Abstract
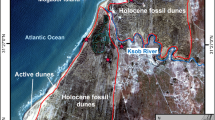
Miankaleh coastal barrier system has about 71 km length with an average of 3 km width in southeast of Caspian Sea. Forty sandy samples, collected from 5 coastal dune zones, in Miankaleh were analyzed compositionally, texturally and chemically and 31 samples from 4 nebkha field zones were analyzed for textural and geomorphological interpretation. Samples from stoss and lee sides of coastal dunes and nebkha dune field are mainly composed of medium to fine grains of sand that are well sorted, fine skewed and leptokurtic. Modal analyses of coastal dune sands show that they comprise 61% quartz, 14.74% feldspar and 24.26% rock fragments. The chemical index of alteration (CIA) value in coastal dune samples is high because of relatively warm and humid climatic condition with high amount of feldspar and rock fragments. Sedimentary and plutonic rock fragments are more than the other lithic fragments in sand samples. Nekaroud is the main source of sediments supply and as move to the east, the amount of Fe2O3, TiO2, MgO and heavy minerals in coastal dune sands decreases. The changes of the ratios of Al2O3/Na2O and Rb/Sr can be used to evaluate the CIA value in the study area. High Zr value is another evidence of high zircon content and recycled sedimentary rocks in the source area. From west to the east, sand moving power index (M) decreases and active coastal dunes change to dormant coastal dunes. There is no coastal dune in the eastern and southern parts of the study area. Based on concentration, stabilization, height and biological cover, nebkha dune fields are classified into 4 zones. There is a meaningful relationship between different morphometrical parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abuodha, J.O.Z., 2003, Grain size distribution and composition of modern dune and beach sediments, Malindi Bay coast, Kenya. Journal of African Earth Sciences 36, 41–54.
Belknap, D.F. and Kraft, J.C., 1981, Preservation potential of transgressive coastal lithosomes on the US Atlantic Coast. Marine Geology, 42, 429–442.
Badyukova, E.N and Kalashnikov, A.Yu, 2009, Dependence of the Types of Coasts and Coastal eolian Relief on the Variations of the Sea Level Using the Example of the Caspian Sea. Oceanology, 49, 858–865.
Carranza-Edwards, A., Centeno-García, L., Rosales-Hoz, L., and Lozano-Santa Cruz, R., 2001, Provenance of beach gray sands from western Mexico. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 14, 291–301.
Davis, R.J. Jr. and Clifton, H.E., 1987, Sea level change and the preservation potential of wave dominated and tide — dominated coastal sequence. In: Nummedal, D., Pilkey, O. H., and Howard, J.D. (eds.), Sea level Fluctuation and coastal Evolution. SEPM, Tulsa, OK, 167–178.
Di Leo, P., Dinelli, E., Mongelli, G., and Schiattarella, M., 2002, Geology and geochemistry of Jurassic pelagic sediments, Scisti silicei Formation, Southern Apennines, Italy. Sedimentary Geology, 150, 229–246.
Fedo, C.M., Nesbitt, H.W., and Young, G.M, 1995, Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology, 23, 921–924.
García, D., Ravenne, C., Maréchal, B., and Moutte, J., 2004, Geochemical variability induced by entrainment sorting; Quantified signals for provenance analysis. Sedimentary Geology, 171, 13–128.
Gao, S., Dong, G., and Li, B., 1985, The variable of chemical elements contents in paleo-Aeolian sand strata and climatic environment at Yulin area, Shaanxi province. Journal of desert research, 5, 25–30.
Glushko, T., 1996, Features of landscape structures of the coastal dunes of the east Caspian sea. Landscape and urban planning, 34, 183–188.
Egli, M., Mirabella, A., Sartori, G., and Fitze, P., 2003, Weathering rates as a function of climate: results from a climosequence of the Val Genova (Trentino, Italian Alps). Geoderma, 111, 99–121.
Hesp, P.A., 1998, Morphology,dynamics and internal stratification of some established foredunes in southeast Australia. Sedimentary Geology, 55, 17–42.
Honda, M. and Shimizu, H., 1998, Geochemical, mineralogical and sedimentological studies on the Taklimakan Desert sands. Sedimentology, 45, 1125–1143.
Honda, M., Yabuki, S., and Shimizu, H., 2004, Geochemical and isotopic studies of aeolian sediments in China. Sedimentology, 51, 211–230.
Jafari, M., 2008, Thunder and storm fluctuations in the Caspian region over the last half century. Journal of Forests and Rangelands Researches Institute, 16, 583–598. (In Persian with English abstract)
Khodabakhsh, D., Rahimi, E., Mahfrozi, A., and Rafee, B., 2006, Study of river type and trend of fine sizing sediments in Nekaroud watershed basin, In: Proceedings of the 10th Conference of Geological Association of Iran, Tarbyat Modares University, p. 2002–2009. (In Persian)
King, C.A.M., 1972, Beaches and Coasts (2nd edition). Edward Arnold, London, 570 p.
Komar, P.O. and Wang, C., 1984, Process of selective grain transport and formation of placers on beaches. Journal of geology, 92, 637–655.
Lancaster, N., 1988, Development of linear dunes in the southwestern Kalahari, southern Africa. Journal of Arid Environments, 14, 233–244.
Lancaster, N., 1995, Geomorphology of desert dunes. Routledge, London, 290 p.
