Abstract
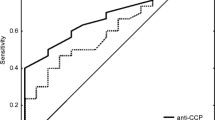
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is the most common inflammatory systemic autoimmune disease, primarily affecting the peripheral joints. Anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin autoantibodies (anti-MCV) of IgG isotype were shown to be a useful diagnostic marker of RA especially in RA patients who were anti-cyclic citrullinated protein autoantibodies (anti-CCP) negative. Nevertheless, published data correlates rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-CCP or anti-MCV antibodies with either erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or serum C-reactive protein (CRP) as markers of disease activity, not investigated the possible correlations of RA autoantibodies towards ESR and CRP in comparison. Herein, we aim to evaluate the usefulness of anti-MCV as a dependable marker in established RA compared with anti-CCP and RF antibodies and to examine correlations between RF, anti-CCP and anti-MCV antibodies towards ESR and serum CRP. Serum RF-IgA, RF-IgM, anti-CCP and anti-MCV levels were measured in 30 patients with RA and 40 patients with other autoimmune diseases (non-RA) compared with 20 normal subjects. Specificity, sensitivity and AUC for RF antibodies, anti-CCP and anti-MCV were calculated towards RA diagnosis. Our results showed that ESR and CRP had significantly higher values in both RA and non-RA patients compared with our healthy controls with observed significant increment in RA patients compared with non-RA patients. An important finding from our study is that 33.3 % of RA patients were anti-CCP negative but being positive towards anti-MCV. Also, in-between 36.7 up to 40 % of RA patients were RF-IgA and RF-IgM negative while being anti-MCV positive. Anti-MCV antibodies showed the highest specificity and sensitivity (97.5 and 86.6 %, respectively) towards RA diagnosis with the highest AUC value (0.920) compared with anti-CCP and RF antibodies. Correlation analyses revealed that there was no significant correlation between ESR along with CRP towards RF-IgA, RF-IgM and anti-CCP while profound highly significant correlation exhibited between ESR and CRP towards anti-MCV data (r = 0.879 and 0.994, respectively). Thus, our data suggest that the assessment of serum anti-MCV autoantibodies along with ESR and CRP considered as a simple laboratory regime for monitoring RA patients to assess and follow-up disease activity. The addition of anti-MCV autoantibodies to serologic markers in the ACR/EULAR classification criteria for RA will add points for patients with negative anti-CCP and RF antibodies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lutteri L, Malaise M, Chapelle JP. Comparison of second- and third-generation anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies assays for detecting rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;386:76–81.
Kuna AT. Mutated citrullinated vimentin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 2012;413:66–73.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an american college of rheumatology/european league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;62:1580–8.
Sizova L. Diagnostic value of antibodies to modified citrullinated vimentin in early rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 2012;73:389–92.
Wener MH. Laboratory tests for autoimmune rheumatologic disorders. Educational review manual in rheumatology. 4th ed. New York: Castle Connolly Graduate Medical Publishing Ltd; 2007. p. 1–42.
Castro C, Gourley M. Diagnostic testing and interpretation of tests for autoimmunity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125(2):S238–47.
Colglazier CL, Sutej PG. Laboratory testing in the rheumatic diseases: a practical review. South Med J. 2005;98:185–91.
Taylor P, Gartemann J, Hsieh J, Creeden J. A systematic review of serum biomarkers anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide and rheumatoid factor as tests for rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Dis. 2011; Article ID 815038.
Schellekens GA, de Jong BAW, van den Hoogen FHJ, van de Putte LBA, van Venrooij WJ. Citrulline is an essential constituent of antigenic determinants recognized by rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1998;101:273–81.
Szodoray P, Szabó Z, Kapitány A, Gyetvai A, Lakos G, Szántó S, Szücs G, Szekanecz Z. Anti-citrullinated protein/peptide autoantibodies in association with genetic and environmental factors as indicators of disease outcome in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;9:140–3.
van Boekel MA, Vossenaar ER, van den Hoogen FH, van Venrooij WJ. Autoantibody systems in rheumatoid arthritis: specificity, sensitivity and diagnostic value. Arthritis Res. 2002;4:87–93.
