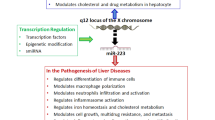
Abstract
In liver diseases, the interplay of different noncoding RNA expressions, and inflammatory biomarkers show high context dependencies. Interrelations between these noncoding RNA and inflammatory biomarkers paved the way for the diagnosis of various diseases. Here, we analyzed the expression of MALAT1, miR-181a in liver cirrhosis and a panel of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-17, SIRT1 and NF-Ƙβ p65). The association between all measured parameters was monitored. Fifty healthy volunteers with normal liver function, hepatic ultrasonography, and negative results for HCV and HBV participated in our study as a healthy control group. In addition, hundred and fifty patients with liver cirrhosis were included. Compared with healthy controls, miR-181a expression was significantly decreased (p < 0.01), while MALAT1 expression was significantly elevated (p < 0.01) in patients with liver cirrhosis. IL-17 and NF-ƘB p65 were significantly increased (p < 0.001), while SIRT1 was significantly decreased (p < 0.001) in cirrhotic patients compared to controls. Serum expression of SIRT1 significantly positively correlated with miR-181a and negatively associated with MALAT-1, NF-Ƙβ p65, and IL-17expression levels. Our results pointed to alterations in the expression levels of miR-181a, and MALAT1 could serve as biomarkers in cirrhotic patients. Reduction of IL-17 and NF-Ƙβ p65 in combination with an elevation of SIRT-1 might refer to the dual effects of miR-181a and MALAT1 in controlling inflammation in liver cirrhosis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanda T, Goto T, Hirotsu Y, Moriyama M, Omata M. Molecular mechanisms driving progression of liver cirrhosis towards hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B and C infections: a review. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6):1358.
Khaliefa AK, Desouky EM, Hozayen WG, Shaaban SM, Hasona NA. MiRNA-1246, HOTAIR, and IL-39 signature as potential diagnostic biomarkers in breast cancer. Non-coding RNA Res. 2023;8(2):205–10.
Khalil EH, Shaker OG, Hasona NA. Impact of rs2107425 polymorphism and expression of lncH19 and miR-200a on the susceptibility of colorectal cancer. Ind J Clin Biochem. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-022-01052-w.
Abdel Hameed NA, Shaker OG, Hasona NA. Significance of LINC00641 and miR-378 as a potential biomarker for colorectal cancer. Comp Clin Pathol. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-022-03384-8.
Hasona NA, Moneim AA, Mohammed EA, et al. Osteocalcin, miR-143, and miR-145 expression in long-standing type 1 diabetes mellitus and their correlation with HbA1c. Ind J Clin Biochem. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-023-01131-6.
Desouky E, Khaliefa A, Hozayen W, Shaaban S, Hasona N. Signature of miR-21 and MEG-2 and their correlation with TGF-β signaling in breast cancer. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2023;42:1–7.
Li H, Liu T, Yang Y, Cho WC, Flynn RJ, Harandi MF, et al. Interplays of liver fibrosis-associated microRNAs: molecular mechanisms and implications in diagnosis and therapy. Genes Dis. 2023;10(4):1457–69.
Iravani SM, Ramzi M, Hesami Z, Kheradmand N, Owjfard M, Abdolyousefi NE, et al. MiR-181a and -b expression in acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its correlation with acute graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, COVID-19 and torque teno viruses. Virus Dis. 2021;32(4):727–36.
Huang Z, Xu H. MicroRNA-181a-5p regulates inflammatory response of macrophages in sepsis. Open Med. 2019;14(1):899–908.
Zhuang X, Chen Y, Wu Z, Xu Q, Chen M, Shao M, et al. Mitochondrial miR-181a-5p promotes glucose metabolism reprogramming in liver cancer by regulating the electron transport chain. Carcinogenesis. 2020;41:972–83.
Zhu J, Yao K, Wang Q, Guo J, Shi H, Ma L, Liu H, et al. Circulating miR-181a as a potential novel biomarker for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;40(6):1591–602.
Mattick JS, Amaral PP, Carninci P, Carpenter S, Chang HY, et al. Long non-coding RNAs: definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24:430–47.
Arun G, Aggarwal D, Spector DL. MALAT1 long non-coding RNA: functional implications. Noncoding RNA. 2020;6(2):22.
Li ZX, Zhu QN, Zhang HB, Hu Y, Wang G, Zhu YS. MALAT1: a potential biomarker in cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2018;10:6757–68.
Singh V, Ubaid S. Role of silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) in regulating oxidative stress and inflammation. Inflammation. 2020;43(5):1589–98.
Ge Y, Huang M, Yao Y. Biology of interleukin-17 and its pathophysiological significance in sepsis. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 548387.
Zhang S, Gang X, Yang S, Cui M, Sun L, Li Z, Wang G. The alterations in and the role of the Th17/Treg balance in metabolic diseases. Front Immunol. 2021;2021(12): 678355.
Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964;1:1–85.
Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–9.
