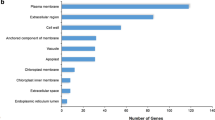
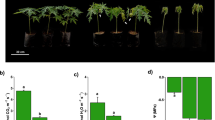
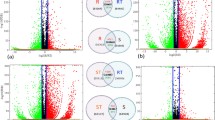
Abstract
It is of great significance to understand the regulatory mechanisms by which plants deal with drought stress. Two EST libraries derived from rapeseed (Brassica napus) leaves in non-stressed and drought stress conditions were analyzed in order to obtain the transcriptomic landscape of drought-exposed B. napus plants, and also to identify and characterize significant drought responsive regulatory genes and microRNAs. The functional ontology analysis revealed a substantial shift in the B. napus transcriptome to govern cellular drought responsiveness via different stress-activated mechanisms. The activity of transcription factor and protein kinase modules generally increased in response to drought stress. The 26 regulatory genes consisting of 17 transcription factor genes, eight protein kinase genes and one protein phosphatase gene were identified showing significant alterations in their expressions in response to drought stress. We also found the six microRNAs which were differentially expressed during drought stress supporting the involvement of a post-transcriptional level of regulation for B. napus drought response. The drought responsive regulatory network shed light on the significance of some regulatory components involved in biosynthesis and signaling of various plant hormones (abscisic acid, auxin and brassinosteroids), ubiquitin proteasome system, and signaling through Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Our findings suggested a complex and multi-level regulatory system modulating response to drought stress in B. napus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahuja I, de Vos RC, Bones AM, Hall RD (2010) Plant molecular stress responses face climate change. Trends Plant Sci 15:664–674
Ashraf M (2010) Inducing drought tolerance in plants: recent advances. Biotechnol Adv 28:169–183
Audic S, Claverie J-M (1997) The significance of digital gene expression profiles. Genome Res 7:986–995
Avin‐Wittenberg T, Tzin V, Angelovici R, Galili G (2012) Deciphering energy‐associated gene networks operating in the response of Arabidopsis plants to stress and nutritional cues. Plant J 70:954–966
Batistič O, Kudla J (2012) Analysis of calcium signaling pathways in plants. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Gen Subj 1820:1283–1293
Carlson JE et al (2006) EST database for early flower development in California poppy (Eschscholzia californica Cham., Papaveraceae) tags over 6000 genes from a basal eudicot. Plant Mol Biol 62:351–369
Carmona-Saez P, Chagoyen M, Tirado F, Carazo JM, Pascual-Montano A (2007) GENECODIS: a web-based tool for finding significant concurrent annotations in gene lists. Genome Biol 8:R3
Cheng M-C, Hsieh E-J, Chen J-H, Chen H-Y, Lin T-P (2012) Arabidopsis RGLG2, functioning as a RING E3 ligase, interacts with AtERF53 and negatively regulates the plant drought stress response. Plant Physiol 158:363–375
Dai X, Zhao PX (2011) psRNATarget: a plant small RNA target analysis server. Nucleic Acids Res 39:W155–W159
Dai X, Sinharoy S, Udvardi M, Zhao P (2013) PlantTFcat: an online plant transcription factor and transcriptional regulator categorization and analysis tool. BMC Bioinforma 14:321
Deokar AA et al (2011) Comparative analysis of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) between drought-tolerant and-susceptible genotypes of chickpea under terminal drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 11:70
Diepenbrock W (2000) Yield analysis of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.): a review. Field Crop Res 67:35–49
Dong J, Keller WA, Yan W, Georges F (2004) Gene expression at early stages of Brassica napus seed development as revealed by transcript profiling of seed-abundant cDNAs. Planta 218:483–491
Duque AS et al. (2013) Abiotic stress responses in plants: unraveling the complexity of genes and networks to survive. INTECH Open Access Publisher
Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N (2009) Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev 29:185–212
Farooq M, Hussain M, Wahid A, Siddique KHM (2012) Drought stress in plants: an overview. In: Aroca R (ed) Plant Responses to Drought Stress. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, pp 1–33. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-32653-0_1
