Abstract
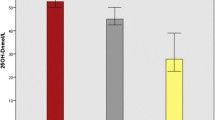
Our study was aimed to assess the levels of serum calcium and phosphorus in pulmonary tuberculosis patients. Blood samples were collected from 40 patients with pulmonary tuberculosis before treatment (PTB-0), at the end of 2 months of intensive phase of treatment (PTB-2) and after 6 months of treatment (PTB-6). Age and weight matched normal healthy volunteers (n = 37) served as normal controls. Serum was analyzed for calcium and phosphorus. Serum calcium significantly decreased to hypocalcemic levels and serum phosphorus significantly decreased but was within normophosphatemic limits in pulmonary tuberculosis. Chemotherapy for tuberculosis managed to raise serum levels of both the ions, with hypocalcemia still persisting in majority of patients during treatment but getting resolved in a significant percentage of patients at the end of 6 months of treatment. Results indicate the need for calcium and phosphorus supplements in tuberculosis patients during chemotherapy. This study also warrants the need for regular monitoring of serum calcium and phosphorus in patients undergoing anti-tuberculosis treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lind L, Ljunghall S. Hypercalcemia in pulmonary tuberculosis. Ups J Med Sci. 1990;95(2):157–60.
Pruitt B, Onarecker C, Coniglione T. Hypercalcemic crisis in a patient with pulmonary tuberculosis. J Okla State Med Assoc. 1995;88(12):518–20.
Hournay J, Mehta JB, Hournay V, Byrd RP Jr, Roy TM. Hypercalcaemia and pulmonary tuberculosis in east Tennessee. Tenn Med. 1997;90(12):493–5.
Roussos A, Lagogianni I, Gonis A, Ilias I, Kazi D, Patsopoulos D, Philippou N. Hypercalcaemia in Greek patients with tuberculosis before the initiation of anti-tuberculosis treatment. Respir Med. 2001;95(3):187–90.
Liam CK, Lim KH, Srinivas P, Poi PJ. Hypercalcaemia in patients with newly diagnosed tuberculosis in Malaysia. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 1998;2(10):818–23.
Meuthen I, Kirsch L, Saborowski F. Hypercalcemia in florid pulmonary and cervical lymph node tuberculosis. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1991;116(23):899–902.
Chan TY, Poon P, Pang J, Swaminathan R, Chan CH, Nisar M, Williams CS, Davies PD. A study of calcium and vitamin D metabolism in Chinese patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;97(1):26–30.
Shirai M, Sato A, Suda T, Shichi I, Yasuda K, Iwata M, Okano A, Genma H. Chida Calcium metabolism in tuberculosis. Kekkaku. 1990;65(6):415–20.
Hafiez AA, Abdel-Hafez MA, Salem D, Abdou MA, Helaly AA, Aarag AH. Calcium homeostasis in untreated pulmonary tuberculosis. I-Basic study. Kekkaku. 1990;65(5):309–16.
Ali-Gombe A, Onadeko BO. Serum calcium levels in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis. Afr J Med Med Sci. 1997;26(1–2):67–8.
Ijaz A, Mehmood T, Saeed W, Qureshi AH, Dilawar M, Anwar M, Hussain S, Khan FA, Khan IA, Khan DA. Calcium abnormalities in pulmonary tuberculosis. Pak J Med Res. 2004;43:4.
Wells HG, Dewitt LM, Long ER. The chemistry of tuberculosis. London: Bailliere Tindall and Cox; 1923.
Sweany HC, Weathers AT, MccCluskey KL. The chemistry of blood in tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1923;8:405.
Sharma SC. Serum calcium in pulmonary tuberculosis. Postgrad Med J. 1981;57:694.
Godwin AO, Johnson DJ, Otimenbhor JO. Total serum calcium and inorganic phosphate levels in tuberculosis patients in benin city Nigeria sierra leone. J Biomed Res. 2010;2(2):87–90.
Endres DB, Rude RK. Mineral and bone metabolism. In: Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, editors. Tietz Fundamentals of Clinical chemistry. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2001. p. 795.
Baig MA, Ghulam Mustafa KK, Lutufullah B, Qureshi MA. Low serum calcium associated with tuberculosis. Prof Med J. 2006;13(4):583–6.
Rohini K, Srikumar PS, Jyoti S, Mahesh Kumar A, Bhat S. Assessment of serum calcium, phosphorus, c-reactive protein and procalcitonin in tuberculosis patients. Int J Collab Res Intern Med Pub Health. 2012;4(12):1868–75.
Rohini K, Diagnostic and prognostic value of procalcitonin in tuberculosis patients, Ph.D thesis, Banasthali University (‘A’ Accredited Institution), Rajasthan; 2013
Maruna P, Nedelnikova K, Gurlich R. Physiology and genetics of procalcitonin. Physiol Res. 2000;49(Suppl 1):S57–61.
Abbasi AA, Chemplavil JK, Farah S, Muller BF, Arnstein AR. Hypercalcemia in active pulmonary tuberculosis. Ann Intern Med. 1979;90(3):324–8.
Kitrou MP, Phytou-Pallikari A, Tzannes SE, Virvidakis K, Mountokalakis TD. Hypercalcemia in active pulmonary tuberculosis. Ann Intern Med. 1982;96(2):255.
Kitrou MP, Phytou-Pallikari A, Tzannes SE, Virvidakis K, Mountokalakis TD. Serum calcium during chemotherapy for active pulmonary tuberculosis. Eur J Resp Dis. 1983;64(5):347–54.
Goldberg B. Calcium therapy in tuberculosis. (1935). In: Diseases of the chest: http://173.193.11.217/. Accessed Dec 13 2012.
Rohini K, Bhat S, Srikumar PS, Jyoti S, Mahesh Kumar A. Diagnostic and prognostic value of procalcitonin in tuberculosis patients. Br J Med Med Res. 2013;3(4):2189–96.
Khan A, Timothy Sterling R, Reves R, Vernon A, Robert Horsburgh C, Tuberculosis Trials Consortium. Lack of weight gain and relapse risk in a large tuberculosis treatment trial. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2006;174:344–8.
Kardjito T, Ediyanto SP, Grange JM. Serum phosphorus levels in pulmonary tuberculosis. Postgrad Med J. 1984;60:394–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rohini, K., Bhat, S., Srikumar, P.S. et al. Assessment of Serum Calcium and Phosphorus in Pulmonary Tuberculosis Patients Before, During and After Chemotherapy. Ind J Clin Biochem 29, 377–381 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0383-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0383-3