Clinch Mountain Area Virginia and Tennessee. Technical Report No. 3, Columbia University, New York, 30 p.
Misra, A., Agarwal, K., Kothyari, G.C., Talukdar, R., and Joshi, G., 2020, Quantitative geomorphic approach for identifying active deformation in the foreland region of central Indo-Nepal Himalaya. Geotectonics, 54, 543–562. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016852120040093
Misra, D., 2007, Geomorphic features along the active faults in the Lohit and Dibang Valleys, Eastern Arunachal Pradesh, India. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, 51, 327–336. https://doi.org/10.1127/0372-8854/2007/0051-0327
Misra, D., 2009, River response to continuing movements along the active faults in the Siang Valley, North-Eastern Himalaya, India. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, 53, 455–468. https://doi.org/10.1127/0372-8854/2009/0053-0455
Moiya, J.N., Luirei, K., Longkumer, L., Kothyari, G.C., and Thong, G.T., 2019, Late Quaternary deformation in parts of the Belt of Schuppen of Dimapur and Peren districts, Nagaland, NE India. Geological Journal, 55, 457–476. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3413
Mukhopadhyay, B. and Dasgupta, S., 2015, Earthquake swarms near eastern Himalayan Syntaxis along Jiali Fault in Tibet: a seismotectonic appraisal. Geoscience Frontiers, 6, 715–722.
Mundetia, N., Sharma, D., and Dubey, S.K., 2018, Morphometric assessment and sub-watershed prioritization of Khari River basin in semi-arid region of Rajasthan, India. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 11, 1–18.
Nandy, D., 2017, Geodynamics of Northeastern India and the Adjoining Region. Scientific Book Centre, Guwahati, 272 p.
Nath, S.K., Vyas, M., Pal, I., and Sengupta, P., 2005, A seismic hazard scenario in the Sikkim Himalaya from seismotectonics, spectral amplification, source parameterization, and spectral attenuation laws using strong motion seismometry. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 110. https://doi.org/10.1029/2004JB003199
Ningthoujam, P., Dubey, C., Lolee, L., Shukla, D., Naorem, S., and Singh, S., 2015, Tectonic studies and crustal shortening across Easternmost Arunachal Himalaya. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 111, 339–349.
Pandey, M., Tandukar, R., Avouac, J., Lave, J., and Massot, J., 1995, Interseismic strain accumulation on the Himalayan crustal ramp, Nepal. Geophysical Research Letters, 22, 751–754.
Panthi, A., Singh, H., and Shanker, D., 2013, Revisiting state of stress and geodynamic processes in Northeast India Himalaya and its adjoining region. Geosciences, 3, 143–152.
Paul, A. and Biswas, M., 2019, Changes in river bed terrain and its impact on flood propagation — a case study of River Jayanti, West Bengal, India. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 10, 1928–1947.
Pérez-Peña, J.V., Azor, A., Azañón, J.M., and Keller, E.A., 2010, Active tectonics in the Sierra Nevada (Betic Cordillera, SE Spain): insights from geomorphic indexes and drainage pattern analysis. Geomorphology, 119, 74–87.
Pike, R.J. and Wilson, S.E., 1971, Elevation-relief ratio, hypsometric integral, and geomorphic area-altitude analysis. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 82, 1079–1084.
Prasad, S. and Singh, C., 2015, Evolution of b-values before large earthquakes of mb ≥ 6.0 in the Andaman region. Geologica Acta, 13, 205–210. https://doi.org/10.1344/GeologicaActa2015.13.3.3
Pudi, R., Roy, P., Martha, T.R., Kumar, K.V., and Rao, P.R., 2018, Spatial potential analysis of earthquakes in the western Himalayas using b-value and thrust association. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 91, 664–670.
Raj, R., 2012, Active tectonics of NE Gujarat (India) by morphometric and morphostructural studies of Vatrak River basin. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 50, 66–78.
