Abstract
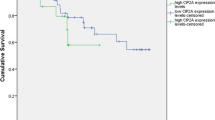
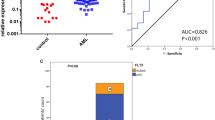
Protein Phosphatase 2A (PP2A) is a crucial regulator of the cellular signalling pathways, proliferation, cell cycle checkpoints and apoptosis. The PPP2R5C gene encodes PP2A regulatory B56γ subunit. Malignant transformation may occur, if mRNA of PPP2R5C is functionally deregulated, structurally altered, decreased or overexpressed. Therefore, the purpose of the study was to examine PPP2R5C mRNA expression, evaluate its association with the different clinical and haematological parameters and determine its prognostic impact in Egyptian adult acute myeloid leukaemia patients with normal cytogenetics (CN-AML). Peripheral blood samples of 50 de novo CN-AML patients and 20 age- and gender-matched healthy controls were examined for PPP2R5C expression by Quantitative Real Time-Polymerase Chain Reaction. The expression levels of PPP2R5C mRNA were significantly higher in the CN-AML samples than in the control samples (P ≤ 0.001). There was a statistical significant difference between the low and high expression levels of PPP2R5C with regard to age (P = 0.005, r = − 0.447, P = 0.001). The patients with an unfavourable response to induction chemotherapy had significant higher PPP2R5C expression levels than those with a favourable response (P = 0.002). There was a significant influence of high PPP2R5C expression levels on the overall survival and progression free survival (P = 0.03, 0.026), respectively. PPP2R5C overexpression is an adverse prognostic factor which affects leukaemogenesis in the CN-AML, it may predict the disease progression and overall survival during the follow-up of the patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shi Y (2009) Serine/threonine phosphatases: mechanism through structure. Cell 139:468–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.10.006
Heijman J, Dewenter M, El-Armouche A, Dobrev D (2013) Function and regulation of serine/threonine phosphatases in the healthy and diseased heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 64:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.09.006
Wlodarchak N, Xing Y (2016) PP2A as a master regulator of the cell cycle. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 51(3):162–184. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2016.1143913
Yang J, Phiel C (2010) Functions of B56-containing PP2As in major developmental and cancer signalling pathways. Life Sci 87:659–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2010.10.003
Haesen D, Sents W, Lemaire K, Hoorne Y, Janssens V (2014) The basic biology of PP2A in hematologic cells and malignancies. Front Oncol 4:347. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2014.00347
Xu Y, Xing Y, Chen Y, Chao Y, Lin Z, Fan E, Yu JW, Strack S, Jeffrey PD, Shi Y (2006) Structure of the protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme. Cell 127(6):1239–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.11.033
Seshacharyulu P, Pandey P, Datta K, Batra SK (2013) Phosphatase: PP2A structural importance, regulation and its aberrant expression in cancer. Cancer Lett 335(1):9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.02.036
Perrotti D, Neviani P (2013) Protein phosphatase 2A: a target for anti-cancer therapy. Lancet Oncol 14:e229–e238. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(12)70558-2
Eichhorn PJ, Creyghton MP, Bernards R (2009) Protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1795:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2008.05.005
Ruvolo PP (2016) The broken “off” switch in cancer signalling PP2A as a regulator of tumorigenesis, drug resistance, and immune surveillance. BBA Clin 6:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbacli.2016.08.002
Shouse GP, Nobumori Y, Panowicz J, Liu X (2011) ATM-mediated phosphorylation activates the tumor-suppressive function of B56γ-PP2A. Oncogene 30:3755–3765. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.95
Shouse GP, Cai X, Liu X (2008) Serine 15 phosphorylation of p53 directs its interaction with B56γ and the tumor suppressor activity of B56γ-specific protein phosphatase 2A. Mol Cell Biol 28:448–456. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.00983-07
Li HH, Cai X, Shouse GP, Piluso LG, Liu X (2007) A specific PP2A regulatory subunit, B56γ, mediates DNA damage-induced de-phosphorylation of P53 at Thr55. EMBO J 26(2):402–411. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601519
Lin SS, Bassik MC, Suh H, Nishino M, Arroyo JD, Hahn WC, Korsmeyer SJ, Roberts TM (2006) PP2A regulates BCL-2 phosphorylation and proteasome-mediated degradation at the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 281:23003–23012. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m602648200
Letourneux XC, Rocher G, Porteu F (2006) B56 containing PP2A dephosphorylate ERK and their activity is controlled by the early gene IEX1and ERK. EMBO J 25(4):727–738. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600980
