Abstract
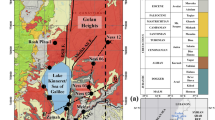
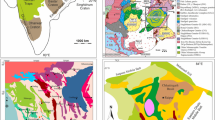
On the basis of the variations of sediment properties such as biogenic opal, grain size, natural gamma radiation (NGR), and clay mineralogy, we differentiate two types of late Neogene marine sediments that record paleoclimate changes associated with the growth and retreat of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) and associated changes in sea ice cover. The first type of sediments are massive muds characterized by high biogenic opal (30~55%), low NGR (15~30 counts per second (cps)), large mean grain size (>8.3 μm), and low smectite/(illite + chlorite) [S/(I + C)] ratios (<~0.2). We interpret these sediments as the result from deposition by hemipelagic sedimentation during interglacial conditions. In contrast, the second type of sediments are laminated muds characterized by low biogenic opal (5~7%), high NGR (45~67 cps), small mean grain size (<6.3 μm), and high S/(I + C) ratios (>~0.2). We interpret these sediments as the result from deposition by either turbiditic or contouritic processes during glacial conditions. All these sediment properties indicate that the Wilkes Land continental rise recorded late Neogene paleoclimatic changes in terms of surface water productivity, sediment provenance and transport pathway, and depositional processes that are related to the growth and retreat of EAIS. In addition, the decreased maxima of biogenic opal content at Hole U1359A highlights the temporal climatic change between the late Pliocene (~2.0 Ma to ~3.7 Ma) and the early Pliocene to late Miocene (~3.7 Ma to ~6.3 Ma), confirming the important role of sea ice to the surface water productivity associated with the global cooling trend in the East Antarctica.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelmann, A. and Gersonde, R., 1991, Biosiliceous particle flux in the Southern Ocean. Marine Chemistry, 35, 503–536.
Bardin, V.I., 1982, Composition of east Antarctic moraines and some problems of Cenozoic history. In: Craddock, C. (ed.), Antarctic Geoscience. University of Wisconsin Press, Madison, p. 1069–1076.
Bareille, G., Labracherie, M., Bertrand, P., Labeyrie, L., Lavaux, G., and Dignan, M., 1998, Glacial-interglacial changes in the accumulation rates of major biogenic components in Southern Indian Ocean sediments. Journal of Marine Systems, 17, 527–539.
Bindoff, N.L., Rosenberg, M.A., and Warner, M.J., 2000, On the circulation and water masses over the Antarctic continental slope and rise between 80 and 150°E. Deep-Sea Research II, 47, 2299–2326
Biscaye, P.E., 1965, Mineralogy and sedimentation of recent deep-sea clay in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas and oceans. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 76, 803–832.
Blum, P., 1997, Physical properties handbook: a guide to the shipboard measurement of physical properties of deep-sea cores. ODP Technical Note 26. http://www-odp.tamu.edu/publications/tnotes/tn26/INDEX.HTM
Bradtmiller, L.I., Anderson, R.F., Fleisher, M.Q., and Burckle, L.H., 2009, Comparing glacial and Holocene opal fluxes in the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean. Paleoceanography, 24, 2214. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2008PA001693
Brown, G. and Brindley, G.W., 1980, X-ray diffraction procedures for clay mineral identification. In: Brindley, G.W. and Brown, G. (eds.), Crystal structures of clay minerals and their X-ray identification. Mineralogical Society, London, p. 305–359.
Busetti, M., Carbulotto, A., Armand, L., Damiani, D., Giorgetti, R.G., Lucchi, P.G., Quilty, P.G., and Villa, G., 2003, Plio-Quaternary sedimentation on the Wilkes Land continental rise. Preliminary results. Deep-Sea Research II, 50, 1529–1562.
Cande, S.C. and Mutter, J.C., 1982, A revised identification of the oldest sea-floor spreading anomalies between Australia and Antarctica. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 58, 151–160.
Carburlotto, A., Lucchi, R.G., De Santis, L., Marcci, P., and Tolotti, R., 2010, Sedimentary processes on the Wilkes Land continental rise reflect changes in glacial dynamics and bottom water flow. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 99, 909–926.
Chamley, H., 1989, Clay Sedimentology. Springer, Berlin, 623 p.