Fourmann M, Barret P, Froger N, Baron C, Charlot F, Delourme R, Brunel D (2002) From Arabidopsis thaliana to Brassica napus: development of amplified consensus genetic markers (ACGM) for construction of a gene map. Theor Appl Genet 105:1196–1206
Friedrichsen DM et al (2002) Three redundant brassinosteroid early response genes encode putative bHLH transcription factors required for normal growth. Genetics 162:1445–1456
Fujita Y, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2011) ABA-mediated transcriptional regulation in response to osmotic stress in plants. J Plant Res 124:509–525
Gao W-R et al (2008) Comparative analysis of ESTs in response to drought stress in chickpea (C. arietinum L.). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:578–583
Golldack D, Lüking I, Yang O (2011) Plant tolerance to drought and salinity: stress regulating transcription factors and their functional significance in the cellular transcriptional network. Plant Cell Rep 30:1383–1391
Gorantla M, Babu P, Lachagari VR, Reddy A, Wusirika R, Bennetzen JL, Reddy AR (2007) Identification of stress-responsive genes in an indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) using ESTs generated from drought-stressed seedlings. J Exp Bot 58:253–265
Griffiths-Jones S, Grocock RJ, van Dongen S, Bateman A, Enright AJ (2006) miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D140–D144. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj112
Gruber M et al (2012) Analysis of expressed sequence tags in Brassica napus cotyledons damaged by crucifer flea beetle feeding. Genome 55:118–133
Guo N et al (2014) Computational identification of novel microRNAs and targets in Glycine max. Mol Biol Rep 1–11
Haake V, Cook D, Riechmann J, Pineda O, Thomashow MF, Zhang JZ (2002) Transcription factor CBF4 is a regulator of drought adaptation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 130:639–648
Hadiarto T, Tran L-SP (2011) Progress studies of drought-responsive genes in rice. Plant Cell Rep 30:297–310
Halford N, Hey S (2009) Snf1-related protein kinases (SnRKs) act within an intricate network that links metabolic and stress signalling in plants. Biochem J 419:247–259
Han J, Xie H, Kong M, Sun Q, Li R, Pan J (2014) Computational identification of miRNAs and their targets in Phaseolus vulgaris. Genet Mol Res 13:310
He L, Yang X, Wang L, Zhu L, Zhou T, Deng J, Zhang X (2013) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel cotton CBL-interacting protein kinase gene (GhCIPK6) reveals its involvement in multiple abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 435:209–215
Himmelbach A, Hoffmann T, Leube M, Höhener B, Grill E (2002) Homeodomain protein ATHB6 is a target of the protein phosphatase ABI1 and regulates hormone responses in Arabidopsis. EMBO J 21:3029–3038
Hwang E-W, Shin S-J, Kwon H-B (2011) Identification of microRNAs and their putative targets that respond to drought stress in Solanum tuberosum. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 54:317–324
Jammes F et al (2009) MAP kinases MPK9 and MPK12 are preferentially expressed in guard cells and positively regulate ROS-mediated ABA signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:20520–20525
Khraiwesh B, Zhu J-K, Zhu J (2012) Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Gene Regul Mech 1819:137–148
Kim T-H, Maik B (2010) Guard cell signal transduction network: advances in understanding abscisic acid, CO2, and Ca2+ signaling. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:561
Lata C, Sahu PP, Prasad M (2010) Comparative transcriptome analysis of differentially expressed genes in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) during dehydration stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:720–727
Lechner E et al (2011) MATH/BTB CRL3 receptors target the homeodomain-leucine zipper ATHB6 to modulate abscisic acid signaling. Dev Cell 21:1116–1128
Leung J, Merlot S, Giraudat J (1997) The Arabidopsis ABSCISIC ACID-INSENSITIVE2 (ABI2) and ABI1 genes encode homologous protein phosphatases 2C involved in abscisic acid signal transduction. Plant Cell Online 9:759–771
Lin R-C, Park H-J, Wang H-Y (2008) Role of Arabidopsis RAP2. 4 in regulating light-and ethylene-mediated developmental processes and drought stress tolerance. Mol Plant 1:42–57
Liu Y (2012) Roles of mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in ABA signaling. Plant Cell Rep 31:1–12
Lu X-Y, Huang X-L (2008) Plant miRNAs and abiotic stress responses. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368:458–462
