Abstract
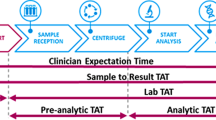
This is the result of a Survey of diagnostics laboratories in the Asia Pacific (APAC) region with perspectives on India, investigating the three key aspects that are central to the success of a laboratory: quality, cost and speed. This Survey provides a comparison in selected performance indicators in a large number of diagnostic laboratories in a broad range of countries in the APAC region. The Survey provides data on some key performance characteristics such as quality improvement activities, staff productivity and Turnaround Time (TAT). This Survey also demonstrates in India the common issues facing all the laboratories surveyed but also common solutions using a Quality Systems approach which involves Accreditation, customer responsiveness, greater use of IT, automation and Lean principles. Indian laboratories reported less automation and fewer laboratories have Laboratory Information Systems. The productivity by various measures in Indian laboratories was less than in other APAC laboratories. TAT was more commonly monitored in the Indian specimens though there were fewer laboratories compared with the APAC specimens where there were separate TATs for Short Turnaround Time and Routine specimens.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schiff GD, Hasan O, Kim S, Abrams R, Cosby K, Lambert BL, et al. Diagnostic error in medicine: analysis of 583 physician-reported errors. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169:1881–7.
The Institute of Medicine. Improving diagnosis in healthcare. Washington: National Academies of Sciences, Engineering and Medicine; 2015.
Sciacovelli L, Aita A, Plebani M. Extra-analytical quality indicators and laboratory performances. Clin Biochem. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.03.020.
Sciacovelli L, Lippi G, Sumarac Z, West J, Garcia Del Pino CI, Furtado VK, et al. Quality indicators in laboratory medicine: the status of the progress of IFCC working group “Laboratory Errors and Patient Safety” project. CCLM. 2016;5(3):348–57.
Leatherman S, Ferris TG, Berwick D, Omaswa F, Crisp N. The role of quality improvement in strengthening health systems in developing countries. Int J Qual Health Care. 2010;22(4):237–43.
Shin BM, Chae SL, Min WK, Lee WG, Lim YA, Lee DH. The implementation and effects of a clinical laboratory accreditation program in Korea from 1999 to 2006. Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29(2):163–70.
Wattanasri N, Manoroma W, Viriyayudhagorn S. Laboratory accreditation in Thailand: a systemic approach. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134(4):534–40.
Peter TF, Rotz PD, Blair DH, Khine A, Freeman RF, Murtagh RM. Impact of laboratory accreditation on patient care and the health system. Am J Clin Pathol. 2010;134(4):550–5.
Tholen DW. Improvements in performance in medical diagnostics tests documented by inter-laboratory comparison programs. Accred Qual Assur. 2002;7(4):146–52.
Chaudary R, Das SS, Ojha S, Khetan D, Sonker A. The external quality assessment scheme: five years’ experience as a participating laboratory. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2010;4(1):28–30.
Badrick TC, Gutscher A, Sakamoto N, Chin D. Diagnostic laboratories in Asia Pacific region: investigation on quality characteristics and time of reporting. Clin Biochem. 2017. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.03.017.
Plebani M, Carraro P. Mistakes in a stat laboratory: types and frequency. Clin Chem. 1997;43:1348–51.
Kristensen GBB, Aakre KM, Sandberg S. How to conduct external quality assessment schemes for the pre-analytical phase? Biochemia Medica. 2014;24(1):114–22.
Khoury M, Burnett L, Mackay M. Error rate in Australian chemical pathology laboratories. Med J Aust. 1996;165:128–30.
Mainz J. Defining and classifying clinical indicators for quality improvement. Int J Qual Health Care. 2003;15:523–30.
Plebani M, Sciacovelli L, Lippi G. Quality indicators for laboratory diagnostics: consensus is needed. Ann Clin Biochem. 2011;48:479.
Sciacovelli L, O’Kane M, Skaik YA, Caciagli P, Pellegrini C, Da Rin G, et al. IFCC WG-LEPS. Quality indicators in laboratory medicine: from theory to practice. Preliminary data from the IFCC Working Group Project “Laboratory errors and patient safety”. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2011;49:835–44.
Nakhleh RE, Souers RJ, Bashleben CP, Talbert ML, Karcher DS, Meier F, et al. Fifteen years’ experience of a college of american pathologists program for continuous monitoring and improvement. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2014;138(9):1150–5.
Adyanthaya S, Jose M. Quality and safety aspects in histopathology laboratory. J Oral Maxill Path. 2013;17(3):402–7.
Agarwal R, Chaturvedi S, Chhillar N, Goyal R, Pant I, Tripathi CB. Role of intervention on laboratory performance: evaluation of quality indicators in a tertiary care hospital. Ind J Clin Biochem. 2012;27(1):61–8.
Dolnicar S, Laesser C, Matus K. Online versus paper: format effects in tourism surveys. J Travel Res. 2009;47(3):295–316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
TCB declares that they have no conflict of interest. AG declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. AG declares that he/she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badrick, T.C., Gutscher, A. & Chin, D. Diagnostic Laboratories in India: Investigating Quality Characteristics, Productivity and Time of Reporting. Ind J Clin Biochem 33, 304–313 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0679-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-017-0679-9