Abstract
Purpose
Long-term follow-up of Japanese women with breast cancer who underwent hypofractionated whole-breast irradiation (HF-WBI) has not been well documented. Therefore, we compared the treatment results of HF-WBI and conventional fractionated (CF)-WBI.
Methods
Patients with stage 0–II breast cancer receiving partial mastectomy were eligible for this prospective observational study. The HF-WBI consisted of 43.2 Gy in 16 fractions to the whole breast, with an additional tumor-bed boost of 8.1 Gy in three fractions for patients with positive or less than 5 mm surgical margins. A total of 615 patients (400: HF-WBI and 215: CF-WBI) who were treated between 2006 and 2008 were investigated. Propensity score matching was conducted based on age, tumor grade, and margin status, and 372 matched cases were investigated for examining factors relating to intrabreast tumor recurrence (IBTR).
Results
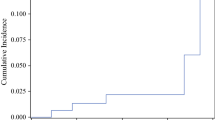
With a median follow-up period of 9.4 years, age and margin status were independent factors associated with IBTR occurrence (P = 0.006 and 0.016, respectively). The 10-year ipsilateral breast tumor control (IBTC) rates after HF-WBI and CF-WBI were 96.5% and 95.3%, respectively (P = 0.606). The 10-year IBTC rates according to margin status were 88.0% with positive margins, 94.9% with 5 mm margins, and 98.0% with negative margins (P = 0.014).
Conclusions
There was no difference in IBTC between CF-WBI and HF-WBI in our patients. Positive surgical margin was a risk factor independently associated with IBTC rates after CF-WBI and HF-WBI. Further investigation is required to establish adequate treatment strategies for patients with positive surgical margins.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clarke M, Collins R, Darby S, Davies C, Elphinstone P, Evans V, et al. Effects of radiotherapy and of differences in the extent of surgery for early breast cancer on local recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;366:2087–106.
Haviland JS, Owen JR, Dewar JA, Agrawal RK, Barrett J, Barrett-Lee PJ, et al. The UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) trials of radiotherapy hypofractionation for treatment of early breast cancer: 10-year follow-up results of two randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:1086–94.
Smith BD, Bentzen SM, Correa CR, Hahn CA, Hardenbergh PH, Ibbott GS, et al. Fractionation for whole breast irradiation: an American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based guideline. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2011;81:59–68.
Whelan TJ, Pignol JP, Levine MN, Julian JA, MacKenzie R, Parpia S, et al. Long-term results of hypofractionated radiation therapy for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:513–20.
Smith BD, Bellon JR, Blitzblau R, Freedman G, Haffty B, Hahn C, et al. Radiation therapy for the whole breast: Executive summary of an American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based guideline. Pract Radiat Oncol. 2018;8:145–52.
Nozaki M, Kagami Y, Shibata T, Nakamura K, Ito Y, Nishimura Y, et al. A primary analysis of a multicenter, prospective, single-arm, confirmatory trial of hypofractionated whole breast irradiation after breast-conserving surgery in Japan: JCOG0906. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2019;49:57–62.
Moran MS, Schnitt SJ, Giuliano AE, Harris JR, Khan SA, Horton J, et al. Society of Surgical Oncology-American Society for Radiation Oncology consensus guideline on margins for breast-conserving surgery with whole-breast irradiation in stages I and II invasive breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014;88:553–64.
Karasawa K, Kunogi H, Hirai T, Hojo H, Hirowatari H, Izawa H, et al. Comparison of hypofractionated and conventionally fractionated whole-breast irradiation for early breast cancer patients: a single-institute study of 1,098 patients. Breast Cancer. 2014;21:402–8.
Salerno KE. NCCN guidelines update: evolving radiation therapy recommendations for breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2017;15:682–4.
Japanese Breast Cancer Society. The Japanese Breast Cancer Society clinical practice guideline for breast cancer 2018. Treatment Chapter. 2018. p. 328–30.
Houssami N, Macaskill P, Marinovich ML, Morrow M. The association of surgical margins and local recurrence in women with early-stage invasive breast cancer treated with breast-conserving therapy: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21:717–30.
Society JBC. The Japanese Breast Cancer Society clinical practice guideline for breast cancer 2018. Epidemiology and Diagnostics Chapter. 2018. p. 269–71.
Recht A, McArthur H, Solin LJ, Tendulkar R, Whitley A, Giuliano A. Contemporary guidelines in whole-breast irradiation: an alternative perspective. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2019;104:567–73.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank T. Kawai for his assistance with pathological data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshida-Ichikawa, Y., Horimoto, Y., Shikama, N. et al. Ipsilateral breast tumor control following hypofractionated and conventional fractionated whole-breast irradiation for early breast cancer: a long-term follow-up. Breast Cancer 28, 92–98 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-020-01134-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-020-01134-8