Bang H, Egerer K, Gauliard A, Luthke K, Rudolph PE, Fredenhagen G, et al. Mutation and citrullination modifies vimentin to a novel autoantigen for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2503–11.
Luime JJ, Colin EM, Hazes JM, Lubberts E. Does anti-mutated citrullinated vimentin have additional value as a serological marker in the diagnostic and prognostic investigation of patients with rheumatoid arthritis? A systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:337–44.
Vossenaar ER, Despres N, Lapointe E, Van Der Heijden A, Lora M, Senshu T, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis specific anti-Sa antibodies target citrullinated vimentin. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6:142–50.
Nicaise Roland P, Grootenboer Mignot S, Bruns A, Hurtado M, Palazzo E, Hayem G, et al. Antibodies to mutated citrullinated vimentin for diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis in anti-CCP-negative patients and for monitoring infliximab therapy. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10:R142.
Wiik AS, van Venrooij WJ, van Beers J, Pruijn G. All you wanted to know about anti-CCP but were afraid to ask. Autoimmun Rev. 2010;10:90–3.
Syversen SW, Goll GL, van der Heijde D, Landewé R, Lie BA, Odegård S, et al. Prediction of radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis and the role of antibodies against mutated citrullinated vimentin: results from a 10-year prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(2):345–51.
Ursum J, Nielen MM, van Schaardenburg D, van der Horst AR, van de Stadt RJ, Dijkmans BA, et al. Antibodies to mutated citrullinated vimentin and disease activity score in early arthritis: a cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2008;10:R12.
Sahin O, Kaptanoglu E, Bakici MZ, Sezer H, Elden H, Hizmetli S. Dianostic value of autoantibodies against citrullinated peptide antigens in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of different commercial kits. Turk J Rheum. 2011;26:13–8.
Mathsson L, Mullazehi M, Wick MC, Sjöberg O, van Vollenhoven R, Klareskog L, et al. Antibodies against citrullinated vimentin in rheumatoid arthritis: higher sensitivity and extended prognostic value concerning future radiographic progression as compared with antibodies against cyclic citrullinated peptides. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):36–45.
Keskin G, Inal A, Keskin D, Pekel A, Baysal O, Dizer U, et al. Diagnostic utility of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide and anti-modified citrullinated vimentin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Protein Pept Lett. 2008;15(3):314–7.
van Steendam K, Tilleman K, Deforce D. The relevance of citrullinated vimentin in the production of antibodies against citrullinated proteins and the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2011;50:830–70.
Damjanovska L, Thabet MM, Levarth EW, Stoeken-Rijsbergen G, van der Voort EI, Toes RE, et al. Diagnostic value of anti-MCV antibodies in differentiating early inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:730–2.
Raza K, Mathsson L, Buckley CD, Filer A, Ronnelid J. Anti-modified citrullinated vimentin (MCV) antibodies in patients with very early synovitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:627–8.
Wagner E, Skoumal M, Bayer PM, Klaushofer K. Antibody against mutated citrullinated vimentin: a new sensitive marker in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Int. 2009;29:1315–21.
Wolfe F. Comparative usefulness of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheum. 1997;24:1477–85.
Lindqvist E, Eberhardt K, Bendtzen K, Heinegard D, Saxne T. Prognostic laboratory markers of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:196–201.
Greiner A, Plischke H, Kellner H, Gruber R. Association of anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, anti-citrullin antibodies, and IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors with serological parameters of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005;1050:295–303.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zahran, W.E., Mahmoud, M.I., Shalaby, K.A. et al. Unique Correlation Between Mutated Citrullinated Vimentine IgG Autoantibodies and Markers of Systemic Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Ind J Clin Biochem 28, 272–276 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-012-0272-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-012-0272-1