Abstract
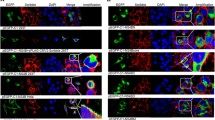
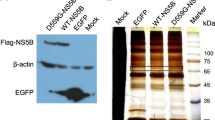
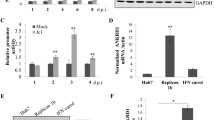
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) life cycle is highly dependent on cellular proteins for viral propagation. In order to identify the cellular factors involved in HCV propagation, we previously performed a protein microarray assay using the HCV nonstructural 5A (NS5A) protein as a probe. Of ∼9,000 human cellular proteins immobilized in a microarray, adenosylhomocysteinase like 1 (AHCYL1) was among 90 proteins identified as NS5A interactors. Of these candidates, AHCYL1 was selected for further study. In the present study, we verified the physical interaction between NS5A and AHCYL1 by both in vitro pulldown and coimmunoprecipitation assays. Furthermore, HCV NS5A interacted with endogenous AHCYL1 in Jc1-infected cells. Both NS5A and AHCYL1 were colocalized in the cytoplasmic region in HCV-replicating cells. siRNAmediated knockdown of AHCYL1 abrogated HCV propagation. Exogenous expression of the siRNA-resistant AHCYL1 mutant, but not of the wild-type AHCYL1, restored HCV protein expression levels, indicating that AHCYL1 was required specifically for HCV propagation. Importantly, AHCYL1 was involved in the HCV internal ribosome entry site-mediated translation step of the HCV life cycle. Finally, we demonstrated that the proteasomal degradation pathway of AHCYL1 was modulated by persistent HCV infection. Collectively, these data suggest that HCV may modulate the AHCYL1 protein to promote viral propagation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando, H., Kawaai, K., and Mikoshiba, K. 2014. IRBIT: a regulator of ion channels and ion transporters. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1843, 2195–2204.
Appel, N., Pietschmann, T., and Bartenschlager, R. 2005. Mutational analysis of hepatitis C virus nonstructural protein 5A: potential role of differential phosphorylation in RNA replication and identification of a genetically flexible domain. J. Virol. 79, 3187–3194.
Cooper, B.J., Key, B., Carter, A., Angel, N.Z., Hart, D.N.J., and Kato, M. 2006. Suppression and overexpression of adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase-like protein 1 (AHCYL1) influences zebrafish embryo development: a possible role for AHCYL1 in inositol phospholipid signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 22471–22484.
Csordás, G., Weaver, D., and Hajnóczky, G. 2018. Endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial contactology: structure and signaling functions. Trends Cell Biol. 28, 523–540.
Devogelaere, B., Beullens, M., Sammels, E., Derua, R., Waelkens, E., vanLint, J., Parys, J.B., Missiaen, L., Bollen, M., and DeSmedt, H. 2007. Protein phosphatase-1 is a novel regulator of the interaction between IRBIT and the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. Biochem. J. 407, 303–311.
El-Shamy, A., Shindo, M., Shoji, I., Deng, L., Okuno, T., and Hotta, H. 2013. Poly-morphisms of the Core, NS3, and NS5A proteins of hepatitis C virus genotype 1b associate with development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 58, 555–563.
Feldman, R.M., Correll, C.C., Kaplan, K.B., and Deshaies, R.J. 1997. A complex of Cdc4p, Skp1p, and Cdc53p/cullin catalyzes ubiquitination of the phosphorylated CDK inhibitor Sic1p. Cell 91, 221–230.
Gong, G., Waris, G., Tanveer, R., and Siddiqui, A. 2001. Human hepatitis C virus NS5A protein alters intracellular calcium levels, induces oxidative stress, and activates STAT-3 and NF-κB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9599–9604.
Hoofnagle, J.H. 2002. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology 36, S21–S29.
Jadhav, T. and Wooten, M.W. 2009. Defining an embedded code for protein ubiquitination. J. Proteomics Bioinform. 2, 316.
Jeong, W., Kim, J., Ahn, S.E., Lee, S.I., Bazer, F.W., Han, J.Y., and Song, G. 2012. AHCYL1 is mediated by estrogen-induced ERK1/2 MAPK cell signaling and microRNA regulation to effect functional aspects of the avian oviduct. PLoS ONE 7, e49204.
LeMay, K.L., Treadaway, J., Angulo, I., and Tellinghuisen, T.L. 2013. A hepatitis C virus NS5A phosphorylation site that regulates RNA replication. J. Virol. 87, 1255–1260.
