Abstract
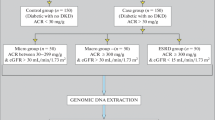
Genetic polymorphism as described with angiotensin-converting enzyme gene has been proposed as a putative mediator of diabetic nephropathy. We substantiate the hypothesis that genetic variants of the ACE have significant impacts on diabetic nephropathy. To assess the possible association between the three ACE polymorphic variants and DN in an ethnically homogeneous type 2 diabetic population from Kutch region. A 287-bp insertion/deletion polymorphism in intron 16 of the ACE gene was examined by polymerase chain reaction using a case–control approach conducted with 309 unrelated type 2 diabetic patients of Kutch origin (159 Ahir and 150 Rabari, with >10 years duration of T2DM). Of the patients, 143 had nephropathy {AER >30 mg/day (Ahir, n:73 and Rabari, n:70)} and were considered as cases; all others {n:166 (86 Ahir and 80 Rabari)} were normoalbuminuric (AER <30 mg/day) and were treated as controls. Suitable descriptive statistics was used for different variables. Genotype frequencies in all groups were all in accordance with the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. Genotypic distribution was significantly different between cases and controls (Ahir: x2 :8.87, 2 d.f. p = 0.0118; Rabari: x2 :11.01, 2 d.f. p = 0.0041). Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that DD genotype was a significant and strongest independent predictor of microalbuminuria (Ahir: p = 0.0362, OR = 2.65, 95 % CI 1.89–6.36; Rabari: p = 0.024, OR = 2.81, 95 % CI 1.9–6.65). However, it did not independently change the odds of having macroalbuminuria versus microalbuminuria. Analysis of the association under various genetic models revealed that ACE I/D polymorphic variant contribute to DN susceptibility under recessive mode only. Genetic variation at the ACE locus as D/D variant in intron 16, contribute to an increased risk of nephropathy in T2DM patients but not extent of DN severity, and thus this polymorphism might be considered as genetic risk factors for DN among patients with type 2 diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Molitch ME, DeFronzo RA, Franz MJ, Keane WF, Mogensen CE, Parving HH, et al. American Diabetes Association. Nephropathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(Suppl 1):79–83.
Williams ME. Diabetic CKD/ESRD 2010: a progress report. Semin Dial. 2010;23:129–33.
Agius E, Attard G, Shakespeare L, Clark P, Vidya MA, Hattersley AT, et al. Familial factors in diabetic nephropathy: an offspring study. Diabet Med. 2006;23:331–4.
Gohda T, Tanimoto M, Watanabe-Yamada K, Matsumoto M, Kaneko S, Hagiwara S, et al. Genetic susceptibility to type 2 diabetic nephropathy in human and animal models. Nephrology (Carlton). 2005;10(Suppl 2):22–5.
Vijay V, Snehalatha C, Sinha K, Lalitha S, Ramachandran A. Familial aggregation of diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes in south India. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 1999;43:167–71.
Kanakamani J, Ammini AC, Gupta N, Dwivedi SN. Prevalence of microalbuminuria among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus—a hospital based study from north India. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2010;12:161–6.
Debnath S, Thameem F, Alves T, Nolen J, Al-Shahrouri H, Bansal S, et al. Diabetic nephropathy among Mexican Americans. Clin Nephrol. 2012;77:332–44.
ESRD Incidence Study Group, Stewart JH, McCredie MR, Williams SM. Geographic, ethnic, age-related and temporal variation in the incidence of end-stage renal disease in Europe, Canada and the Asia-Pacific region, 1998–2002. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2006;21:2178–83.
Young BA, Maynard C, Boyko EJ. Racial differences in diabetic nephropathy, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in a national population of veterans. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2392–9.
Hostetter TH, Troy JL, Brenner BM. Glomerular hemodynamics in experimental diabetes mellitus. Kidney Int. 1981;19:410–5.
Ezzidi I, Mtiraoui N, Kacem M, Chaieb M, Mahjoub T, Almawi WY. Identification of specific angiotensin-converting enzyme variants and haplotypes that confer risk and protection against type 2 diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009;25:717–24.
Osawa N, Koya D, Araki S, Uzu T, Tsunoda T, Kashiwagi A, et al. Combinational effect of genes for the renin–angiotensin system in conferring susceptibility to diabetic nephropathy. J Hum Genet. 2007;52:143–51.
