Abstract
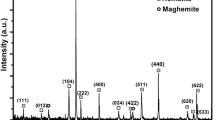
Minerals that contain ferric iron, such as amorphous Fe(III) oxides (A), can inhibit methanogenesis by competitively accepting electrons. In contrast, ferric iron reduced products, such as magnetite (M), can function as electrical conductors to stimulate methanogenesis, however, the processes and effects of magnetite production and transformation in the methanogenic consortia are not yet known. Here we compare the effects on methanogenesis of amorphous Fe (III) oxides (A) and magnetite (M) with ethanol as the electron donor. RNA-based terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism with a clone library was used to analyse both bacterial and archaeal communities. Iron (III)-reducing bacteria including Geobacteraceae and methanogens such as Methanosarcina were enriched in iron oxide-supplemented enrichment cultures for two generations with ethanol as the electron donor. The enrichment cultures with A and non-Fe (N) dominated by the active bacteria belong to Veillonellaceae, and archaea belong to Methanoregulaceae and Methanobacteriaceae, Methanosarcinaceae (Methanosarcina mazei), respectively. While the enrichment cultures with M, dominated by the archaea belong to Methanosarcinaceae (Methanosarcina barkeri). The results also showed that methanogenesis was accelerated in the transferred cultures with ethanol as the electron donor during magnetite production from A reduction. Powder X-ray diffraction analysis indicated that magnetite was generated from microbial reduction of A and M was transformed into siderite and vivianite with ethanol as the electron donor. Our data showed the processes and effects of magnetite production and transformation in the methanogenic consortia, suggesting that significantly different effects of iron minerals on microbial methanogenesis in the iron-rich coastal riverine environment were present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achtnich, C., Bak, F., and Conrad, R. 1995. Competition for electron donors among nitrate reducers, ferric iron reducers, sulfate reducers, and methanogens in anoxic paddy soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 19, 65–72.
Boga, H.I., Ludwig, W., and Brune, A. 2003. Sporomusa aerivorans sp. nov., an oxygen-reducing homoacetogenic bacterium from the gut of a soil-feeding termite. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53, 1397–1404.
Bokulich, N.A., Bamforth, C.W., and Mills, D.A. 2012. A review of molecular methods for microbial community profiling of beer and wine. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 70, 150–162.
Bond, D.R. and Lovley, D.R. 2002. Reduction of Fe(III) oxide by methanogens in the presence and absence of extracellular quinones. Environ. Microbiol. 4, 115–124.
Cadillo-Quiroz, H., Yavitt, J.B., and Zinder, S.H. 2009. Methanosphaerula palustris gen. nov., sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic methanogen isolated from a minerotrophic fen peatland. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 59, 928–935.
Cummings, D.E., March, A.W., Bostick, B., Spring, S., Caccavo, F., Fendorf, S., and Rosenzweig, R.F. 2000. Evidence for microbial Fe (III) reduction in anoxic, mining-impacted lake sediments (Lake Coeur d’Alene, Idaho). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 154–162.
Dong, H.L., Fredrickson, J.K., Kennedy, D.W., Zachara, J.M., Kukkadapu, R.K., and Onstott, T.C. 2000. Mineral transformation associated with the microbial reduction of magnetite. Chem. Geol. 169, 299–318.
Gonnerman, M.C., Benedict, M.N., Feist, A.M., Metcalf, W.W., and Price, N.D. 2013. Genomically and biochemically accurate metabolic reconstruction of Methanosarcina barkeri Fusaro, iMG746. Biotech. J. 8, 1070–1129.
Hori, T., Aoyagi, T., Itoh, H., Narihiro, T., Oikawa, A., Suzuki, K., Ogata, A., Friedrich, M.W., Conrad, R., and Kamagata, Y. 2015. Isolation of microorganisms involved in reduction of crystalline iron (III) oxides in natural environments. Front. Microbiol. 6, 386.
Jablonski, S., Rodowicz, P., and Lukaszewicz, M. 2015. Methanogenic archaea database containing physiological and biochemical characteristics. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65, 1360–1368.
Kang, Y.S., Risbud, S., Rabolt, J.F., and Stroeve, P. 1996. Synthesis and characterization of nanometer-size Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3 particles. Chem. Mater. 8, 2209–2211.
Kato, S., Hashimoto, K., and Watanabe, K. 2012a. Methanogenesis facilitated by electric syntrophy via (semi) conductive iron-oxide minerals. Environ. Microbiol. 14, 1646–1654.