Luan S (2009) The CBL–CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci 14:37–42
Masoudi-Nejad A et al (2006) EGassembler: online bioinformatics service for large-scale processing, clustering and assembling ESTs and genomic DNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 34:W459–W462
Mazzucotelli E, Mastrangelo AM, Crosatti C, Guerra D, Stanca AM, Cattivelli L (2008) Abiotic stress response in plants: when post-transcriptional and post-translational regulations control transcription. Plant Sci 174:420–431
Meng X, Xu J, He Y, Yang K-Y, Mordorski B, Liu Y, Zhang S (2013) Phosphorylation of an ERF transcription factor by Arabidopsis MPK3/MPK6 regulates plant defense gene induction and fungal resistance. Plant Cell Online 25:1126–1142
Min JH, Chung JS, Lee KH, Kim CS (2014) The CONSTANS‐like 4 transcription factor, AtCOL4, positively regulates abiotic stress tolerance through an abscisic acid‐dependent manner in Arabidopsis. J Integr Plant Biol
Murata Y, Pei Z-M, Mori IC, Schroeder J (2001) Abscisic acid activation of plasma membrane Ca2+ channels in guard cells requires cytosolic NAD (P) H and is differentially disrupted upstream and downstream of reactive oxygen species production in abi1-1 and abi2-1 protein phosphatase 2C mutants. Plant Cell Online 13:2513–2523
Nam KH, Li J (2002) BRI1/BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110:203–212
Nikitin A, Egorov S, Daraselia N, Mazo I (2003) Pathway studio—the analysis and navigation of molecular networks. Bioinformatics 19:2155–2157
Niu Y et al (2009) Global analysis of gene expression profiles in Brassica napus developing seeds reveals a conserved lipid metabolism regulation with Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant 2:1107–1122
Panda D, Dehury B, Sahu J, Barooah M, Sen P, Modi MK (2014) Computational identification and characterization of conserved miRNAs and their target genes in garlic (Allium sativum L.) expressed sequence tags. Gene 537:333–342
Park J, Lee N, Kim W, Lim S, Choi G (2011) ABI3 and PIL5 collaboratively activate the expression of SOMNUS by directly binding to its promoter in imbibed Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Cell Online 23:1404–1415
Parkin IA, Lydiate D, Trick M (2002) Assessing the level of collinearity between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus for A. thaliana chromosome 5. Genome 45:356–366
Patanun O, Lertpanyasampatha M, Sojikul P, Viboonjun U, Narangajavana J (2013) Computational identification of microRNAs and their targets in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz.). Mol Biotechnol 53:257–269
Pratt LH et al (2005) Sorghum expressed sequence tags identify signature genes for drought, pathogenesis, and skotomorphogenesis from a milestone set of 16,801 unique transcripts. Plant Physiol 139:869–884
Raymer PL (2002) Canola: an emerging oilseed crop. Trends New Crops New Uses 1:122–126
Romualdi C, Bortoluzzi S, d’Alessi F, Danieli GA (2003) IDEG6: a web tool for detection of differentially expressed genes in multiple tag sampling experiments. Physiol Genomics 12:159–162
Sakuma Y, Maruyama K, Osakabe Y, Qin F, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2006) Functional analysis of an Arabidopsis transcription factor, DREB2A, involved in drought-responsive gene expression. Plant Cell Online 18:1292–1309
Seki M, Kamei A, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2003) Molecular responses to drought, salinity and frost: common and different paths for plant protection. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:194–199
Seki M, Umezawa T, Urano K, Shinozaki K (2007) Regulatory metabolic networks in drought stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:296–302
Shaik R, Ramakrishna W (2013) Genes and co-expression modules common to drought and bacterial stress responses in Arabidopsis and rice. PLoS One 8:e77261. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0077261
Shamloo-Dashtpagerdi R, Razi H, Lindlöf A, Niazi A, Dadkhodaie A, Ebrahimie E (2013) Comparative analysis of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) from Triticum monococcum shoot apical meristem at vegetative and reproductive stages. Genes Genomics 35:365–375
Shi H, Chen L, Ye T, Liu X, Ding K, Chan Z (2014) Modulation of auxin content in Arabidopsis confers improved drought stress resistance. Plant Physiol Biochem 82:209–217