Prasad P, Tiwari AK, Kumar KM, Ammini AC, Gupta A, Gupta R, et al. Chronic renal insufficiency among Asian Indians with type 2 diabetes: I. role of RAAS gene polymorphisms. BMC Med Genet. 2006;7:42–50.
Ballerman BJ, Zeidel ML, Gunning ME, Brenner BM. Vasoactive peptides and the kidney. In: Brenner BM, Rector FC, editors. The kidney. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 1991. p. 510–83.
Ruíz-Ortega M, Gómez-Garre D, Alcázar R, Palacios I, Bustos C, González S, et al. Involvement of angiotensin II and endothelin in matrix protein production and renal sclerosis. J Hypertens. 1994;12:S51–8.
Burns KD. Angiotensin II and its receptors in the diabetic kidney. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;36:449–67.
Kim S, Iwao H. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated cardiovascular and renal diseases. Pharmacol Rev. 2000;52:11–34.
Thomas GN, Tomlinson B. Prevention of macrovascular disease in type 2 diabetic patients: blockade of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2008;4:63–78.
Berl T. Renal protection by inhibition of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2009;10:1–8.
Mehdi UF, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P, Vega GL, Toto RD. Addition of angiotensin receptor blockade or mineralocorticoid antagonism to maximal angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:2641–50.
Hubert C, Houot AM, Corvol P, Soubrier F. Structure of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene. Two alternate promoters correspond to evolutionary steps of a duplicated gene. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:15377–83.
Mattei MG, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Roeckel N, Corvol P, Soubrier F. Angiotensin converting enzyme gene is on chromosome 17. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1989;51:1041.
Rigat B, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrier F. An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J Clin Invest. 1990;86:1343–6.
Tiret L, Rigat B, Visvikis S, Breda C, Corvol P, Cambien F, et al. Evidence, from combined segregation and linkage analysis, that a variant of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene controls plasma ACE levels. Am J Hum Genet. 1992;51:197–205.
Crisan D, Carr J. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme: geno-type and disease associations. J Mol Diagn. 2000;2:105–15.
Ahluwalia TS, Ahuja M, Rai TS, Kohli HS, Bhansali A, Sud K, et al. ACE variants interact with the RAS pathway to confer risk and protection against type 2 diabetic nephropathy. DNA Cell Biol. 2009;28:141–50.
Tien KJ, Hsiao JY, Hsu SC, Liang HT, Lin SR, Chen HC, et al. Gender-dependent effect of ACE I/D and AGT M235T polymorphisms on the progres-sion of urinary albumin excretion in Taiwanese with type 2 diabetes. Am J Nephrol. 2009;29:299–308.
Wang F, Fang Q, Yu N, Zhao D, Zhang Y, Wang J, et al. Association between genetic polymorphism of the angiotensin-converting enzyme and diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis comprising 26,580 subjects. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012;13:161–74.
Okuno S, Utsugi T, Ohno T, Ohyama Y, Uchiyama T, Tomono S, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism as a potent risk factor for developing microalbuminuria in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 9-year follow-up study. J Int Med Res. 2003;31:290–8.
Ortega-Pierres LE, Gómez García A, Rodríguez-Ayala E, Figueroa-Núñez B, Figueroa-Núñez VM, Higareda-Mendoza AE, et al. Angiotensin 1 converting enzyme insertion/deletion gene polymorphism in a Mexican population with diabetic nephropathy. Med Clin (Barc). 2007;129:6–10.
Movva S, Alluri RV, Komandur S, Vattam K, Eppa K, Mukkavali KK, et al. Relationship of angiotensin-converting enzyme gene polymorphism with nephropathy associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian Indians. J Diabetes Complicat. 2007;21:237–41.
Jayapalan JJ, Muniandy S, Chan SP. Null association between ACE gene I/D polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy among multiethnic Malaysian subjects. Indian J Hum Genet. 2010;16:78–86.
Eroglu Z, Cetinkalp S, Erdogan M, Kosova B, Karadeniz M, Kutukculer A, et al. Association of the angiotensinogen M235T and angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion gene polymorphisms in Turkish type 2 diabetic patients with and without nephropathy. J Diabetes Complicat. 2008;22:186–90.
