Abstract
Introduction
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers among women in the world. Different therapeutic strategies such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy and surgery have been used either individually or in combination. Oncolytic virotherapy is a rising treatment methodology, which utilizes replicating viruses to eliminate tumor cells. The aim of this study was to investigate the oncolytic activity of live-attenuated poliovirus in breast cancer cell lines.
Materials and methods
The CD155 expression level in two human breast cancer cell lines and a normal breast cell line were evaluated using real-time PCR and flow cytometry. Virus titration was assessed by TCID50. The cytotoxicity of poliovirus on cell line and apoptosis response was investigated by MTT and Caspase 8 and Caspase 9 ELISA kits, respectively.
Results
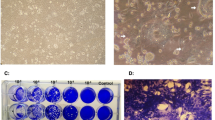
This study showed that CD155 gene was expressed significantly (p = 0.001) higher in both human breast cancer cell lines compared to the normal cell line. The protein expression level of CD155 was 98.1%, 96.7%, in MDA_MB231 and MCF_7 cell lines, respectively, whereas the CD155 expression level was 1.3% in MCF_10A. The cytopathic effect of poliovirus in breast cancer cell lines was significantly higher than normal cells (p < 0.05). Extrinsic apoptosis response was more effective than intrinsic apoptosis in both breast cancer cell lines (p < 0.05).
Conclusion
In summary, administration of live-attenuated poliovirus can be a promising treatment to breast cancer. However, in vitro and in vivo studies will be required to evaluate the safety of this strategy.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Network CGA. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012;490(7418):61.
Mittal S, Kaur H, Gautam N, Mantha AK. Biosensors for breast cancer diagnosis: a review of bioreceptors, biotransducers and signal amplification strategies. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;88:217–31.
Kirn D, Martuza RL, Zwiebel J. Replication-selective virotherapy for cancer: biological principles, risk management and future directions. Nat Med. 2001;7(7):781.
Khuri FR, Nemunaitis J, Ganly I, Arseneau J, Tannock IF, Romel L, et al. A controlled trial of intratumoral ONYX-015, a selectively-replicating adenovirus, in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil in patients with recurrent head and neck cancer. Nat Med. 2000;6(8):879.
Biesecker M, Kimn JH, Lu H, Dingli D, Bajzer Ž. Optimization of virotherapy for cancer. Bull Math Biol. 2010;72(2):469–89.
Zhand S, Hosseini SM, Tabarraei A, Saeidi M, Jazi MS, Kalani MR, Moradi A. Oral poliovirus vaccine-induced programmed cell death involves both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways in human colorectal cancer cells. Oncolytic Virother. 2018;7:95.
Babaei A, Soleimanjahi H, Soleimani M, Arefian E. Mesenchymal stem cells loaded with oncolytic reovirus enhances antitumor activity in mice models of colorectal cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;190: 114644.
Sinkovics JG, Horvath JC. Newcastle disease virus (NDV): brief history of its oncolytic strains. J Clin Virol. 2000;16(1):1–15.
Cattaneo R, Russell SJ, Galanis E, Peng K-W, Fielding A, Springfeld C. Measles virus: improving natural oncolytic properties by genetic engineering. Viral therapy of human cancers. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2004. p. 469–90.
Stojdl DF, Lichty B, Knowles S, Marius R, Atkins H, Sonenberg N, et al. Exploiting tumor-specific defects in the interferon pathway with a previously unknown oncolytic virus. Nat Med. 2000;6(7):821.
Gromeier M, Lachmann S, Rosenfeld MR, Gutin PH, Wimmer E. Intergeneric poliovirus recombinants for the treatment of malignant glioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2000;97(12):6803–8.
Autret A, Martin-Latil S, Mousson L, Wirotius A, Petit F, Arnoult D, Colbère-Garapin F, Estaquier J, Blondel B. Poliovirus induces Bax-dependent cell death mediated by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase. J Virol. 2007;81(14):7504–16.
Brown MC, Dobrikova EY, Dobrikov MI, Walton RW, Gemberling SL, Nair SK, Desjardins A, Sampson JH, Friedman HS, Friedman AH, Tyler DS. Oncolytic polio virotherapy of cancer. Cancer. 2014;120(21):3277–86.
Sun D, Wen X, Wang M, Mao S, Cheng A, Yang X, Jia R, Chen S, Yang Q, Wu Y, Zhu D. Apoptosis and autophagy in picornavirus infection. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:2032.
Meier P, Finch A, Evan G. Apoptosis in development. Nature. 2000;407(6805):796.
Dockrell D. Apoptotic cell death in the pathogenesis of infectious diseases. J Infect. 2001;42(4):227–34.
Krammer PH. CD95’s deadly mission in the immune system. Nature. 2000;407(6805):789.
Desagher S, Martinou J-C. Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10(9):369–77.
