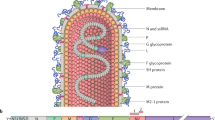
Abstract
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes severe respiratory disease in both the very young and the elderly. Nearly all individuals become infected in early childhood, and reinfections with the virus are common throughout life. Despite its clinical impact, there remains no licensed RSV vaccine. RSV infection in the respiratory tract induces an inflammatory response by the host to facilitate efficient clearance of the virus. However, the host immune response also contributes to the respiratory disease observed following an RSV infection. RSV has evolved several mechanisms to evade the host immune response and promote virus replication through interactions between RSV proteins and immune components. In contrast, some RSV proteins also play critical roles in activating, rather than suppressing, host immunity. In this review, we discuss the interactions between individual RSV proteins and host factors that modulate the immune response and the implications of these interactions for the course of an RSV infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious, D. and American Academy of Pediatrics Bronchiolitis Guidelines, C. 2014. Updated guidance for palivizumab prophylaxis among infants and young children at increased risk of hospitalization for respiratory syncytial virus infection. Pediatrics 134, 415–420.
American Academy of Pediatrics Subcommittee on, D. and Management of, B. 2006. Diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis. Pediatrics 118, 1774–1793.
Arnold, R., Konig, B., Werchau, H., and Konig, W. 2004. Respiratory syncytial virus deficient in soluble G protein induced an increased proinflammatory response in human lung epithelial cells. Virology 330, 384–397.
Beeler, J.A. and van Wyke Coelingh, K. 1989. Neutralization epitopes of the F glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus: effect of mutation upon fusion function. J. Virol. 63, 2941–2950.
Bembridge, G.P., Garcia-Beato, R., Lopez, J.A., Melero, J.A., and Taylor, G. 1998. Subcellular site of expression and route of vaccination influence pulmonary eosinophilia following respiratory syncytial virus challenge in BALB/c mice sensitized to the attachment G protein. J. Immunol. 161, 2473–2480.
Bermingham, A. and Collins, P.L. 1999. The M2-2 protein of human respiratory syncytial virus is a regulatory factor involved in the balance between RNA replication and transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 11259–11264.
Bitko, V., Shulyayeva, O., Mazumder, B., Musiyenko, A., Ramaswamy, M., Look, D.C., and Barik, S. 2007. Nonstructural proteins of respiratory syncytial virus suppress premature apoptosis by an NFkappaB-dependent, interferon-independent mechanism and facilitate virus growth. J. Virol. 81, 1786–1795.
Blondot, M.L., Dubosclard, V., Fix, J., Lassoued, S., Aumont-Nicaise, M., Bontems, F., Eleouet, J.F., and Sizun, C. 2012. Structure and functional analysis of the RNA-and viral phosphoprotein-binding domain of respiratory syncytial virus M2-1 protein. PLoS Pathog. 8, e1002734.
Bohmwald, K., Espinoza, J.A., Becerra, D., Rivera, K., Lay, M.K., Bueno, S.M., Riedel, C.A., and Kalergis, A.M. 2015. Inflammatory damage on respiratory and nervous systems due to hRSV infection. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 36, 14–21.
Bolt, G., Pedersen, L.O., and Birkeslund, H.H. 2000. Cleavage of the respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein is required for its surface expression: role of furin. Virus Res. 68, 25–33.
Borchers, A.T., Chang, C., Gershwin, M.E., and Gershwin, L.J. 2013. Respiratory syncytial virus—a comprehensive review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 45, 331–379.
Boyapalle, S., Wong, T., Garay, J., Teng, M., San Juan-Vergara, H., Mohapatra, S., and Mohapatra, S. 2012. Respiratory syncytial virus NS1 protein colocalizes with mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein MAVS following infection. PLoS One 7, e29386.
Boyoglu-Barnum, S., Chirkova, T., Todd, S.O., Barnum, T.R., Gaston, K.A., Jorquera, P., Haynes, L.M., Tripp, R.A., Moore, M.L., and Anderson, L.J. 2014. Prophylaxis with a respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) anti-G protein monoclonal antibody shifts the adaptive immune response to RSV rA2-line19F infection from Th2 to Th1 in BALB/c mice. J. Virol. 88, 10569–10583.
Brandenburg, A.H., Groen, J., van Steensel-Moll, H.A., Claas, E.C., Rothbarth, P.H., Neijens, H.J., and Osterhaus, A.D. 1997. Respiratory syncytial virus specific serum antibodies in infants under six months of age: limited serological response upon infection. J. Med. Virol. 52, 97–104.
Brinkmann, V., Reichard, U., Goosmann, C., Fauler, B., Uhlemann, Y., Weiss, D.S., Weinrauch, Y., and Zychlinsky, A. 2004. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 303, 1532–1535.
Bukreyev, A., Serra, M.E., Laham, F.R., Melendi, G.A., Kleeberger, S.R., Collins, P.L., and Polack, F.P. 2006. The cysteine-rich region and secreted form of the attachment G glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus enhance the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response despite lacking major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted epitopes. J. Virol. 80, 5854–5861.
