Abstract
Background
Topoisomerase II alpha (Topo IIa) is involved in DNA replication and is a molecular target for anthracycline-based chemotherapy. The Ki-67 labeling index (LI) is an evaluation of tumor cell proliferation. The objective of this study was to evaluate relationships among Topo IIa expression, the Ki-67 LI, and prognostic factors in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, human epidermal growth factor type-2 (HER2)-negative breast cancer.
Materials and methods
Seventy-one patients were diagnosed with ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer between July 2003 and December 2004. Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor specimens were stained for Topo IIa expression and Ki-67 LI. We investigated the correlation of the level of Topo IIa expression and the Ki-67 LI with clinical factors such as age, tumor size, progesterone receptor status, nodal status, nuclear grade, and lymphovascular invasion (LVI).
Results
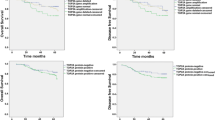
Statistically significant differences were observed between Topo IIa overexpression, nuclear grade (p = 0.036), and LVI (p = 0.029). Topo IIa overexpression was statistically correlated with the Ki-67 LI (p < 0.0001). A statistically significant difference was observed between the Ki-67 LI and nuclear grade (p = 0.01). Survival analysis revealed the significant prognostic value of Ki-67 LI in patients with ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer (p = 0.003).
Conclusions
Ki-67 LI is a strong prognostic factor in ER-positive HER2-negative breast cancer. Topo IIa overexpression was significantly correlated with the Ki-67 LI, nuclear grade, and LVI. These findings suggest use of Topo IIa expression as a proliferation marker and a prognostic factor in ER-positive, HER2-negative breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry DA, Cronin KA, Plevritis SK, Fryback DG, Clarke L, Zelen M, et al. Effect of screening and adjuvant therapy on mortality from breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1784–92.
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ, 10th St Gallen conference. Progress and promise: highlights of the international expert consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2007. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:1133–44.
Goldhirsch A, Ingle JN, Gelber RD, Coates AS, Thürlimann B, Senn HJ, Panel members. Thresholds for therapies: highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 2009. Ann Oncol. 2009;20:1319–29.
Piccart MJ, Di Leo A, Hamilton A. HER2. a ‘predictive factor’ ready to use in the daily management of breast cancer patients? Eur J Cancer. 2000;36:1755–61.
Yamauchi H, Stearns V, Hayes DF. When is a tumor marker ready for prime time? A case study of c-erbB-2 as a predictive factor in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2334–56.
Järvinen TA, Tanner M, Rantanen V, Bärlund M, Borg A, Grénman S, et al. Amplification and deletion of topoisomerase IIalpha associate with ErbB-2 amplification and affect sensitivity to topoisomerase II inhibitor doxorubicin in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 2000;156:839–47.
Tan KB, Dorman TE, Falls KM, Chung TDY, Mirabelli CK, Crooke ST, et al. Topoisomerase II alpha and topoisomerase II beta differentially spliced forms of topoisomerase II alpha mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993;21:3719–23.
Withoff S, De Jong S, De Vries EGE, Mulder NH. Human DNA topoisomerase II: biochemistry and role in chemotherapy resistance. Anticancer Res. 1996;16:1867–80.
Chung DU, Drake SH, Tan KB, Per SR, Crooke ST, Mirabelli CK. Characterization and immunological identification of cDNA clones encoding to human topoisomerase isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:9431–5.
Roca J, Wang JC. DNA transport by a type II DNA topoisomerase: evidence in favor of a two-gate mechanism. Cell. 1994;77:609–16.
Osheroff N. Biochemical basis for the interactions of type I and type II topoisomerase with DNA. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41:223–41.
Gerdes J, Schwab U, Lemke H, Stein H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer. 1983;31:13–20.
Cattoretti G, Becker MH, Key G, Duchrow M, Schlüter C, Galle J, et al. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992;168:357–63.
Umemura S, Komaki K, Noguchi S, Shiba E, Toi M, Kimijima I, et al. Prognostic factors for node-negative breast cancers: results of a study program by the Japanese Breast Cancer Society. Breast Cancer. 1998;5:243–9.
Railo M, Nordling S, von Boguslawsky K, Leivonen M, Kyllönen L, von Smitten K. Prognostic value of Ki-67 immunolabelling in primary operable breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1993;68:579–83.
Nishimura R, Nagao K, Miyayama H, Matsuda M, Baba K, Matsuoka Y, et al. An evaluation of predictive factors involved in clinical or pathological response to primary chemotherapy in advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2002;9:145–52.
Giuseppe Viale, Anita Giobbie-Hurder, Regan MM, Coates AS, Mastropasqua MG, Dell’Orto P, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of centrally reviewed Ki-67 labeling index in postmenopausal women with endocrine-responsive breast cancer: results from Breast International Group Trial 1–98 comparing adjuvant tamoxifen with letrozole. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:5569–75.
