Abstract
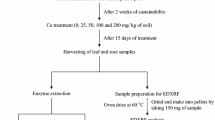
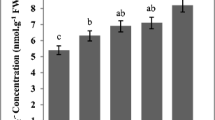
The present study aimed to analyze the biological effects induced by bioaccumulation of metals in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Effects of mineral nutrient imbalance, total antioxidants level and DNA damage induced by accumulation of heavy metals, were investigated in bean seedlings treated with two selected metal concentrations for 7 days. Metal content is analyzed by inductively coupled plasma – atomic emission spectrometer (ICP-AES), for total antioxidants level assessment the Ferric-Reducing Antioxidant Power (FRAP) assay is used and Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) method was applied for investigation of DNA damages. The increasing metal concentration in the treatment medium changed synchronously metal content in samples, and decreased total antioxidant activity in all samples with exception only for samples treated with Ni and Cd. The obtained “DNA fingerprints” demonstrated that the increasing metal concentrations induced changes in RAPD profiles (disappearance and/or appearance of bands in comparison with untreated control samples). The highest number of missing bands was observed in samples treated with zinc (total 4 bands) and nickel (total 4 bands) at both concentrations. These results suggested that mineral nutrient imbalance is involved in changes of antioxidant levels and DNA damages of the seedlings, which may help to understand the mechanism of metal toxicity in plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Qurainy F (2009) Toxicity of heavy metals and their molecular detection on Phaseolus vulgaris L. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 3(3):3025–3035
Antosiewicz DM (1992) Adaptation of plants to an environment polluted with heavy metals. Acta Soc Bot Polon 61:281–299
Aqil F, Ahmed I, Mehmood Z (2006) Antioxidant and free radical scavenging properties of twelve traditionally used Indian medicinal plants. Turk J Biol 30:177–183
Atienzar FA, Jha AN (2006) The random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) assay and related techniques applied to genotoxicity and carcinogenesis studies: a critical review. Mutat Res 613:76–102
Atienzar FA, Conradi M, Evenden AJ, Jha AN, Depledge MH (1999) Qualitative assessment of genotoxicity using random amplified polymorphic DNA: comparison of genomic template stability with key fitness parameters in Daphnia magna exposed to benzo a pyrene. Environ Toxicol Chem 18(10):2275–2282
Baker AJM, Reeves RD, Hajar ASM (1994) Heavy metal accumulation and tolerance in British populations of the metallophyte Thlaspi caerulescens J. & C. Presl (Brassicaceae). New Phytol 127:61–68
Benzarti S, Mohri S, Yoshiro O (2008) Plant response to heavy metal toxicity: Comparative study between the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (ecotype Ganges) and nonaccumulator plants: Lettuce, radish, and alfalfa. Environ Toxicol 23:607–616
Benzie IFF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric-reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239:70–76
Broughton WJ, Hernández G, Blair M, Beebe S, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.): model food legume. Plant Soil 252:55–128
Cargnelutti D, Tabaldi LA, Spanevello RM, Jucoski GO, Battisti V, Redin M, Linares CEB, Dressler VL, Flores EMM, Nicoloso FT, Morsch VM, Schetinger MRC (2006) Mercury toxicity induces oxidative stress in growing cucumber seedlings. Chemosphere 65:999–1006
Cenkci S, Yildiz M, Ciǧerci IH, Konuk M, Bozdaǧ A (2009) Toxic chemicals-induced genotoxicity detected by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seedlings. Chemosphere 76:900–906
Cenkci S, Ciǧerci IH, Yildiz M, Özay C, Bozdaǧ A, Terzi H (2010) Lead contamination reduces chlorophyll biosynthesis and genomic template stability in Brassica rapa L. Environ Exp Bot 67:467–473
Chandra S, Chauhan LK, Pande PN, Gupta SK (2004) Cytogenetic effects of leachates from tannery solid waste on the somatic cells of Vicia faba. Environ Toxicol 19(2):129–133
Chaoui A, Mazhoudi S, Ghorbal MH, El Ferjani E (1997) Cadmium and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Sci 127:139–147
Dixit V, Pandey V, Shyam R (2001) Differential antioxidative responses to cadmium in roots and leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Azad). J Exp Bot 52:101–1109
Enan MR (2006) Application of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to detect the genotoxic effect of heavy metals. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 43:147–154
Erturk FA, Ay H, Nardemir G, Agar G (2012) Molecular determination of genotoxic effects of cobalt and nickel on maize (Zea mays L.) by RAPD and protein analyses. Toxicol Ind Health. doi:10.1177/0748233712442709
Erturk FA, Nardemir G, Ay H, Arslan E, Agar G (2013) Determination of genotoxic effects of boron and zinc on Zea mays using protein and random amplification of polumorphic DNA analyses. Toxicol Ind Health. doi:10.1177/0748233713485888
Foyer CH, Lopez-Delgado H, Dat JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signaling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254
Halvorsen BL, Holte K, Myhrstad MSW, Barikmo I, Hvattum E, Remberg SF, Wold A-B, Haffner K, Baugerød H, Andersen LF, Moskaug JØ, Jacobs DR, Blomhoff R (2002) A systematic screening of total antioxidants in dietary plants. J Nutr 132(3):461–471
Hon CC, Chow YC, Zeng FY, Leung FCC (2003) Genetic authentication of ginseng and other traditional Chinese medicine. Acta Pharmacol Sin 24:841–846
Hou W, Chen X, Song G, Wang Q, Chang CC (2007) Effects of copper and cadmium on heavy metal polluted waterbody restoration by duckweed (Lemna minor). Plant Physiol Boichem 45:62–69