Arzu Ergen H, Hatemi H, Agachan B, Camlica H, Isbir T. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme gene polymorphism in Turkish type 2 diabetic patients. Exp Mol Med. 2004;36:345–50.
Declaration of Helsinki. Recommendations Guiding Physicians in Biomedical Research Involving Human Subjects. 52nd World Medical Assembly, Edinburgh, October, 2000.
Mauer M, Fioretto P, Woredekal Y, Friedman EA, Gottschalk RW. Diabetic nephropathy. In: Schrier CW, editor. Diseases of the kidney. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. p. 2083–128.
Laakso M, Pyorala K. Age of onset and type of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1985;8:114–7.
World health Organization Expert Consultation. Appropriate body mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet. 2004;363:157–63.
Rose GA, Blackburn H. Cardiovascular survey methods. WHO Monogr Series. 1968;56:90–5.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, et al. The Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA. 2003;289:2560–72.
Medcalf E, Newman DJ, Gorman EG, Price CP. Rapid, robust method for measuring low concentrations of albumin in urine. Clin Chem. 1990;36:446–9.
Myers GL, Miller WG, Coresh J, Fleming J, Greenberg N, Greene T, et al. National Kidney Disease Education Program Laboratory Working Group. Recommendations for improving serum creatinine measurement: a report from the Laboratory Working Group of the National Kidney Disease Education Program. Clin Chem. 2006;52:5–18.
Trinder P. Determination of blood glucose using an oxidase–peroxidase system with a non-carcinogenic chromogen. J Clin Pathol. 1969;22:158–61.
Allain CC, Poon LS, Chan CSG, Richmond W, Fu PC. Enzymatic determination of total serum cholesterol. Clin Chem. 1974;20:470–5.
Fossati P, Prencipe L. Serum triglycerides determined colorimetrically with an enzyme that produces hydrogen peroxide. Clin Chem. 1982;28:2077–80.
Burstein M, Morfin R. Precipitation of alpha lipoproteins in serum by sodium phosphotungstate in the presence of magnesium chloride. Life Sci. 1969;8:345–8.
Assmann G, Jabs HU, Kohnert U, Nolte W, Schriewer H. LDL-cholesterol determination in blood serum following precipitation of LDL with polyvinyl sulfate. Clin Chim Acta. 1984;140:77–83.
Metus P, Ruzzante N, Bonvicini P, Meneghetti M, Zaninotto M, Plebani M. Immunoturbidimetric assay of glycated hemoglobin. J Clin Lab Anal. 1999;13:5–8.
Chasson AL, Grady HJ, Stanley MA. Determination of creatinine by means of automatic chemical analysis. Tech Bull Regist Med Technol. 1960;30:207–12.
Jeanpierre M. A rapid method for the purification of DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15(22):9611.
Tataurov AV, You Y, Owczarzy R. Predicting ultraviolet spectrum of single stranded and double stranded deoxyribonucleic acids. Biophys Chem. 2008;133:66–70.
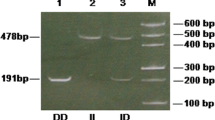
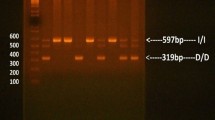
Rigat B, Hubert C, Corvol P, Soubrier F. PCR detection of the insertion/deletion polymorphism of the human angiotensin converting enzyme gene (DCP1) (dipeptidyl carboxypeptidase 1). Nucleic Acids Res. 1992;20:1433–6.
Lindpaintner K, Pfeffer MA, Kreutz R, Stampfer MJ, Grodstein F, LaMotte F, et al. A prospective evaluation of an angiotensin converting enzyme gene polymorphism and the risk of ischemic heart disease. New Engl J Med. 1995;332:706–11.
Rodriguez S, Gaunt TR, Day IN. Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium testing of biological ascertainment for Mendelian randomization studies. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;169(4):505–14.
Arfa I, Abid A, Nouira S, Elloumi-Zghal H, Malouche D, Mannai I, et al. Lack of association between the angiotensin-converting enzyme gene (I/D) polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy in Tunisian type 2 diabetic patients. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2008;9:32–6.
Hadjadj S, Gallois Y, Alhenc-Gelas F, Chatellier G, Marre M, Genes N, et al. Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and high urinary albumin concentration in French type 2 diabetes patients. Diabet Med. 2003;20:677–82.