Ramírez-Herrera, M.T., 1998, Geomorphic assessment of active tectonics in the Acambay Graben, Mexican volcanic belt. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 23, 317–332.
Rao, M.R., 1973, The subsurface geology of the Indo-Gangetic plains. Journal of Geological Society of India, 14, 217–242.
Raoof, J., Mukhopadhyay, S., Koulakov, I., and Kayal, J., 2017, 3-D seismic tomography of the lithosphere and its geodynamic implications beneath the northeast India region. Tectonics, 36, 962–980.
Sassolas-Serrayet, T., Cattin, R., and Ferry, M., 2018, The shape of watersheds. Nature Communications, 9, 1–8.
Schoenbohm, L., Whipple, K., Burchfiel, B., and Chen, L., 2004, Geomorphic constraints on surface uplift, exhumation, and plateau growth in the Red River region, Yunnan Province, China. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 116, 895–909.
Schumm, S.A., 1956, Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 67, 597–646.
Sharma, G. and Mohanty, S., 2018, Morphotectonic analysis and GNSS observations for assessment of relative tectonic activity in Alaknanda basin of Garhwal Himalaya, India. Geomorphology, 301, 108–120.
Sharma, S. and Sarma, J.N., 2017, Application of drainage basin morphotectonic analysis for assessment of tectonic activities over two regional structures of the northeast India. Journal of the Geological Society of India, 89, 271–280.
Shukla, D., Dubey, C., Ningreichon, A., Singh, R., Mishra, B., and Singh, S., 2014, GIS-based morpho-tectonic studies of Alaknanda river basin: a precursor for hazard zonation. Natural Hazards, 71, 1433–1452.
Silva, P.G., Goy, J.L., Zazo, C., and Bardajı, T., 2003, Fault-generated mountain fronts in southeast Spain: geomorphologic assessment of tectonic and seismic activity. Geomorphology, 50, 203–225.
Singh, C. and Singh, S., 2015, Imaging b-value variation beneath the Pamir-Hindu Kush region. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 105, 808–815.
Singh, M.D. and Kumar, A., 2013, Active deformation measurements at Mishmi complex of Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis. International Journal of Geosciences, 4, 746–758.
Sreejith, K., Sunil, P., Agrawal, R., Saji, A.P., Rajawat, A., and Ramesh, D., 2018, Audit of stored strain energy and extent of future earthquake rupture in central Himalaya. Scientific Reports, 8, 16697. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35025-y
Sreejith, K., Sunil, P., Agrawal, R., Saji, A.P., Ramesh, D., and Rajawat, A., 2016, Coseismic and early postseismic deformation due to the 25 April 2015, Mw 7.8 Gorkha, Nepal, earthquake from InSAR and GPS measurements. Geophysical Research Letters, 43, 3160–3168.
Srivastava, P. and Misra, D.K., 2008, Morpho-sedimentary records of active tectonics at the Kameng river exit, NE Himalaya. Geomorphology, 96, 187–198.
Strahler, A.N., 1952, Hypsometric (area-altitude) analysis of erosional topography. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 63, 1117–1142.
Strahler, A.N., 1964, Quantitative geomorphology of drainage basins and channel networks. In: Chow, V.T. (ed.), Handbook of Applied Hydrology. McGraw Hill, New York, p. 439–476.
Sukhija, B., Rao, M., Reddy, D., Nagabhushanam, P., Hussain, S., Chadha, R., and Gupta, H., 1999, Paleoliquefaction evidence and periodicity of large prehistoric earthquakes in Shillong Plateau, India. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 167, 269–282.
Supriya, S., 1966, Geological and geophysical studies in western part of Bengal basin, India. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 50, 1001–1017.