Charles, C.D., Froelich, P.N., Zibello, M.A., Mortlock, R.A., and Morley, J.J., 1991, Biogenic opal in southern ocean sediments over the last 450, 000 years: implications for surface water chemistry and circulation. Paleoceanography, 6, 697–728.
Chase, Z., Anderson, R.F., Fleisher, M.Q, and Kubik, P.W., 2003, Accumulation of biogenic and lithogenic material in the Pacific sector of the Southern Ocean during the past 40, 000 years. Deep-Sea Research II, 50, 799–832.
Claridge, G.G.C., 1965, The clay mineralogy and chemistry of some soils from the Ross dependency, Antarctica. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 3, 186–200.
Cook, C.P., van de Flierdt, T., Williams, T., Hemming, S.R., Iwai, M., Kobayashi, M., Jimenez-Espejo, F.J., Escutia, C., Gonzáez, J.J., Khim, B.K., McKay, R.M., Passchier, S., Tauxe, L., Sugisaki, S., Lopez, A., Patterson, A.M.O., Bohaty, S.M., Riesselman, C.R., Sangiorgi, F., Pierce, E.L., Brinkhuis, H., and IODP Expedition 318 Scientists, 2013, Dynamic behaviour of the East Antarctic Ice Sheet during Pliocene warmth. Nature Geoscience, 6, 765–769.
Damiani, D., Giorgetti, G., and Turbanti, I.M., 2006, Clay mineral fluctuations and surface textural analysis of quartz grains in Pliocene–Quaternary marine sediments from Wilkes Land continental rise (east-Antarctica): paleoenvironmental significance. Marine Geology, 226, 281–295.
de Baar, H.J.W., Boyd, P.W., Coale, K.H., Landry, M.R., Tsuda, A., Assmy, P., Bakker, D.C.E., Bozec, Y., Croot, P.L., Gervais, F., Gorbunov, M.Y., Harrison, P.J., Hiscock, W.T., Lann, P., Lancelot, C., Law, C.S., Levasseur, M., Marchetti, A., Millero, F.J., Nishioka, J., Nojiri, Y., Oijen, T.V., Rieesell, U., Rijkenberg, M.J.A., Saito, H., Takeda, S., Timmermans, K.R., Veldhuis, M.J.W., Waite, A.M., and Wong, C.S., 2005, Synthesis of iron fertilization experiments: from the iron age in the age of enlightenment. Journal of Geophysical Research (Ocean) 110, C09S16. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2004jc002601
DeMaster, D.J., 1981, The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45, 1715–1732.
De Santis, L., Brancolini, G., and Donda, F., 2003, Seismic-stratigraphic analysis of the Wilkes Land continental margin (East Antarctica). Influence of glacially-driven processes on the Cenozoic deposition. Deep-Sea Research II, 50, 1563–1594.
Dezileau, L., Reyss, J.L., and Lemoine, F., 2003, Late Quaternary changes in biogenic opal fluxes in the Southern Indian Ocean. Marine Geology, 202, 143–158.
Diekmann, B., Falker, M., and Kuhn, G., 2003, Environmental history of the south-eastern South Atlantic since the Middle Miocene: evidence from the sedimentological records of ODP Sites 1088 and 1092. Sedimentology, 50, 511–529.
Donda, F., Brancolini, G., De Santis, L., and Trincardi, F., 2003, Seismic facies and sedimentary processes on the continental rise off Wilkes Land (East Antarctica): Evidence of bottom current activity. Deep- Sea Research II, 50, 1509–1528.
Ebert, E., Schramm, J., and Curry, J., 1995, Disposition of solar radiation in sea ice and the upper ocean. Journal of Geophysical Research (Ocean), 100, 15965–15975.
Ehrmann, W., 1998, Implications of late Eocene to early Eiocene clay mineral assemblages in McMurdo Sound (Ross Sea, Antarctica) on paleoclimate and ice dynamics. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 139, 213–231.
Ehrmann, W.U., Melles, M., Kuhn, G., and Grobe, H., 1992, Significance of clay mineral assemblages in the Antarctic Ocean. Marine Geology, 107, 249–273.
Ehrmann, W., Setti, M., and Marinoni, L., 2005, Clay minerals in Cenozoic sediments off Cape Robert (McMurdo Sound, Antarctica) reveal palaeoclimatic history. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 229, 187–211.