Lee TY, Lai T-Y, Lin S-C, Wu C-W, Ni I-F, Yang Y-S, Hung L-Y, Law BK, Chiang C-W (2010) The B56γ3 regulatory subunit of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) regulates S phase-specific nuclear accumulation of PP2A and the G1 to S transition. J Biol Chem 285:21567–21580. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m109.094953
Naetar N, Soundarapandian V, Litovchick L, Goguen KL, Sablina AA, Bowman-Colin C, Sicinski P, Hahn WC, DeCaprio JA, Livingston DM (2014) PP2A-mediated regulation of Ras signalling in G2 is essential for stable quiescence and normal G1 length. Mol Cell 54:932–945. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.04.023
Peng XU, Virshup DM, Lee SH (2014) B56-PP2A regulates dynamics for mitotic chromosome alignment. J Cell Sci 127:4567–4573. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.154609
Arriazu E, Pippa R, Odero MD (2016) Protein phosphatase 2A as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Front Oncol 6(78):1–14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2016.00078
Suzuki HI, Matsuyama H, Noguchi M, Yao T, Komatsu N, Mano H, Sugimoto K, Miyazono K (2013) Computational dissection of distinct microRNA activity signatures associated with peripheral T cell lymphoma subtypes. Leukemia 27:2107–2111. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2013.121
Deichmann M, Polychronidis M, Wacker J, Thome M, Naher H (2001) The protein phosphatase 2A subunit B gamma gene is identified to be differentially expressed in malignant melanomas by subtractive suppression hybridization. Melanoma Res 11:577–585. https://doi.org/10.1097/00008390-200112000-00004
Chen W, Possemato R, Campbell KT, Plattner CA, Pallas DC, Hahn WC (2004) Identification of specific PP2A complexes involved in human cell transformation. Cancer Cell 5:127–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(04)00026-1
Zheng H, Chen Y, Chen S, Niu Y, Yang L, Li B, Lu Y, Geng S, Du X, Li Y (2011) Expression and distribution of PPP2R5C gene in leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 4:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-4-21
Falt S, Merup M, Gahrtonb G, Lamberta B, Wennborg A (2005) Identification of progression markers in B-CLL by gene expression profiling. Exp Hematol 33:883–893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exphem.2005.05.007
World Medical Association (2008) Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. The 59th WMA General Assembl, Seoul
Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM, Bloomfield CD, Cazzola M, Vardiman JW (2016) The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 127(20):2391–2405. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544
O’Donnell MR, Tallman MS, Abboud CN, Altman JK, Appelbaum FR, Arber DA, Bhatt V, Bixby D, Blum W, Coutre SE, De Lima M, Fathi AT, Fiorella M, Foran JM, Gore SD, Hall AC, Kropf P, Lancet J, Maness LJ, Marcucci G, Martin MG, Moore JO, Olin R, Peker D, Pollyea DA, Pratz K, Ravandi F, Shami PJ, Stone RM, Strickland SA, Wang ES, Wieduwilt M, Gregory K, Ogba N (2017) Acute myeloid leukemia, version 3. 2017, Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 15(7):926–957. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2017.0116
Dznelade I, He R, Wooly JF, Son MH, Sharobim MH, Greenberg SA, Gabra M, Langlois C, Rashid A, HakemA, Ibrahimova N, Arruda A, Lowenberg B, Valk PJ, Minden MD, Salmena L (2015) INPP4B overexpression is associated with poor clinical outcome and therapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 29(7):1485–1495. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2015.51
Aly A, Shahin D, Azmy E (2012) Prognostic significance of Flt3 internal tandem duplication in Egyptian acute myeloid leukemia and normal cytogenetics. Comp Clin Pathol 21(5):1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-011-1223-6
El Gammal MM, Ebied GT, Madney YM, Abo-Elazm OM, Kelany AK, Torra OS, Radich JP (2019) Clinical impact of combined mutations in DNMT3A, FLT3-ITD and NPM1 among Egyptian acute myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2019.02.001
Huang X, Chen S, Shen Q, Yang L, Li B, Zhong L, Geng S, Du X, Li Y (2010) Analysis of the expression pattern of the BCL11B gene and its relatives in patients with T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol 3:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-3-44
Tallman MS (2005) New strategies for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia including antibodies and other novel agents. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Prog 1:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2005.1.143
EL-Zawahry H, Zeeneldin AA, Samra MA, Mattar MM, EL-Gammal MM, Abdel-Samee A, Darwish T (2007) Cost and outcome of treatment of adults with acute myeloid leukemia at the National Cancer Institute-Egypt. J Egypt Natl Cancer Inst 19:106–113
Döhner H, Estey E, Grimwade D, Amadori S, Appelbaum FR, Thomas Büchner T, Dombret H, Ebert BL, Fenaux P, Larson RA, Levine RL, Lo-Coco F, Naoe T, Niederwieser D, Ossenkoppele GJ, Sanz M, Sierra J, Tallman MS, Tien H-F, Wei AH, Löwenberg B, Bloomfield CD (2017) Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2017 ELN recommendations from an international expert panel. Blood 129:424–447. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-08-733196
