Abstract
Background
When performing breast-conserving surgery (BCS), it is essential to achieve a complete resection of the tumor while preserving the cosmetic outcome. The aim of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of a MRI marking technique for planning of BCS.
Methods
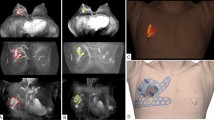
A retrospective review was performed of 14 consecutive patients who underwent MRI in the supine position (supine MRI) using a MRI marking technique. The preoperative histopathological diagnosis was ductal carcinoma in situ in 11 and invasive ductal carcinoma in 3. All of the patients with invasive ductal carcinoma were treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The pills of Breath Care® used as MRI markers were placed in the Penrose drain with 2-cm intervals, and drains were put on the resection lines as determined by ultrasonography (US). The final resection lines were modified using information obtained by supine MRI. The rate of the margin-tumor distance (RMTD: longer margin-tumor distance/shorter margin-tumor distance) was calculated.
Results
Thirteen patients (93%) needed modification of the first resection line, whereas one patient (7%) needed no modification. Twelve patients (86%) had negative margins, but two patients (14%) had positive margins: one patient had a medial margin, while the other had a distal margin. One patient showed a pathologically complete response after chemotherapy; the RMTD was not evaluated. Among the 12 patients with medial and lateral negative margins, the medial and lateral margin-tumor distances ranged from 1.0 to 3.5 cm (average 2.1 cm), and the RMTD ranged from 1 to 3.0 (average 1.5).
Conclusion
Our MRI marking technique may be useful for evaluating the extent of the tumor as determined by the US examination in difficult cases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sonoo H, Noguchi S, Academic Committee of the Japanese Breast Cancer Society. Results of questionnaire survey on breast cancer surgery in Japan 2004–2006. Breast Cancer. 2008;15:3–4.
Park CC, Mitsumori M, Nixon A, Recht A, Connolly J, Gelman R, et al. Outcome at 8 years after breast-conserving surgery and radiation therapy for invasive breast cancer: influence of margin status and systemic therapy on local recurrence. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18:1668–75.
Wazer DE, Jabro G, Ruthazer R, Schmid C, Safaii H, Schmidt-Ullrich RK. Extent of margin positivity as a predictor for local recurrence after breast conserving irradiation. Radiat Oncol Investig. 1999;7:111–7.
Spivack B, Khanna MM, Tafra L, Juillard G, Giuliano AE. Margin status and local recurrence after breast-conserving surgery. Arch Surg. 1994;129:952–6.
Vrieling C, Collette L, Fourquet A, Hoogenraad WJ, Horiot JH, Jager JJ, et al. The influence of patient, tumor and treatment factors on the cosmetic results after breast-conserving therapy in the EORTC ‘boost vs. no boost’ trial. EORTC Radiotherapy and Breast Cancer Cooperative Groups. Radiother Oncol. 2000;55:219–32.
Kaiser WA, Zeitler E. MR imaging of the breast: fast imaging sequences with and without Gd-DTPA. Preliminary observations. Radiology. 1989;170:681–6.
Orel SG, Schnall MD. MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology. 2001;220:13–30.
Schouten van der Velden AP, Boetes C, Bult P, Wobbes T. The value of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis and size assessment of in situ and small invasive breast carcinoma. Am J Surg. 2006;192:172–8.
Boetes C, Mus RD, Holland R, Barentsz JO, Strijk SP, Wobbes T, et al. Breast tumors: comparative accuracy of MR imaging relative to mammography and US for demonstrating extent. Radiology. 1995;197:743–7.
Nishikawa K, Tozaki M, Fukuda K. Supine MR mammography with parallel imaging technique. Jpn J Magn Reson Med. 2004;24:34–9 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Tozaki M, Fukuda K. Supine MR mammography using VIBE with parallel acquisition technique for the planning of breast-conserving surgery: clinical feasibility. Breast. 2006;15:137–40.
Ogawa T, Tozaki M, Yamashiro N, Kawano N, Suzuki T, Ozaki S, et al. New preoperative MRI marking technique for a patient with ductal carcinoma in situ. Breast Cancer. 2008;15:309–14.
World Health Organization Classification. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the breast and female genital organs. Lyon: IARC; 2003.
Fukuma E. Endoscopic breast surgery for breast cancer. Nippon Geka Gakkai Zasshi. 2006;107:64–8 (in Japanese with English abstract).
Klein Zeggelink WF, Deurloo EE, Muller SH, Schultze Kool LJ, Gilhuijs KG. Reproducibility of mammary gland structure during repeat setups in a supine position. Med Phys. 2002;29:2062–9.
Nakamura R, Nagashima T, Sakakibara M, Sangai T, Fujimoto H, Arai M, et al. Breast-conserving surgery using supine magnetic resonance imaging in breast cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast. 2008;17:245–51.
Tozaki M, Kobayashi T, Uno S, Aiba K, Takeyama H, Shioya H, et al. Breast-conserving surgery after chemotherapy: value of MDCT for determining tumor distribution and shrinkage pattern. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186:431–9.
Partridge SC, Gibbs JE, Lu Y, Esserman LJ, Sudilovsky D, Hylton NM. Accuracy of MR imaging for revealing residual breast cancer in patients who have undergone neoadjuvant chemotherapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179:1193–9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashiro, N., Tozaki, M., Ogawa, T. et al. Preoperative MRI marking technique for the planning of breast-conserving surgery. Breast Cancer 16, 223–228 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-008-0088-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-008-0088-2