Levin, N., Kidron, G.J., and Ben-Dor, E., 2007, Surface properties of stabilizing coastal dunes — combining spectral and field analyses. Sedimentology, 54, 771–788.
Livingstone, I., Bullard, J.E., Wing, G.F.S., and Thomas, D.S.G., 1999, Grain-size variation on dune in southwest Kalahari, Southern Aferica. Journal of sedimentary research, 69, 546–552.
Mackee, E.D., 1979, Introduction to a study of global sand seas. In: McKee, E.D. (ed.), A Study of Global Sand Seas, United States Geological Survey, Professional Paper, 1052, 3–19.
Mansimov, M. and Aliyev, A., 1994, Reasons of Caspian Sea level fluctuations and predictions for future. Azerbaijan International A1, 48–49.
Martinez, M.L. and Psuty, N.P. (eds.), 2008, Coastal Dunes: Ecology and Conservation. Springer, Berlin, 386 p.
Mountney, N.P. and Russell, A.J., 2006, Coastal aeolian dune development, Solheimasandur, Southern Iceland. Sedimentary Geology, 192, 167–181.
Muhs, L.A. and Maat, P.B., 1993, The potential response of eolian sands to Greenhouse Warming and precipitation reduction on the Great Plains of the United States. Journal of Arid Environments, 25, 351–361.
Nazemi, A., 2005, Final Report of “Investigation of Golestan province coastline changes”, Project Code No. 81-0500012000-01, Soil conservation and watershed management Institute, 95 p. (In Persian with English abstract)
Nesbitt, H.W. and Young, G.M., 1982, Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature, 299, 715–717.
Nesbitt, H.W. and Young, G.M., 1996, Petrogenesis of sediments in the absence of chemical weathering: effects of abrasion and sorting on bulk composition and mineralogy. Sedimentology, 43, 341–356.
Nordstorm, K., Psuty, N., and Carter, B., 1990, Coastal dunes: form and process. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, 392 p.
Ohta, T., 2004, Geochemistry of Jurassic to earliest Cretaceous deposits in the Nagato Basin, SW Japan: implication of factor analysis to sorting effects and provenance signatures. Sedimentary Geology, 171, 159–180.
Pye, K., Says, S., and Blott, N., 2007, Sand dune processes and management for flood and coastal defence, Part 2. R&D Technical Report FD1392/TR, UK Department for environment, Food and Rural Affairs, London, 21 p.
Kasper-Zubillaga, J.J., Zolezzi-Ruiz, H., Carranza-Edwards, A., Grion-Garcia, P., Ortiz-Zamora, G., and Palma, M., 2007, Sedimentological, modal analysis and geochemical studies of desert and coastal dunes, Altar Desert, NW Mexico. Earth surface process and Lanforms, 32, 489–508.
Kravtsova, V.I. and Ilyukhina, Yu.A., 2002, The Evolution of the Eastern Part of the Terek Mouth Area in the Period of the Caspian Sea Level Rise: Mapping Based on Aerospace Materials. Water Resources, 29, 43–54.
Kroonenberg, S.B., Storms, J.A., Ignatov, E.I., and Kasimov, N.S., 2000, A full sea level cycle in 65 years: barrier dynamics along Caspian shores. Sedimentary Geology, 134, 257–274.
Rooney, C.B. and Basu, A., 1994, Provenance analysis of muddy sandstones. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 64, 2–7.
Sawakuchi, A.O., Giannini, P.C.F., Martinho, C.T., and Tanaka, A.P.B., 2009, Grain size and heavy minerals of the Late Quaternary aeolian sediments from the Imbituba-Jaguaruna coast, Southern Brazil: Depositional controls linked to relative sea-level changes. Sedimentary Geology, 222, 226–240.
Says, S.E., 2003, Morphology and Sedimentology of Coastal Sand Dune Systems in England and Wales. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, 614 p.
Says, S.E. and Pye, K., 2006, Variations in chemical composition and particle size of dune sediments along the west coast of Jutland, Denmark. Sedimentary Geology, 183, 217–242.
Storms, J.E.A., Weltje, G.J., Van-Dijke, J.J., Geel, C.R., and Kroonenberg, S.B., 2002, Process-response modeling of wave-dominated coastal systems: simulating evolution and stratigraphy on geological timescales. Journal of Sedimentological Research, 72, 226–239.
Svitoch, A.A. and Yanina, T.A., 2006, Holocene marine sediments on the iranian coast of the caspian sea. Doklady Earth Sciences, 410, 1166–1169.
Thomas, D.S.G. and Tsoar, H., 1990, The geomorphological role of vegetation in desert dune systems. In: Thornes, J.B. (eds.), Vegetation and Erosion, John Wiley, Chichester, p. 471–489.
Tengberg, A. and Deliang, C., 1998, A comparative analysis of nebkhas in central Tunisia and northern Burkina Faso. Geomorphology, 22, 181–192.
Yang, S. and Jung, H.S., 2004, Two unique weathering regimes in Changjiang and Huanghe drainage basins: geochemical evidence from river sediments. Sedimentary Geology, 164, 19–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amini, A., Moussavi-Harami, R., Lahijani, H. et al. Sedimentological, geochemical and geomorphological factors in formation of coastal dunes and nebkha fields in Miankaleh coastal barrier system (Southeast of Caspian Sea, North Iran). Geosci J 16, 139–152 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-012-0014-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12303-012-0014-7