Gadhia PK, Patel MV, Vaniawala SN (2016) Role of cytogenetics evaluation in diagnosis of AML. Am J Biomed Life Sci 4(6):98–102. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.ajbls.20160406.13
Janssens V, Rebollo A (2012) The role and therapeutic potential of Ser/Thr phosphatase PP2A in apoptotic signalling networks in human cancer cells. Curr Mol Med 12:268–287. https://doi.org/10.2174/156652412799218930
Hu C, Yu M, Ren Y, Li K, Maggois DM, Mei C, Ye L, Wei J, Jin J, Zhuangs Z, Tong H (2017) PP2A inhibition from LB100 therapy enhances daunorubicin cytotoxicity in secondary acute myeloid leukemia via miR-181b-1 upregulation. Sci Rep 7:2894–2908. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-030584
Lai TY, Yen CJ, Tsai HW, Yang YS, Hong WF, Chiang CW (2016) The B56γ3 regulatory subunit-containing protein phosphatase 2A out competes Akt to regulate p27KIP1 subcellular localization by selectively dephosphorylating phospho-Thr157 of p27KIP1. Oncotarget 7:4542–4558. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6609
Ayatollahi H, Rostami E, Sadeghian MH, Keramati MR, Zeinali E (2016) Expression level of the PPP2R5C gene in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and chronic myeloid leukemia. J Biomed 1(1):e5334. https://doi.org/10.17795/jbm-5334
Benton CB, Ruvolo VR, Konopleva M, Palla SL, Nogueras-Gonzalez G, McQueen T, Kornblau SM, Andreeff M, Ruvolo PP (2015) Expression of differential protein phosphatase 2A subunit isoforms correlates with survival in acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 15: Supplement 2:S22
Kawahara E, Maenaka S, Shimada E, Nishimura Y, Sakurai H (2013) Dynamic regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) by protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunits in nuclei induces cell migration. PLoS ONE 8(5):e63729. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063729
Ito A, Kataoka TR, Watanabe M, Nishiyama K, Mazaki Y, Sabe H, Kitamura Y, Nojima H (2000) A truncated isoform of the PP2AB56 subunit promote cell motility through paxillin phosphorylation. EMBO J 19:562–571. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/19.4.562
Janssens V, Goris J, Van Hoof C (2005) PP2A: the expected tumor suppressor. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15:34–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2004.12.004
Ito A, Koma Y, Watabe K, Nagano T, Endo Y, Nojima H, Kitamara Y (2003) A truncated isoform of the protein phosphatase 2A B56 regulatory subunit may promote genetic instability and cause tumor progression. Am J Pathol 162:81–91
Ruvolo PP (2019) Role of protein phosphatases in the cancer microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1866(1):144–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.07.006
Cristobal I, Gracia-Orti L, Cirauqui C, Alonso MM, Calasanz MJ, Odero MD (2011) PP2A impaired activity is a common event in acute myeloid leukemia and its activation by forskolin has a potent anti-leukemic effect. Leukemia 25:606–614. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.294
Chen Y, Liu S, Shen Q, Zha X, Zheng H, Yang L, Chen S, Wu X, Li B, Li Y (2013) Differential gene expression profiles of PPP2R5C-siRNA-treated malignant T cell. DNA Cell Biol 10:573–581. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2013.2138
Shen Q, Liu S, Chen Y, Yang L, Chen S, Wu X, Li B, Lu Y, Kanger Zhu K, Li Y (2013) Proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction of imatinib resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells via PPP2R5C down-regulation. J Hematol Oncol 6:64–75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-6-64
Liu S, Shen Q, Chen Y, Zeng C, Cao C, Yang L, Chen S, Wu X, Li B, Li Y (2015) Alteration of gene expression profile following PPP2R5C knockdown may be associated with proliferation suppression and increased apoptosis of K56 cells. J Oncol Heamatol 8:34–37. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-015-0125-5
Sangodkar J, Farrington CC, McClinch K, Galsky MD, Kastrinsky DB, Narla G (2016) All roads lead to PP2A: exploiting the therapeutic potential of this phosphatase. FEBS J 283:1004–1024. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ME supervised and revised the study; RG shared in the practical work and in writing the article; RA provided the AML samples and share in the writing. All the authors approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving in human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the NCI (Egypt) research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals participating in this research.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Taweel, M., Gawdat, R.M. & Abdelfattah, R. Prognostic Impact of PPP2R5C Gene Expression in Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients with Normal Cytogenetics. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 36, 37–46 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-019-01142-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-019-01142-5