Abstract
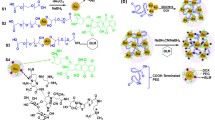
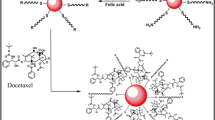
New hopes in cancer treatment have been emerged using functional nanoparticles. In this work, we tried to synthesize gold nanoparticles and gold nanoparticles conjugated with DNA extracted from human breast cancer cells. After synthesizing, gold nanoparticles were mixed with nanoliposomal hydroxyurea and corresponding compounds were formed. They were described by UV–Visible spectrophotometry and Zeta sizer. Amount of drug loading into liposomes was determined by spectrophotometry and cytotoxicity effect on MCF-7 cells was measure by MTT assay. Drug loading was determined to be 70 %. Size, size distribution and Zeta potential of particles were 473 nm, 0.46 and −21 mV for control nanoliposomal ones and 351 nm, 0.38 and −25 mV for nanoliposomal particles containing hydroxyurea. This was 29 nm, 0.23 and −30 mV for gold nanoparticles and 502 nm, 0.41 and −38 mV for nanoliposomes containing drug loaded by gold nanoparticles conjugated with DNA. It was found that nano conjugated complex in concentrations less than 20 μM of hydroxyurea can improve efficiency compared with liposomal drug. In maximum concentration of drug (2,500 μM), cytotoxicity was equal to 95 %. In minimum concentration of drug (5 μM), cytotoxicity of liposomal drug and conjugated complex were 70 and 81 %, respectively which probably comes from increased drug entry into cells due to the presence of gold nanoparticles. Free drug resulted in toxicity of 32 % in 5 μM and 88 % in 2,500 μM. Results demonstrated higher drug efficiency in nanoparticle form compared with free form which can be used in in vivo studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chithrani DB, Dunne M, Stewart J, Allen C, Jaffray DA. Cellular uptake and transport of gold nanoparticles incorporated in a liposomal carrier. Nanomedicine. 2010;6:161–9.
Mozafari MR. Nanocarrier technologies. Front Nanother. 2006;237:1–12.
Costantino L, Boraschi D. Is there a clinical future for polymeric nanoparticles as brain-targeting drug delivery agents? Drug Discov Today. 2012;17:367–78.
Vinogradov SV, Bronich TK, Kabanov AV. Nanosized cationic hydrogels for drug delivery: preparation, properties and interactions with cells. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2002;54:135–47.
Immordino ML, Dosio F, Cattel L. Stealth liposomes: review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int J Nanomed. 2006;1:297–315.
Al-Jamal WT, Kostarelos K. Liposome-nanoparticle hybrids for multimodal diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2007;2:85–98.
Burda C, Chen X, Narayanan R, El-Sayed MA. Chemistry and properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Rev. 2005;105:1025–102.
Daniel MC, Astruc D. Gold nanoparticles: assembly, supramolecular chemistry, quantum-size-related properties, and applications toward biology, catalysis, and nanotechnology. Chem Rev. 2004;104:293–346.
Mady MM, Fathy MM, Youssef T, Khalil WM. Biophysical characterization of gold nanoparticles-loaded liposomes. Phys Med. 2012;28:288–95.
Liebelt EL, Balk SJ, Faber W, Fisher JW, Hughes CL, Lanzkron SM, Lewis KM, Marchetti F, Mehendale HM, Rogers JM, Shad AT, Skalko RG, Stanek EJ. NTP-CERHR expert panel report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of hydroxyurea. Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 2007;80:259–366.
SE Alavi, MKM Esfahani, F Alavi, F Movahedi, A Akbarzadeh. Drug delivery of hydroxyurea to breast cancer using liposomes. Ind J Clin Biochem. 2012. doi:10.1007/s12291-012-0291-y.
Huang H, Yang X. Chitosan mediated assembly of gold nanoparticles multilayer. Coll Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects. 2003;226:77–86.
Shipway AN, Katz E, Willner I. Nanoparticle arrays on surfaces for electronic, optical, and sensor applications. Chem Phys Chem. 2000;1:18–52.
Strauss WM. Preparation of genomic DNA from mammalian tissue. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2001;Chapter 2:Unit2.2.
Jung T, Kamm W, Breitenbach A, Kaiserling E, Xiao JX, Kissel T. Biodegradable nanoparticles for oral delivery of peptides: is there a role for polymers to affect mucosal uptake? Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2000;50:147–60.
Nimesh S, Manchanda R, Kumar R, Saxena A, Chaudhary P, Yadav V, Mozumdar S, Chandra R. Preparation, characterization and in vitro drug release studies of novel polymeric nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 2006;323:146–52.
Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Kulkarni AR, Rudzinski WE. Biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles as drug delivery devices. J Control Release. 2001;70:1–20.
Paolino D, Fresta M, Sinha P, Ferrari M. Drug delivery systems. In: Webester JG, editor. Encyclopedia of medical devices and instrumentation. New Jersey: Wiley; 2006. p. 437–95.
Wang X, Yang L, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Application of nanotechnology in cancer therapy and imaging. CA Cancer J Clin. 2008;58:97–110.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shahabi, J., Shahmabadi, H.E., Alavi, S.E. et al. Effect of Gold Nanoparticles on Properties of Nanoliposomal Hydroxyurea: An In Vitro Study. Ind J Clin Biochem 29, 315–320 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0355-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-013-0355-7