Israr M, Sahi V, Jain J (2006) Cadmium accumulation and antioxidative responses in the Sesbania drummondii callus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:121–127
Jaio H, Wang SY (2000) Correlation of antioxidant capacities to oxygen radical scavenging enzyme activities in blackberry. J Agr Food Chem 48:5672–5676
Kekec G, Sakcali MS, Uzonur I (2010) Assessment of genotoxic effects of boron on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by using RAPD analysis. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 84(6):759–764
Kumar NPBA, Dushenkov V, Motto H, Raskin I (1995) Phytoextraction: the use of plants to remove heavy metals from soils. Environ Sci Technol 29:1232–1238
Lane SD, Martin ES (1977) A histochemical investigation of lead uptake in Raphanus sativus. New Phytol 79:281–286
Liu W, Li PJ, Qi XM, Zhou QX, Zheng L, Sun TH, Yang YS (2005) DNA changes in barley (Hordeum vulgare) seedlings induced by cadmium pollution using RAPD analysis. Chemosphere 61:158–167
Malkowski E, Kita A, Galas W, Karez W, Michael K (2002) Lead distribution in corn seedlings (Zea mays L.) and its effect on growth and the concentration of potassium and calcium. Plant Growth Regul 37:69–76
Miller HE, Rigelhof F, Marquart L, Prakash A, Kanter M (2000a) Whole-grain products and antioxidants. Cereal Foods World 45(2):59–63
Miller HE, Rigelhof F, Marquart L, Prakash A, Kanter M (2000b) Antioxidant content of whole grain breakfast cereals, fruits and vegetables. J Am Coll Nutr 19(3):312S–319S
Murashige T, Skoog FA (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–479
Nagajyoti PC, Lee KD, Sreekanth TVM (2010) Heavy metals, occurrence and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem Lett 8:199–216
Ozgen M, Tulio AZ, JrRN R, Scheerens JC, Miller AR (2006) Modified 2,2-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid method to measure antioxidant capacity of selected small fruits and comparison to ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) and 2,2#-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) methods. J Agr Food Chem 54:1151–1157
Paganaga G, Miller N, Rice-Evans CA (1999) The polyphenolic content of fruit and vegetables and their antioxidant activities: what does a serving constitute? Free Radic Res 30:153–162
Quariti O, Boussama N, Zarrouk M, Cherif A, Ghorbal MH (1997) Cadmium and copper induced changes in tomato membrane lipids. Phytochemistry 45:1343–1350
Radić S, Cvjetko P, Glavaš K, Roje V, Pevalek-Kozlina B, Pavlica M (2009) Oxidative stress and DNA damage in broad bean (Vicia faba L.) seedlings induced by thallium. Environ Toxicol Chem 28(1):189–196
Rank J, Nielsen MH (1998) Genotoxicity testing of wastewater sludge using the Allium cepa anaphase-telophase chromosome aberration assay. Mutat Res 418(2–3):113–119
Reddy AM, Kumar SG, Jyotsnakumari G, Thimmanayak S, Sudhakar C (2005) Lead induced changes in antioxidant metabolism of horsegram (Macrotyloma uniflorum (Lam.) Verdc.) and bengalgram (Cicer arietinum L.). Chemosphe 60:97–104
Rohlf FJ (1994) Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 1.70. Exeter Software, Setauker
Savva D (1998) Use of DNA fingerprinting to detect genotoxic effects. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 41:103–106
Shainberg O, Rubin B, Rabinowitch HD, Libal Y, Tel OE (2000) Acclimation of beans to oxidative stress by treatment with subletal iron levels. J Plant Physiol 157:93–99
Sharma P, Dubey RS (2005) Lead toxicity in plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17(1):35–52
Sidlecka A, Baszynsky T (1993) Inhibition of electron flow around photosystem in chloroplast of cadmium treated maize plants is due to cadmium induced iron deficiency. Physiol Plant 87:199–202
Stoch SJ, Bagchi D (1995) Oxidative mechanism in the toxicity of metal ions. Free Radic Biol Med 18:321–336
Taspinar MS, Agar G, Alpsoy L, Yildirim N, Bozari S, Sevsay S (2011) The protective role of zinc and calcium in Vicia faba seedlings subjected to cadmium stress. Toxicol Ind Health 27(1):73–80
Van Assche F, Clijsters H (1990) Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13:95–206
Verma S, Dubey RS (2003) Lead toxicity induces lipid peroxidation and alters the activities of antioxidant enzymes in growing rice plants. Plant Sci 164:645–655
Wang XF, Zhou QX (2006) Ecotoxicological effects of cadmium on three ornamental plants. Chemosphere 60:16–21
Wan-Ibrahim WI, Sidik K, Kuppusamy UR (2010) A high antioxidant level in edible plants is associated with genotoxic properties. Food Chem 122:1139–1144
Weckx JEJ, Clijster HMM (1996) Oxidative damage and defense mechanisms in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris as a result of root assimilation of toxic amounts of copper. Physiol Plant 96:506–512
Wong MH, Bradshaw AD (1982) a comparison of the toxicity of heavy metals, using root elongation of rye grass, Lolium perenne. New Phytol 91:255–261
Wu X, Beecher GR, Holden JM, Haytowitz DB, Gebhardt SE, Prior RL (2004) Lipophilic and hydrophilic antioxidant capacities of common foods in the United States. J Agr Food Chem 52:4026–4037
Yoon J, Cao X, Zhou Q, Ma LQ (2006) Accumulation of Pb, Cu, and Zn in native plants growing on a contaminated Florida site. Sci Total Environ 368:456–464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gjorgieva, D., Kadifkova Panovska, T., Ruskovska, T. et al. Mineral nutrient imbalance, total antioxidants level and DNA damage in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) exposed to heavy metals. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 19, 499–507 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-013-0196-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-013-0196-0