Abstract
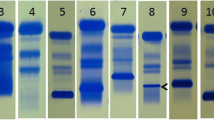
Serum and urine protein electrophoresis and immunofixation are essential for identification and categorization of M protein/monoclonal protein. Based on the number of discrete bands identified the condition can be a monoclonal, biclonal or triclonal gammopathy. A subset of cases show an interesting pattern on immunofixation electrophoresis, with a complete immunoglobulin molecule, along with excess free light chains where in one light chain band shows similar mobility as the heavy chain, while the other light chain band of same isotype has a different mobility. Over a 3 year study period, 420 immunofixation electrophoresis gels were studied to select the cases with the typical pattern as described. The clinical records where searched for data of baseline evaluations done prior to starting therapy, including clinical presentation, biochemical parameters, hemogram and bone marrow examination. Twenty cases (4.7%) were identified from the records, of these 77.8% cases had renal impairment and 33.3% presented with rapidly progressive renal failure. The possible explanation is the toxic effects of excess free light chains, in our cohort. The bound LCs show mobility similar to the HC bands on serum immunofixation gels, however the free light chains, exist in polymeric forms and show a different mobility. The identification and reporting of this pattern provides additional information regarding the high load of light chains, and indicates that patient may have a poor renal outcome/performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Attaelmannan M, Levinson SS (2000) Understanding and identifying monoclonal gammopathies. Clin Chem 46(8 Pt 2):1230–1238
Mullikin TC, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A, Buadi FK, Lacy MQ, Lin Y et al (2016) Clinical characteristics and outcomes in biclonal gammopathies. Am J Hematol 91(5):473–475
Kyle RA, Robinson RA, Katzmann JA (1981) The clinical aspects of biclonal gammopathies. Review of 57 cases. Am J Med 71(6):999–1008
Yang G, Geng C, Chen W (2015) Clinical characteristics of a group of patients with multiple myeloma who had two different λ light chains by immunofixation electrophoresis: a retrospective study from a single center. Exp Ther Med 9(5):1895–1900
Misra A, Mishra J, Chandramohan J, Sharma A, Raina V, Kumar R et al (2016) Old but still relevant: high resolution electrophoresis and immunofixation in multiple myeloma. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 32(1):10–17
Nair B, Waheed S, Szymonifka J, Shaughnessy JD Jr, Crowley J, Barlogie B (2009) Immunoglobulin isotypes in multiple myeloma: laboratory correlates and prognostic implications in total therapy protocols. Br J Haematol 145(1):134–137
Kyle RA, Gertz MA, Witzig TE, Lust JA, Lacy MQ, Dispenzieri A et al (2003) Review of 1027 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Mayo Clin Proc 78(1):21–33
Cook L, Macdonald DH (2007) Management of paraproteinaemia. Postgrad Med J 83(978):217–223
Irish AB, Winearls CG, Littlewood T (1997) Presentation and survival of patients with severe renal failure and myeloma. QJM 90(12):773–780
Knudsen LM, Hjorth M, Hippe E (2000) Renal failure in multiple myeloma: reversibility and impact on the prognosis. Nordic Myeloma Study Group. Eur J Haematol 65(3):175–181
Sölling K (1976) Polymeric forms of free light chains in serum from normal individuals and from patients with renal diseases. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 36(5):447–452
Kaplan B, Livneh A, Sela BA (2011) Immunoglobulin free light chain dimers in human diseases. Sci World J 22(11):726–735
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standard
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
This was a retrospective study and for this type of study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vani, B., Ritu, A., Praveen, S. et al. Excess Free Light Chains in Serum Immunofixation Electrophoresis: Attributes of a Distinctive Pattern. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus 34, 632–635 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-018-0926-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12288-018-0926-0