Huang J, Choi K, Im S, Yarimaga O, Yoon E, Kim S. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST/GOT) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT/GPT) detection techniques. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland). 2006;6(7):756–82.
Westwood A. The analysis of bilirubin in serum. Ann Clin Biochem. 1991. https://doi.org/10.1177/000456329102800202.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–8.
Harlow E, Lane D. Using antibodies: a laboratory manual. New York, NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1999.
Liu YB, Chen MK. Epidemiology of liver cirrhosis and associated complications: current knowledge and future directions. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28(41):5910–30.
Fouad Y, Esmat G, Elwakil R, Zakaria S, Yosry A, Waked I, El-Razky M, Doss W, El-Serafy M, Mostafa E, Anees M, Sakr MA, AbdelAty N, Omar A, Zaki S, Al-Zahaby A, Mahfouz H, Abdalla M, Albendary M, Hamed AK, Gomaa A, Hasan A, Abdel-Baky S, El Sahhar M, Shiha G, Attia D, Saeed E, Kamal E, Bazeed S, Mehrez M, Abdelaleem S, Gaber Y, Abdallah M, Salama A, Tawab DA, Nafady S. The egyptian clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2022;28(1):3–20.
Procopet B, Berzigotti A. Diagnosis of cirrhosis and portal hypertension: imaging, non-invasive markers of fibrosis and liver biopsy. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2017;5(2):79–89.
Ahmed Z, Ahmed U, Walayat S, Ren J, Martin DK, Moole H, Koppe S, Yong S, Dhillon S. Liver function tests in identifying patients with liver disease. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2018;11:301–7.
Monin L, Gaffen SL. Interleukin 17 family cytokines: signaling mechanisms, biological activities, and therapeutic implications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(4): a028522.
Sun Q, Wang Q, Feng N, Meng Y, Li B, Luo D, Shang X, Lv J, Monsaf AM, Wang C, Ma X. The expression and clinical significance of serum IL-17 in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(16):389.
Yang Y, Dai J, Yan M, et al. Expression of interleukin-17 is associated with different immune phases in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Eur J Inflam. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1177/2058739218796886.
Yang Y, Liu Y, Wang Y, Chao Y, Zhang J, Jia Y, Tie J, Hu D. Regulation of SIRT1 and Its roles in inflammation. Front Immunol. 2022;13: 831168.
Wu T, Liu Y, Fu Y, Liu X, Zhou X. Direct evidence of sirtuin downregulation in the liver of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2014;44:410–8.
Zhang T, Ma C, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Hu H. NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. MedComm. 2020;2(4):618-53. https://doi.org/10.1002/mco2.104.
Abdel-Samed SA, Hozyen WG, Shaaban SM, et al. Biochemical significance of miR-155 and miR-375 as diagnostic biomarkers and their correlation with the NF-κβ/TNF-α axis in breast cancer. Ind J Clin Biochem. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-022-01101-4.
Luedde T, Schwabe RF. NF-κB in the liver–linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8(2):108–18.
Zhao Y, Liu X, Ding C, Gu Y, Liu W. Dihydromyricetin reverses thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis through inhibiting NF-κB-mediated inflammation and TGF-β1-regulated of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 783886.
Ganguly N, Chakrabarti S. Role of long non-coding RNAs and related epigenetic mechanisms in liver fibrosis (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(3):04856.
Lima RVC, Stefano JT, Malta FM, Pinho JRR, Carrilho FJ, Arrese M, Oliveira CP. Ability of a combined FIB4/miRNA181a score to predict significant liver fibrosis in NAFLD patients. Biomedicines. 2021;9(12):1751.
Gupta P, Sata TN, Yadav AK, Mishra A, Vats N, Hossain MM, et al. TGF-β induces liver fibrosis via miRNA-181a-mediated down regulation of augmenter of liver regeneration in hepatic stellate cells. PLoS One. 2019;14(6): e0214534.
Wang Z, Yang X, Gui S, Yang F, Cao Z, Cheng R, Xia X, Li C. The roles and mechanisms of lncRNAs in liver fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12: 779606.
Brahmbhatt HD, Gupta R, Gupta A, Rastogi S, Misri R, Mobeen A, Ghosh A, Kothari P, Sitaniya S, Scaria V, Singh A. The long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses miR-211 to confer protection from ultraviolet-mediated DNA damage in vitiligo epidermis by upregulating sirtuin 1. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184(6):1132–42.
Funding
The authors declare that no funding for the research received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
Our study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the Research Ethical Committee, Faculty of Medicine, University of Beni-Suef, Egypt provided its approval (FMBSUREC/07062022).
Informed Consent
All study participants provided their informed consent permission for participation in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khalaf, S.E., Abdelfattah, S.N. & Hasona, N.A. Crosstalk Between Long Non-coding RNA MALAT1, miRNA-181a, and IL-17 in Cirrhotic Patients and Their Possible Correlation SIRT1/NF-Ƙβ Axis. Ind J Clin Biochem (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-024-01203-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-024-01203-1