Eittreim, S.L., 1994, Transition from continental to oceanic crust on the Wilkes–Adélie margin of Antarctica. Journal of Geophysical Research, 99, 24189–24205.
Eittreim, S.L., Cooper, A.K., and Wannesson, J., 1995, Seismic stratigraphic evidence of ice-sheet advances on the Wilkes Land margin of Antarctica. Sedimentary Geology, 96, 131–156.
Escutia, C., Bárcena, M.A., Lucchi, R.G., Ballegeer, A.M., Gonzalez, J.J., and Harwood, D.M., 2009, Circum-Antarctic warming events between 4 and 3.5 Ma recorded in marine sediments from the Prydz Bay (ODP Leg 188) and the Antarctic Peninsual (ODP Leg 178) margins. Global and Planetary Change, 69, 170–184.
Escutia, C., Brinkhuis, H., Klaus, A., and the Expedition 318 Scientists, 2011, Proceedings of the IODP, vol. 318. Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Management International, Inc., Tokyo, 59 p. http://dx.doi.org/10.2204/iodp.proc.318.101.2011
Escutia, C., De Santis, L., Donda, F., Dunbar, R.B., Cooper, A.K., Brancolini, G., and Eittereim, S.L., 2005, Cenozoic ice sheet history from East Antarctic Wilkes Land continental margin sediments. Global and Planetary Change, 45, 51–81.
Escutia, C., Eittreim, S.L., and Cooper, A.K., 1997, Cenozoic glaciomarine sequences on the Wilkes Land continental rise, Antarctica. Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium of Antarctic Earth Sciences on the Antarctic Region: Geological Evolution and Processes, Sienna, Sept. 10–15, p. 791–795.
Escutia, C., Eittreim, S.L., Cooper, A.K., and Nelson, C.H., 2000, Morphology and acoustic character of the Antarctic Wilkes Land turbidite systems: ice-sheet sourced vs. river-sourced fans. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 70, 84–93.
Escutia, C., Nelson, C.H., Acton, G.D., Cooper, A.K., Eittreim, S.L., Warnke, D.A., and Jaramillo, J., 2002, Current controlled deposition on the Wilkes Land continental rise. In: Stow, D.A.V., Pudsey, C.J., Howe, J.A., Faugeres, J.C., and Viana, A.R. (eds.), Deep-Water Contourite Systems: Modern Drifts and Ancient Series, Seismic and Sedimentary Characteristics. Memoirs of Geological Society of London, 22, p. 373–384.
Escutia, C., Warnke, D.A., Acton, G.D., Barcena, A., Burckle, L., Canals, M., and Frazee, C.S., 2003, Sediment distribution and sedimentary processes across the Antarctic Wilkes Land margin during the Quaternary. Deep-Sea Research II, 50, 1481–1508.
Expedition 318 Scientists, 2011, Site U1359. In: Escutia, C., Brinkhuis, H., Klaus, A., and the Expedition 318 Scientists (eds.), Proceedings of the IODP, vol. 318. Integrated Ocean Drilling Program Management International, Inc., Tokyo, 121 p. http://dx.doi.org/10.2204/iodp.proc.318.107.2011
Gordon, A.L. and Tchernia, P., 1972, Waters of the continental margin off Adélie coast, Antarctica. In: Hayes, D.E. (ed.), Antarctic Oceanology II: The Australian–New Zealand Sector. Antarctic Research Series, vol. 19, American Geophysical Union, Washington, p. 59–69.
Gradstein, F.M., Ogg, J.G., and Smith, A.G., 2004, A Geologic Time Scale 2004. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 401 p.
Grützner, J., Hillenbrand, C.-D., and Rebesco, M., 2005, Terrigenous flux and biogenic silica deposition at the Antarctic continental rise during the late Miocene to early Pliocene: implications for ice sheet stability and sea ice coverage. Global and Planetary Change, 45, 131–149.
Hampton, M.A., Kravitz, J.H., and Luepke, G., 1987, Geology of sediment cores from the George V continental margin, Antarctica. In: Eittreim, S.L. and Hampton, M.A. (eds.), The Antarctic Continental Margin: Geology and Geophysics of Offshore Wilkes Land. CPCEMR Earth Science Series, vol. 5A: Circum Pacific Council for Energy and Mineral Resources, p. 75–88.