Kato, S., Hashimoto, K., and Watanabe, K. 2012b. Microbial interspecies electron transfer via electric currents through conductive minerals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 10042–10046.
Kern, T., Linge, M., and Rother, M. 2015. Methanobacterium aggregans sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic methanogenic archaeon isolated from an anaerobic digester. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 65, 1975–1980.
Kostka, J.E. and Nealson, K.H. 1995. Dissolution and reduction of magnetite by bacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 2535–2540.
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., and Tamura, K. 2016. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 33, 1870–1874.
Li, H., Chang, J., Liu, P., Fu, L., Ding, D., and Lu, Y. 2015. Direct interspecies electron transfer accelerates syntrophic oxidation of butyrate in paddy soil enrichments. Environ. Microbiol. 17, 1533–1547.
Liu, F. and Conrad, R. 2010. Thermoanaerobacteriaceae oxidize acetate in methanogenic rice field soil at 50 degrees C. Environ. Microbiol. 12, 2341–2354.
Lovley, D.R. and Phillips, E.J.P. 1986. Organic-matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 51, 683–689.
Oren, A. 2014. The family Methanosarcinaceae, pp. 259–281. In Rosenberg, E., De Long, E.F., Lory, S., Stackebrandt, E., and Thomson, F. The Prokaryotes. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany.
Peng, Q.A., Shaaban, M., Wu, Y., Hu, R., Wang, B., and Wang, J. 2016. The diversity of iron reducing bacteria communities in subtropical paddy soils of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 101, 20–27.
Piepenbrock, A., Dippon, U., Porsch, K., Appel, E., and Kappler, A. 2011. Dependence of microbial magnetite formation on humic substance and ferrihydrite concentrations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 75, 6844–6858.
Rotaru, A.E., Shrestha, P.M., Liu, F., Markovaite, B., Chen, S., Nevin, K., and Lovley, D. 2014. Direct interspecies electron transfer between Geobacter metallireducens and Methanosarcina barkeri. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 80, 4599–4605.
Schirmack, J., Mangelsdorf, K., Ganzert, L., Sand, W., Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A., and Wagner, D. 2014. Methanobacterium movilense sp. nov., a hydrogenotrophic, secondary-alcohol-utilizing methanogen from the anoxic sediment of a subsurface lake. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 64, 522–527.
Shrestha, P.M., Kube, M., Reinhardt, R., and Liesack, W. 2009. Transcriptional activity of paddy soil bacterial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 11, 960–970.
Tang, J., Zhuang, L., Ma, J., Tang, Z., Yu, Z., and Zhou, S. 2016. Secondary mineralization of ferrihydrite affects microbial methanogenesis in Geobacter-Methanosarcina cocultures. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 82, 5869–5877.
Viggi, C.C., Rossetti, S., Fazi, S., Paiano, P., Majone, M., and Aulenta, F. 2014. Magnetite particles triggering a faster and more robust syntrophic pathway of methanogenic propionate degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 48, 7536–7543.
Yamada, C., Kato, S., Ueno, Y., Ishii, M., and Igarashi, Y. 2014. Inhibitory effects of ferrihydrite on a thermophilic methanogenic community. Microbes Environ. 29, 227–230.
Yang, Z.M., Shi, X.S., Wang, C.S., Wang, L., and Guo, R.B. 2015. Magnetite nanoparticles facilitate methane production from ethanol via acting as electron acceptors. Sci. Rep. 5, 16118.
Zhang, J., Dong, H.L., Liu, D., Fischer, T.B., Wang, S., and Huang, L.Q. 2012. Microbial reduction of Fe(III) in illite-smectite minerals by methanogen Methanosarcina mazei. Chem. Geol. 292, 35–44.
Zheng, S., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, O., Zhang, J., and Liu, F. 2015. Co-occurrence of Methanosarcina mazei and Geobacteraceae in an iron (III)-reducing enrichment culture. Front. Microbiol. 6, 941.
Zhou, S., Xu, J., Yang, G., and Zhuang, L. 2014. Methanogenesis affected by the co-occurrence of iron (III) oxides and humic substances. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 88, 107–120.
Zhuang, L., Xu, J.L., Tang, J., and Zhou, S.G. 2015. Effect of ferrihydrite biomineralization on methanogenesis in an anaerobic incubation from paddy soil. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 120, 876–886.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, S., Wang, B., Liu, F. et al. Magnetite production and transformation in the methanogenic consortia from coastal riverine sediments. J Microbiol. 55, 862–870 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7104-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7104-1