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (1996) Molecular responses to drought and cold stress. Curr Opin Biotechnol 7:161–167
Su Z, Ma X, Guo H, Sukiran NL, Guo B, Assmann SM, Ma H (2013) Flower development under drought stress: morphological and transcriptomic analyses reveal acute responses and long-term acclimation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Online 25:3785–3807
Subramanian A et al (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:15545–15550
Sunkar R, Chinnusamy V, Zhu J, Zhu J-K (2007) Small RNAs as big players in plant abiotic stress responses and nutrient deprivation. Trends Plant Sci 12:301–309
Sunkar R, Li Y-F, Jagadeeswaran G (2012) Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 17:196–203
Tabas-Madrid D, Nogales-Cadenas R, Pascual-Montano A (2012) GeneCodis3: a non-redundant and modular enrichment analysis tool for functional genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:W478–W483
Thompson AJ, Jackson AC, Parker RA, Morpeth DR, Burbidge A, Taylor IB (2000) Abscisic acid biosynthesis in tomato: regulation of zeaxanthin epoxidase and 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase mRNAs by light/dark cycles, water stress and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 42:833–845
Tripathi V, Parasuraman B, Laxmi A, Chattopadhyay D (2009) CIPK6, a CBL‐interacting protein kinase is required for development and salt tolerance in plants. Plant J 58:778–790
Umezawa T, Fujita M, Fujita Y, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Engineering drought tolerance in plants: discovering and tailoring genes to unlock the future. Curr Opin Biotechnol 17:113–122
Wang X et al (2008) Sequential transphosphorylation of the BRI1/BAK1 receptor kinase complex impacts early events in brassinosteroid signaling. Dev Cell 15:220–235
Wang P, Du Y, Zhao X, Miao Y, Song C-P (2013) The MPK6-ERF6-ROS-responsive cis-acting Element7/GCC box complex modulates oxidative gene transcription and the oxidative response in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 161:1392–1408
Wang W, Bai M-Y, Wang Z-Y (2014) The brassinosteroid signaling network—a paradigm of signal integration. Curr Opin Plant Biol 21:147–153
Weinl S, Kudla J (2009) The CBL–CIPK Ca2+−decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol 184:517–528
Xie FL, Huang SQ, Guo K, Xiang AL, Zhu YY, Nie L, Yang ZM (2007) Computational identification of novel microRNAs and targets in Brassica napus. FEBS Lett 581:1464–1474
Xing Y, Jia W, Zhang J (2008) AtMKK1 mediates ABA‐induced CAT1 expression and H2O2 production via AtMPK6‐coupled signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant J 54:440–451
Xiong L, Zhu J-K (2003) Regulation of abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 133:29–36
Xiong L, Lee H, Ishitani M, Zhu J-K (2002) Regulation of osmotic stress-responsive gene expression by theLOS6/ABA1 locus in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 277:8588–8596
Xoconostle-Cazares B, Ramirez-Ortega FA, Flores-Elenes L, Ruiz-Medrano R (2010) Drought tolerance in crop plants. Am J Plant Physiol 5:241–256
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2006) Transcriptional regulatory networks in cellular responses and tolerance to dehydration and cold stresses. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:781–803
Ye K, Chen Y, Hu X, Guo J (2013) Computational identification of microRNAs and their targets in apple. Genes Genomics 35:377–385
Young LW, Wilen RW, Bonham‐Smith PC (2004) High temperature stress of Brassica napus during flowering reduces micro‐and megagametophyte fertility, induces fruit abortion, and disrupts seed production. J Exp Bot 55:485–495
Zhang B, Pan X, Cox S, Cobb G, Anderson T (2006) Evidence that miRNAs are different from other RNAs. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:246–254
Zhuang J, Zhu B (2014) Analysis of Brassica napus ESTs: gene discovery and expression patterns of AP2/ERF-family transcription factors. Mol Biol Rep 41:45–56
Zuker M (2003) Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3406–3415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shamloo-Dashtpagerdi, R., Razi, H. & Ebrahimie, E. Mining expressed sequence tags of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) to predict the drought responsive regulatory network. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 21, 329–340 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-015-0311-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-015-0311-5