Al-Salman RA, Al-Basri HA, Al-Sayyad AS, Hearnshaw HM. Prevalence and risk factors of albuminuria in type 2 diabetes in Bahrain. J Endocrinol Invest. 2009;32:746–51.
Cardoso CR, Salles GF. Predictors of development and progression of microvascular complications in a cohort of Brazilian type 2 diabetic patients. J Diabetes Complicat. 2008;22:164–70.
Mtiraoui N, Ezzidi I, Turki A, Chaieb M, Mahjoub T, Almawi WY. Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system genotypes and haplotypes affect the susceptibility to nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2011;12:572–80.
Stolar M. Glycemic control and complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 2010;123(Suppl 3):3–11.
Tu ST, Chang SJ, Chen JF, Tien KJ, Hsiao JY, Chen HC, et al. Prevention of diabetic nephropathy by tight target control in an Asian population with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 4-year prospective analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2010;170:155–61.
Ng DP, Tai BC, Koh D, Tan KW, Chia KS. Angiotensin-I converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism and its association with diabetic nephropathy: a meta analysis of studies reported between 1994 and 2004 and comprising 14,727 subjects. Diabetologia. 2005;48:1008–16.
Naresh VV, Reddy AL, Sivaramakrishna G, Sharma PV, Vardhan RV, Kumar VS. Angiotensin converting enzyme gene polymorphism in type II diabetics with nephropathy. Indian J Nephrol. 2009;19:145–8.
Hadjadj S, Belloum R, Bouhanick B, Gallois Y, Guilloteau G, Chatellier G, et al. Prognostic value of angiotensin I converting enzyme I/D polymorphism for nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus: a prospective study. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12:541–9.
El-Baz R, Settin A, Ismaeel A, Khaleel AA, Abbas T, Tolba W, et al. MTHFR C677T, A1298C and ACE I/D polymorphisms as risk factors for diabetic nephropathy among type 2 diabetic patients. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst. 2012;13:472–7.
Wong TY, Chan JC, Poon E, Li PK. Lack of association of angiotensin-converting enzyme (DD/II) and angiotensinogen M235Tgene polymorphism with renal function among Chinese patients with type II diabetes. Am J Kidney Dis. 1999;33:1064–70.
Felehgari V, Rahimi Z, Mozafari H, Vaisi-Raygani A. ACE gene polymorphism and serum ACE activity in Iranians type II diabetic patients with macroalbuminuria. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;346:23–30.
Rebai M, Kharrat N, Ayadi I, Rebai A. Haplotype structure of five SNPs within the ACE gene in the Tunisian population. Ann Hum Biol. 2006;33:319–29.
Solini A, Vestra M, Saller A, Nosadini R, Crepaldi G, Fioretto P. The angiotensin-converting enzyme DD genotype is associated with glomerulopathy lesions in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:251–5.
Hsieh MC, Lin SR, Hsieh TJ, Hsu CH, Chen HC, Shin SJ, et al. Increased frequency of angiotensin-converting enzyme DD genotype in patients with type 2 diabetes in Taiwan. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2000;15:1008–13.
Feng Y, Niu T, Xu X, Chen C, Li Q, Qian R, et al. Insertion/deletion polymorphism of the ACE gene is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:1986–8.
Lee EJ. Population genetics of the angiotensin-converting enzyme in Chinese. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1994;37:212–4.
Foy CA, McCormack LJ, Knowler WC, Barrett JH, Catto A, Grant PJ. The angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) gene I/D polymorphism and ACE levels in Pima Indians. J Med Genet. 1996;33:336–7.
Culverhouse R, Suarez BK, Lin J, Reich T. A perspective on epistasis: limits of models displaying no main effect. Am J Hum Genet. 2002;70:461–71.
Hattersley AT, McCarthy MI. What makes a good genetic association study? Lancet. 2005;366:1315–23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parchwani, D.N., Palandurkar, K.M., Hema Chandan Kumar, D. et al. Genetic Predisposition to Diabetic Nephropathy: Evidence for a Role of ACE (I/D) Gene Polymorphism in Type 2 Diabetic Population from Kutch Region. Ind J Clin Biochem 30, 43–54 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0402-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0402-4