Li, B., Hu, Q., Xu, R., Ren, H., Fei, E., Chen, D., and Wang, G. 2012. Hax-1 is rapidly degraded by the proteasome dependent on its PEST sequence. BMC Cell Biol. 13, 20.
Lim, Y.S. and Hwang, S.B. 2011. Hepatitis C virus NS5A protein interacts with phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type IIIα and regulates viral propagation. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 11290–11298.
Lindenbach, B.D. and Rice, C.M. 2005. Unravelling hepatitis C virus replication from genome to function. Nature 436, 933–938.
Macdonald, A., Crowder, K., Street, A., McCormick, C., Saksela, K., and Harris, M. 2003. The hepatitis C virus non-structural NS5A protein inhibits activating protein-1 function by perturbing Ras-ERK pathway signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 17775–17784.
Marchal, C., Haguenauer-Tsapis, R., and Urban-Grimal, D. 1998. A PEST-like sequence mediates phosphorylation and efficient ubiquitination of yeast uracil permease. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 314–321.
McGivern, D.R., Masaki, T., Lovell, W., Hamlett, C., Saalau-Bethell, S., and Graham, B. 2015. Protease inhibitors block multiple functions of the NS3/4A protease-helicase during the hepatitis C virus life cycle. J. Virol. 89, 5362–5370.
Nguyen, T.T.T., Park, E.M., Lim, Y.S., and Hwang, S.B. 2018. Nonstructural protein 5A impairs DNA damage repair: implications for hepatitis C virus-mediated hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Virol. 92, e00178–18.
Park, C., Min, S., Park, E.M., Lim, Y.S., Kang, S., Suzuki, T., Shin, E.C., and Hwang, S.B. 2015. Pim kinase interacts with nonstructural 5A protein and regulates hepatitis C virus entry. J. Virol. 89, 10073–10086.
Pawlotsky, J.M., Germanidis, G., Neumann, A.U., Pellerin, M., Frainais, P.O., and Dhumeaux, D. 1998. Interferon resistance of hepatitis C virus genotype 1b: relationship to nonstructural 5A gene quasispecies mutations. J. Virol. 72, 2795–2805.
Pham, H.T., Nguyen, T.T.T., Nguyen, L.P., Han, S.S., Lim, Y.S., and Hwang, S.B. 2019. Hepatitis C virus downregulates ubiquitinconjugating enzyme E2S expression to prevent proteasomal degradation of NS5A, leading to host cells more sensitive to DNA damage. J. Virol. 93, e01240–18.
Rechsteiner, M. and Rogers, S.W. 1996. PEST sequences and regulation by proteolysis. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 267–271.
Rogers, S., Wells, R., and Rechsteiner, M. 1986. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science 234, 364–368.
Roth, A.F., Sullivan, D.M., and Davis, N.G. 1998. A large PEST-like sequence directs the ubiquitination, endocytosis, and vacuolar degradation of the yeast a-factor receptor. J. Cell Biol. 142, 949–961.
Tran, G.V.Q., Luong, T.T.D., Park, E.M., Choi, J.W., Park, C., Lim, Y.S., and Hwang, S.B. 2016. Nonstructural 5A protein of hepatitis C virus regulates soluble resistance-related calcium-binding protein activity for viral propagation. J. Virol. 90, 2794–2805.
Turner, M.A., Yang, X., Yin, D., Kuczera, K., Borchardt, R.T., and Howell, P.L. 2000. Structure and functions of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 33, 101–125.
Zeng, B., Li, Z., Chen, R., Guo, N., Zhou, J., Zhou, Q., Lin, Q., Cheng, D., Liao, Q., Zheng, L., et al. 2012. Epigenetic regulation of miR-124 by hepatitis C virus core protein promotes migration and invasion of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma cells by targeting SMYD3. FEBS Lett. 586, 3271–3278.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Ralf Bartenschlager and Dr. Takaji Wakita for providing cells and reagents. This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2019R1A2C1086914) to Y. S. L. This research was also supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the NRF grant funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1A6A1A03015876) to D.T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
We have no conflicts of interest to report.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, YS., Mai, H.N., Nguyen, L.P. et al. Adenosylhomocysteinase like 1 interacts with nonstructural 5A and regulates hepatitis C virus propagation. J Microbiol. 59, 101–109 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-0470-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-021-0470-8