Taloor, A.K., Joshi, L.M., Kotlia, B.S., Alam, A., Kothyari, G.C., Kandregula, R.S., Singh, A.K., and Dumka, R.K., 2021, Tectonic imprints of landscape evolution in the Bhilangana and Mandakini basin, Garhwal Himalaya, India: a geospatial approach. Quaternary International, 575, 21–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2020.07.021
Utsu, T., 1999, Representation and analysis of the earthquake size distribution: a historical review and some new approaches. In: Wyss, M., Shimazaki, K., and Ito, A. (eds.), Seismicity Patterns, Their Statistical Significance and Physical Meaning. Birkhäuser, Basel, p. 509–535.
Valdia, K.S., 1976, Himalayan transverse fault and their parallelism with subsurface structures of north its aftershocks Indian plane. Tectonophysics, 32, 353–386.
Verma, R., 1991, Seismicity of the Himalaya and the northeast India, and nature of continent-continent collision. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 18, 345–370.
Verma, R., Mukhopadhyay, M., and Bhanja, A., 1980, Seismotectonics of the Hindukush and Baluchistan arc. Tectonophysics, 66, 301–322.
Verma, P. and Tandon, S., 1976, Geological observations in parts of Kameng district, Arunachal Pradesh (NEFA). Himalayan Geology, 6, 259–286.
Viveen, W., Van Balen, R., Schoorl, J., Veldkamp, A., Temme, A., and Vidal-Romani, J., 2012, Assessment of recent tectonic activity on the NW Iberian Atlantic Margin by means of geomorphic indices and field studies of the Lower Miño River terraces. Tectonophysics, 544, 13–30.
Wołosiewicz, B., 2016, Morphotectonic control of the Białka drainage basin (central Carpathians): insights from DEM and morphometric analysis. Contemporary Trends in Geoscience, 5, 61–82. https://doi.org/10.1515/ctg-2016-0005
Wyss, M., 1973, Towards a physical understanding of the earthquake frequency distribution. Geophysical Journal International, 31, 341–359.
Wyss, M., Shimazaki, K., and Wiemer, S., 1997, Mapping active magma chambers by b values beneath the off-Ito volcano, Japan. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102, 20413–20422.
Yadav, R. and Tiwari, V., 2018, Numerical simulation of present day tectonic stress across the Indian subcontinent. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 107, 2449–2462.
Yin, A., Dubey, C., Kelty, T., Gehrels, G., Chou, C., Grove, M., and Lovera, O., 2006, Structural evolution of the Arunachal Himalaya and implications for asymmetric development of the Himalayan orogen. Current Science, 90, 195–206.
Yin, A., Dubey, C., Kelty, T., Webb, A., Harrison, T., Chou, C., and Célérier, J., 2010, Geologic correlation of the Himalayan orogen and Indian craton: Part 2. Structural geology, geochronology, and tectonic evolution of the Eastern Himalaya. The Geological Society of America Bulletin, 122, 360–395. https://doi.org/10.1130/B2646L1
Zhao, W., Nelson, K., Che, J., Quo, J., Lu, D., Wu, C., and Liu, X., 1993, Deep seismic reflection evidence for continental underthrusting beneath southern Tibet. Nature, 366, 557–559.
Zhao, Y., Grujic, D., Baruah, S., Drukpa, D., Elkadi, J., Hetényi, G., King, G.E., Mildon, Z.K., Nepal, N., and Welte, C., 2021, Paleoseismological findings at a new trench indicate the 1714 M8.1 earthquake ruptured the Main Frontal Thrust over all the Bhutan Himalaya. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9, 119–133. https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2021.689457
Ziyad, E.R., 2014, Relationship between tectonic activity, fluvial system and river morphology in the Dohuk catchment, Iraqi Kurdistan. Géomorphologie: Relief, Processus, Environnement, 20, 91–100.
Acknowledgments
The authors convey a token of thanks to the Geography Department, Presidency University, Kolkata. We would like to convey our hearty thanks to the editor, associate editor and reviewers of the journal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, S., Biswas, M. Seismo-tectonic and morphological study of the north-east Himalaya. Geosci J 27, 1–21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-022-0016-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-022-0016-z