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA, et al. Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-β. Nature. 2000;403(6765):98.
Douzandegan Y, Tahamtan A, Gray Z, Nikoo HR, Tabarraei A, Moradi A. Cell death mechanisms in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma induced by vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2019;10(4):246.
Chang HY, Yang X. Proteases for cell suicide: functions and regulation of caspases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2000;64(4):821–46.
Roulston A, Marcellus RC, Branton PE. Viruses and apoptosis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1999;53(1):577–628.
Ochiai H, Moore SA, Archer GE, Okamura T, Chewning TA, Marks JR, Sampson JH, Gromeier M. Treatment of intracerebral neoplasia and neoplastic meningitis with regional delivery of oncolytic recombinant poliovirus. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(14):4831–8.
Zheng Q, Gao J, Yin P, Wang W, Wang B, Li Y, Zhao C. CD155 contributes to the mesenchymal phenotype of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(2):383–94.
Yong H, Cheng R, Li X, Gao G, Jiang X, Cheng H, Zhou X, Zhao W. CD155 expression and its prognostic value in postoperative patients with breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;115: 108884.
Liu T-C, Galanis E, Kirn D. Clinical trial results with oncolytic virotherapy: a century of promise, a decade of progress. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2007;4(2):101.
Molfetta R, Zitti B, Lecce M, Milito ND, Stabile H, Fionda C, Cippitelli M, Gismondi A, Santoni A, Paolini R. CD155: a multi-functional molecule in tumor progression. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):922.
Solecki D, Bernhardt G, Lipp M, Wimmer E. Identification of a nuclear respiratory factor-1 binding site within the core promoter of the human polio virus receptor/CD155 gene. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(17):12453–62.
Zhand S, Hosseini S, Tabarraei A, Moradi A, Saeidi M. Analysis of poliovirus receptor, CD155 expression in different human colorectal cancer cell lines: implications for poliovirus virotherapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 2019;15(1):61–7.
Motalleb G. Virotherapy in cancer. Iran J Cancer Prev. 2013;6(2):101.
Israelsson S, Jonsson N, Gullberg M, Lindberg AM. Cytolytic replication of echoviruses in colon cancer cell lines. Virol J. 2011;8(1):473.
Kooby DA, Carew JF, Halterman MW, Mack JE, Bertino JR, Blumgart LH, et al. Oncolytic viral therapy for human colorectal cancer and liver metastases using a multi-mutated herpes simplex virus type-1 (G207). FASEB J. 1999;13(11):1325–34.
Skelding KA, Barry RD, Shafren DR. Systemic targeting of metastatic human breast tumor xenografts by Coxsackievirus A21. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;113(1):21–30.
Eswaran SP, Col AP, Col YCL, Col AN. Potency titration of oral polio vaccine by estimation of live virus content using tissue culture techniqueMed. J Armed Forces India. 2003;59(2):105–7.
Belov GA, Romanova LI, Tolskaya EA, Kolesnikova MS, Lazebnik YA, Agol VI. The major apoptotic pathway activated and suppressed by poliovirus. J Virol. 2003;77(1):45–56.
Toyoda H, Ido M, Hayashi T, Gabazza EC, Suzuki K, Kisenge RR, et al. Experimental treatment of human neuroblastoma using live-attenuated poliovirus. Int J Oncol. 2004;24(1):49–58.
Gosselin A-S, Simonin Y, Guivel-Benhassine F, Rincheval V, Vayssière J-L, Mignotte B, et al. Poliovirus-induced apoptosis is reduced in cells expressing a mutant CD155 selected during persistent poliovirus infection in neuroblastoma cells. J Virol. 2003;77(1):790–8.
Atsumi S, Matsumine A, Toyoda H, Niimi R, Iino T, Nakamura T, et al. Oncolytic virotherapy for human bone and soft tissue sarcomas using live attenuated poliovirus. Int J Oncol. 2012;41(3):893–902.
Blondel B, Autret A, Brisac C, Martin-Latil S, Mousson L, Pelletier I, et al. Apoptotic signaling cascades operating in poliovirus-infected cells. Front Biosci. 2009;14:2181–92.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from the funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceive and design of the experiments: AM; data analysis: HV, EB; writing of the paper: EB, AH; performance of the experiments: HV; read and confirm of final version of article: AM, EB, HV, AH; revise: EB, AM.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that this research was conducted in the absence of any relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This research project has received the confirmation of the Ethics Committee of Golestan University of Medical Sciences with the code of IR.Goums.REC.1394.220.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Vazeh, H., Behboudi, E., Hashemzadeh-Omran, A. et al. Live-attenuated poliovirus-induced extrinsic apoptosis through Caspase 8 within breast cancer cell lines expressing CD155. Breast Cancer 29, 899–907 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-022-01372-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-022-01372-y