Henjes-Kunst, F. and Schussler, U., 2003, Metasedimentary Units of the Cambro-Ordovician Ross Orogen in Northern Victoria Land and Oates Land: Implications for Their Provenance and Geotectonic Setting from Geochemical and Nd-Sr Isotope Data. Terra Antarctica, 10, 105–128.
Hillenbrand, C.-D. and Ehrmann, W., 2001, Distribution of clay minerals in drift sediments on the continental rise west of the Antarctic Peninsula, ODP Leg 178, Sites 1095 and 1096. In: Barker, P.F., Camerlenghi, A., Acton, G.D., and Ramsay, A.T.S. (eds.), Proceedings of Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 178, College Station, p. 1–29.
Hillenbrand, C.-D. and Ehrmann, W., 2005, Late Neogene to quaternary environmental changes in the Antarctic Peninsula region: evidence from drift sediments. Global and Planetary Change, 45, 165–191.
Juntila, J., Ruikka, M., and Strand, K., 2005, Clay-mineral assemblages in high-resolution Plio-Pleistocene interval at ODP Site 1165, Prydz Bay, Antarctica. Global and Planetary Change, 45, 151–163.
Lucchi, R.G., Rebesco, M., Camerlenghi, A., Busetti, M., Tomadin, L., Villa, G., Persico, D., Morigi, C., Bonci, M.C., and Giorgetti, G., 2002, Mid-late Pleistocene glacimarine sedimentary processes of a high latitude, deep-sea sediment drift (Antarctic Peninsula Pacific margin). Marine Geology, 189, 343–370.
McGinnis, J.P., Hayes, D.E., and Driscoll, N.W., 1997, Sedimentary processes across the continental rise of the southern Antarctic Peninsula. Marine Geology, 141, 91–109.
Michels, K.H., Rogenhagen, J., and Kuhn, G., 2001, Recognition of contour current influence in mixed contourite-turbidite sequences of the western Weddell Sea, Antarctica. Marine Geophysical Research, 22, 465–485.
Moore, D.M. and Reynolds, R.C., 1989, X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 332 p.
Mortlock, R.A. and Froelich, P.N., 1989, A simple method for the rapid determination of biogenic opal in pelagic marine sediments. Deep- Sea Research, 36, 1415–1426.
Mortlock, R.A., Charles, C.D., Froelich, P.N., Zibello, M.A., Saltzman, J., Hats, J.D., and Burckle, L.H., 1991, Evidence for lower productivity in the Antarctic Ocean during the last glaciation. Nature, 351, 220–223.
O’Brien, P.E., Cooper, A.K., Florindo, F., Handwerger, D.A., Lavelle, M., Passchier, J.J., Pospichal, P.G., Quilty, P.G., Richter, C., Theissen, K.M., and Whitehead, J.M., 2004, Prydz channel fan and the history of extreme ice advances in Prydz Bay. In: Cooper, A.K., O’Brien, P.E., and Richter, C. (eds.), Proceedings of Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 188, College Station, p. 1–32.
O’Cofaigh, C., Dowdeswell, J.A., and Pudsey, C.J., 2001, Late Quaternary iceberg rafting along the Antarctic Peninsula continental rise and in the Weddell and Scotia Seas. Quaternary Research, 56, 308–321.
Oliver, R.L. and Fanning, C.M., 2002, Proterozoic geology east and southeast of Commonwealth Bay, George V land, Antarctica, and its relationship to that of adjacent Gondwana terranes. In: Gamble, J.A., Skinner, D.N.B., Henry, S., and Lynch, R. (eds.), International Symposium of Antarctic Earth Sciences 1999: Antarctic at the close of a millennium. Royal Society of New Zealand, Wellington, p. 51–58.
Patterson, M.O., McKay, R., Naish, T., Escutia, C., Jimenez-Espejo, F.J., Raymo, M.E., Meyers, S.R., Tauxe, L., Brinkhuis, H, and IODP Expdition 318 Scientists, 2014, Orbital forcing of the East Antarctic ice sheet during the Pliocene and Early Pleistocene. Nature Geoscience, 7, 841–847.