Dowsett M, Smith IE, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM, Skene A, A’Hern R, et al. Prognostic value of Ki-67 expression after short-term presurgical endocrine therapy for primary breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:167–70.
Nishimura R, Osako T, Okumura Y, Hayashi M, Arima N. Clinical significance of Ki-67 in neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer as a predictor for chemosensitivity and for prognosis. Breast Cancer. 2010;17:269–75.
Kurosumi M, Suemasu K, Tabei T, Inoue K, Matsumoto H, Sugamata N, et al. Relationship between existence of lymphatic invasion in peritumoral breast tissue and presence of axillary lymph node metastasis in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Oncol Rep. 2001;8:1051–5.
Di Leo A, Larsimont D, Gancberg D, Jarvinen T, Beauduin M, Vindevoghel A, et al. HER-2 and topo-isomerase Ha as predictive markers in a population of node-positive breast cancer patients randomly treated with adjuvant CMF or epirubicin plus cyclophosphamide. Ann Oncol. 2001;12:1081–9.
Cardoso F, Durbecq V, Larsimont D, Paensmans M, Leroy J, Rouas G et al. Correlation between complete response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy and topoisomerase II-α gene amplification and protein overexpression in locally advanced/metastatic breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 2004;24:201–9.
Pegram MD, Finn RS, Arzoo K, Beryt M, Pietras RJ, Slamon DJ, et al. The effect of HER-2/neu overexpression on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human breast and ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene. 1997;15:537–47.
Orlando L, Del Curto B, Gandini S, Ghisini R, Pietri E, Torrisi R, et al. Topoisomerase IIα gene status and prediction of pathological complete remission after anthracycline-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in endocrine non-responsive Her2/neu-positive breast cancer. Breast. 2008;17:506–11.
O’Malley FP, Chia S, Tu D, Shepherd L, Levine M, Huntsman D, et al. Topoisomerase II alpha protein overexpression has predictive utility in a randomized trial comparing CMF to CEF in premenopausal women with node positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006;100:S18.
Martin-Richard M, Muñoz J, Albanell L, Colomo M, Bellet MJ, Rey J, et al. Serial topoisomerase II expression in primary breast cancer and response to neoadjuvant anthracycline-based chemotherapy. Oncology. 2004;66:388–94.
Zhu L, Li YF, Chen WG, He JR, Peng CH, Zhu ZG, et al. HER2 and topoisomerase IIα: possible predictors of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer patients. Chin Med J. 2008;121:1965–8.
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984;133:1710–5.
Rody A, Karn T, Ruckhäberle, Müller V, Gehrmann M, Solbach C et al. Gene expression of topoisomerase II alpha (TOP2A) by microarray analysis is prognostic in estrogen receptor (ER) positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;113:457–66.
Lynch BJ, Guinee DG Jr, Holden JA. Human DNA topoisomerase II-alpha: a new marker of cell proliferation in invasive breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1997;28:1180–8.
Järvinen TA, Kononen J, Pelto-Huikko M, Isola J. Expression of topoisomerase IIalpha is associated with rapid cell proliferation, aneuploidy, and c-erbB2 overexpression in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 1996;148:2073–82.
Sandri MI, Hochhauser D, Ayton P, Camplejohn RC, Whitehouse R, Turley H, et al. Differential expression of the topoisomerase II alpha and beta genes in human breast cancers. Br J Cancer. 1996;73:1518–24.
Järvinen TA, Holli K, Kuukasjarvi T, Isola JJ. Predictive value of topoisomerase II alpha and other prognostic factors for epirubicin chemotherapy in advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1998;77:2267–73.
Gómez HL, Pinto JA, Olivera M, Vidaurre T, Doimi FD, Vigil CE, et al. Topoisomerase IIa as a predictive factor of response to therapy with anthracyclines in locally advanced breast cancer. Breast. 2011;20(1):39–45.
Depowski PL, Rosenthal SI, Brien TP, Stylos S, Johnson RL, Ross JS. Topoisomerase IIalpha expression in breast cancer: correlation with outcome variables. Mod Pathol. 2000;13(5):542–7.
Schindlbeck C, Mayr D, Olivier C, Rack B, Engelstaedter V, Jueckstock J, et al. Topoisomerase IIalpha expression rather than gene amplification predicts responsiveness of adjuvant anthracycline-based chemotherapy in women with primary breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2010;136(7):1029–37.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Dean Award (C-002) and the Gunma University Graduate School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Tokiniwa, H., Horiguchi, J., Takata, D. et al. Topoisomerase II alpha expression and the Ki-67 labeling index correlate with prognostic factors in estrogen receptor-positive and human epidermal growth factor type-2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer 19, 309–314 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-011-0291-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-011-0291-4