Abstract
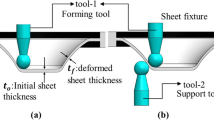
Double-Sided Incremental Forming (DSIF) uses two small, independently moving, hemispherical tools on either side of the sheet to form a desired shape by following a predefined tool path. This study was motivated by the observation that the relative tool position of the tools, specified in the tool path generation algorithm, affects the formed geometric accuracy. A methodology for defining the relative tool positioning in the tool path generation algorithm based on local part geometry is proposed using simplified Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and sample physical experiments combined with Gaussian Process modeling techniques. This approach can take into account the mechanics of deformation in DSIF explicitly and physical compliance of the DSIF machine implicitly. Physical experiments were performed to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- D:
-
the in-plane distance between the two tool axes
- S:
-
distance from top of bottom to bottom of the sheet
- Δz :
-
incremental depth
- θ desired :
-
desired wall angle
- θ formed :
-
formed wall angle
- r t :
-
radius of top tool
- r b :
-
radius of bottom tool
- t0 :
-
initial sheet thickness
References
Jeswiet J, Micari F, Hirt G, Bramley A, Duflou J, Allwood J (2005) Asymmetric single point incremental forming of sheet metal. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 54(2):88–114. doi:10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60021-3
Allwood JM, Braun D, Music O (2010) The effect of partially Cut-out blanks on geometric accuracy in incremental sheet forming. J Mater Process Technol 210:1501–1510
Allwood JM, Music O, Raithathna A, Duncan SR (2009) Closed-loop feedback control of product properties in flexible metal forming processes with mobile tools. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 58(1):287–290. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2009.03.065
Bambach M, Taleb Araghi B, Hirt G (2009) Strategies to improve the geometric accuracy in asymmetric single point incremental forming. Prod Eng 3(2):145–156. doi:10.1007/s11740-009-0150-8
Duflou JR, Verbert J, Belkassem B, Gu J, Sol H, Henrard C, Habraken AM (2008) Process window enhancement for single point incremental forming through multi-step toolpaths. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 57(1):253–256. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2008.03.030
Taleb Araghi B, Göttmann A, Bambach M, Hirt G, Bergweiler G, Diettrich J, Steiners M, Saeed-Akbarii A (2011) Review on the development of a hybrid incremental sheet forming system for small batch sizes and individualized production. Prod Eng 5(4):393. doi:10.1007/s11740-011-0325-y
Behera AK, Lauwers B, Duflou JR (2014) Tool path generation framework for accurate manufacture of complex 3D sheet metal parts using single point incremental forming. Comput Ind 65(4):563–584. doi:10.1016/j.compind.2014.01.002
Göttmann A, Bailly D, Bergweiler G, Bambach M, Stollenwerk J, Hirt G, Loosen P (2012) Laser-assisted asymteric incremental sheet forming (laisf) of titanium sheet metal parts Sub- mitted in production engineering research and development. J: Int J Adv Manuf Technol. doi:10.1007/s00170-012-4640-z
Malhotra R, Cao J, Ren F, Kiridena V, Cedric Xia Z, Reddy NV (2011) “Improvement of geometric accuracy in incremental forming by using a squeezing toolpath strategy with two forming tools”. J Manuf Sci Eng 133(6):61019. doi:10.1115/1.4005179
Meier H, Magnus C, Smukala V (2011) “Impact of superimposed pressure on dieless incremental sheet metal forming with two moving tools”. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 60(1):327–330. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.134
Tekkaya AE, Shankar R, Sebastiani G, Homberg W, Kleiner M (2007) Surface reconstruction for incremental forming. Prod Eng Res Dev 1:71–78
Malhotra R, Cao J, Beltran M, Xu D, Magargee J, Kiridena V, Xia ZC (2012) “Accumulative-DSIF strategy for enhancing process capabilities in incremental forming”. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 61(1):251–254. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2012.03.093
Kiridena V, Xia ZC (2010) A method of incrementally forming a workpiece, patent pending
Jackson K, Allwood J (2009) The mechanics of incremental sheet forming. J Mater Process Technol 209(3):1158–1174. doi:10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2008.03.025
He S, Van Bael A, van Houtte P, Duflou JR, Szekeres A, Henrard C, Habraken AM (2005) “Finite element modeling of incremental forming of aluminum sheets”. Adv Mater Res 6–8:525–532. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR. 6-8.525
Guzmán CF, Gu J, Duflou J, Vanhove H, Flores P, Habraken AM (2012) Study of the geometrical inaccuracy on a SPIF two-slope pyramid by finite element simulations. Int J Solids Struct 49(25):3594–3604. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2012.07.016
Ayed LB, Robert C, Delamézière A, Nouari M, Batoz JL (2014) Simplified numerical approach for incremental sheet metal forming process. Eng Struct 62–63:75–86. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.01.033
Lu B, Chen J, Ou H, Cao J (2013) “Feature-based tool path generation approach for incremental sheet forming process”. J Mater Process Technol 213(7):1221–1233. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.023
Smith J, Malhotra R, Liu WK, Cao J (2013) “Deformation mechanics in single-point and accumulative double-sided incremental forming”. London: Int J Adv Manuf Technol 69(5-8):1185–1201. doi:10.1007/s00170-013-5053-3
Arendt PD, Apley DW, Chen W (2012) “Quantification of model uncertainty: calibration, model discrepancy, and identifiability”. J Mech Des 134(10):100908. doi:10.1115/1.4007390
Higdon D, Kennedy M, Cavendish JC, Cafeo JA et al (2004) “Combining field data and computer simulations for calibration and prediction”. Siam J Sci Comput 26(2):448–466. doi:10.1137/S1064827503426693
Jiang Z, Chen W, Fu Y, Yang R (2013) Reliability-based design optimization with model bias and data uncertainty. SAE Int J Mater Manuf 6(3):502–516. doi:10.4271/2013-01-1384
Kennedy MC, O’Hagan A (2001) Bayesian calibration of computer models. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 63(3):425–464
Liu F, Bayarri MJ, Berger JO, Paulo R et al (2008) “A Bayesian analysis of the thermal challenge problem”. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197(29–32):2457–2466. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2007.05.032
Meier H, Buff B, Laurischkat R, Smukala V (2009) Increasing the part accuracy in dieless robot-based incremental sheet metal forming. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 58(1):233–238. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2009.03.056
Meier H, Magnus C, Smukala V (2011) Impact of superimposed pressure on dieless incremental sheet metal forming with two moving tools. CIRP Ann Manuf Technol 60(1):327–330. doi:10.1016/j.cirp.2011.03.134
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Science Foundation and Department of Energy, USA DE-EE0005764 for their support.
Disclaimer
This work was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Government. Neither the United States Government, nor any agency thereof, nor any of their employees, makes any warranty, express or implied, or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represents that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the United States Government or any agency thereof. Any findings, opinions, and conclusions or recommendations expressed in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the United States Government or any agency thereof.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ndip-Agbor, E., Smith, J., Ren, H. et al. Optimization of relative tool position in accumulative double sided incremental forming using finite element analysis and model bias correction. Int J Mater Form 9, 371–382 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-014-1209-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12289-014-1209-4