Piper, D.J.W. and Pe, G.G., 1977, Cenozoic clay mineralogy from D.S.D.P. Holes on the continental margin of the Australia-New Zealand sector of Antarctica. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics, 20, 905–917.
Pudsey, C.J., 2000, Sedimentation on the continental rise west of the Antarctic Peninsula over the last three glacial cycles. Marine Geology, 167, 313–338.
Pudsey, C.J. and Camerlenghi, A., 1998, Glacial-interglacial deposition on a sediment drift on the pacific margin of the Antarctic Peninsula. Antarctic Science, 10, 286–308.
Roland, N.W., Henjes-Kunst, F., Kleinschmidt, G., and Talarico, F., 2000, Petrographical, geochemical, and radiometric investigations in Northern Victoria Land, Oates Land and George V Coast: towards a better understanding of plate boundary processes in Antarctica. Terra Antarctica Reports, 5, 57–65.
Setti, M., Marinoni, L., Lopez-Galindo, A., and Delgado-Hubertas, A., 2000, Compositional and morphological features of the smectites of the sediments of CRP-2/2A, Victoria Land Basin, Antarctica. Terra Antarctica, 7, 581–587.
Sprenk, D., Weber, M.E., Kuhn, G., Rosén, P., Molina-Kescher, M., Liebetrau, V., and Röhling, H.G., 2013, Southern Ocean bioproductivity during the last glacial cycle-new detection method and decadal-scale insight from the Scotia Sea. In: Hambrey, M., Barker, P., Barrett, P., Bowman, V., Davies, B., Smellie, J., and Tranter, M. (eds.), Antarctic Palaeoenvironments and Earth-Surface Processes. Geological Society of London, Special Publications, vol. 381, p. 245–261. http://dx.doi.org.10.1144/SP381.17
Stokke, P.R. and Carson, B., 1973, Variation in clay mineral X-ray diffraction results with the quantity of sample mounted. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 43, 957–964.
Talarico, F. and Kleinschmidt, G., 2003, Structural and metamorphic evolution of the Mertz Shear Zone (East Antarctic Craton, George V Land): implications for Australia/Antarctica correlations and East Antarctic Craton/Ross Orogen relationships. Terra Antarctica Reports, 10, 229–248.
Tauxe, L., Stickley, C., Sugisaki, S., Bijl, P., Bohaty, S., Brinkhuis, H., Escutia, C., Flores, J.A., Iwai, M., Jiménez-Espejo, F., Mckay, R., Passchier, S., Pross, J., Riesselan, C., Röhl, U., Sangiorgi, F., Welsh, K., Klaus, A., Fehr, A., Bendle, J.A.P., Dunbar, R., Gonzàlez, J., Hayden, T., Olney, M.P., Pekar, S.F., Shrivastava, P.K., van de Fleridt, T., Williams, T., and Yamane, M., 2012, Chronostratigraphic framework for the IODP expedition 318 cores from the Wilkes Land margin: Constraints for paleoceanographic reconstruction. Paleoceanography, 27, 2214. http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2012PA002308
Veevers, J.J. and Saeed, A., 2011, Age and composition of Antarctic bedrock reflected by detrital zircons, erratics, and recycled microfossils in the Prydz Bay–Wilkes Land–Ross Sea–Marie Byrd Land sector (70°–240°E). Gondwana Research, 20, 710–738.
Verma, K., Bhattacharya, S., Biswas, P., Shrivastava, P.K., Pandey, M., Pant, N.C., and IODP Expedition 318 Scientific Party, 2014, Clay mineralogy of the ocean sediments from the Wilkes Land margin, east Antarctica: implications on the paleoclimate, provenance and sediment dispersal pattern. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 103, 2315–2326.
Weber, M.E., 1998, Estimation of biogenic carbonate and opal by continuous non-destructive measurements in deep-sea sediments: application to the eastern equatorial Pacific. Deep-Sea Research I, 45, 1955–1975.
Wefer, G. and Fischer, G., 1991, Annual primary production and export flux in the Southern Ocean from sediment trap data. Marine Chemistry, 35, 597–613.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khim, BK., Song, B., Cho, H.G. et al. Late Neogene sediment properties in the Wilkes Land continental rise (IODP Exp. 318 Hole U1359A), East Antarctica. Geosci J 21, 21–32 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-016-0037-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-016-0037-6