Bukreyev, A., Whitehead, S.S., Bukreyeva, N., Murphy, B.R., and Collins, P.L. 1999. Interferon gamma expressed by a recombinant respiratory syncytial virus attenuates virus replication in mice without compromising immunogenicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 2367–2372.
Bukreyev, A., Whitehead, S.S., Murphy, B.R., and Collins, P.L. 1997. Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus from which the entire SHgene has been deleted grows efficiently in cell culture and exhibits site-specific attenuation in the respiratory tract of the mouse. J. Virol. 71, 8973–8982.
Bukreyev, A., Yang, L., Fricke, J., Cheng, L., Ward, J.M., Murphy, B.R., and Collins, P.L. 2008. The secreted form of respiratory syncytial virus G glycoprotein helps the virus evade antibodymediated restriction of replication by acting as an antigen decoy and through effects on Fc receptor-bearing leukocytes. J. Virol. 82, 12191–12204.
Cannon, M.J., Stott, E.J., Taylor, G., and Askonas, B.A. 1987. Clearance of persistent respiratory syncytial virus infections in immunodeficient mice following transfer of primed T cells. Immunology 62, 133–138.
Cartee, T.L. and Wertz, G.W. 2001. Respiratory syncytial virus M2-1 protein requires phosphorylation for efficient function and binds viral RNA during infection. J. Virol. 75, 12188–12197.
Carter, S.D., Dent, K.C., Atkins, E., Foster, T.L., Verow, M., Gorny, P., Harris, M., Hiscox, J.A., Ranson, N.A., Griffin, S., et al. 2010. Direct visualization of the small hydrophobic protein of human respiratory syncytial virus reveals the structural basis for membrane permeability. FEBS Lett. 584, 2786–2790.
Castagne, N., Barbier, A., Bernard, J., Rezaei, H., Huet, J.C., Henry, C., da Costa, B., and Eleouet, J.F. 2004. Biochemical characterization of the respiratory syncytial virus P-P and P-N protein complexes and localization of the P protein oligomerization domain. J. Gen. Virol. 85, 1643–1653.
Cespedes, P.F., Bueno, S.M., Ramirez, B.A., Gomez, R.S., Riquelme, S.A., Palavecino, C.E., Mackern-Oberti, J.P., Mora, J.E., Depoil, D., Sacristan, C., et al. 2014. Surface expression of the hRSV nucleoprotein impairs immunological synapse formation with T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 111, e3214–3223.
Chirkova, T., Boyoglu-Barnum, S., Gaston, K.A., Malik, F.M., Trau, S.P., Oomens, A.G., and Anderson, L.J. 2013. Respiratory syncytial virus G protein CX3C motif impairs human airway epithelial and immune cell responses. J. Virol. 87, 13466–13479.
Collins, P.L., Chanock, R.M., and Murphy, B.R. 2001. Respiratory syncytial virus. In Knipe, D.M. and Howley, P.M. (eds.), Fields Virology, pp. 1443–1486. Lippincott, Williams, & Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA.
Collins, P.L. and Crowe, J.E. 2007. Respiratory syncytial virus and metapneumovirus. In Knipe, D.M. and Howley, P.M. (eds.), Fields Virology, pp. 1601–1646. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA.
Collins, P.L., Dickens, L.E., Buckler-White, A., Olmsted, R.A., Spriggs, M.K., Camargo, E., and Coelingh, K.V. 1986. Nucleotide sequences for the gene junctions of human respiratory syncytial virus reveal distinctive features of intergenic structure and gene order. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 4594–4598.
Collins, P.L., Fearns, R., and Graham, B.S. 2013. Respiratory syncytial virus: virology, reverse genetics, and pathogenesis of disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 372, 3–38.
Collins, P.L. and Mottet, G. 1991. Post-translational processing and oligomerization of the fusion glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial virus. J. Gen. Virol. 72 (Pt 12), 3095–3101.
Collins, P.L. and Wertz, G.W. 1983. cDNA cloning and transcriptional mapping of nine polyadenylylated RNAs encoded by the genome of human respiratory syncytial virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 3208–3212.
Costello, H.M., Ray, W.C., Chaiwatpongsakorn, S., and Peeples, M.E. 2012. Targeting RSV with vaccines and small molecule drugs. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 12, 110–128.
Day, N.D., Branigan, P.J., Liu, C., Gutshall, L.L., Luo, J., Melero, J.A., Sarisky, R.T., and Del Vecchio, A.M. 2006. Contribution of cysteine residues in the extracellular domain of the F protein of human respiratory syncytial virus to its function. Virol. J. 3, 34.
Durant, L.R., Makris, S., Voorburg, C.M., Loebbermann, J., Johansson, C., and Openshaw, P.J. 2013. Regulatory T cells prevent Th2 immune responses and pulmonary eosinophilia during respiratory syncytial virus infection in mice. J. Virol. 87, 10946–10954.
Elliott, J., Lynch, O.T., Suessmuth, Y., Qian, P., Boyd, C.R., Burrows, J.F., Buick, R., Stevenson, N.J., Touzelet, O., Gadina, M., et al. 2007. Respiratory syncytial virus NS1 protein degrades STAT2 by using the Elongin-Cullin E3 ligase. J. Virol. 81, 3428–3436.
Falsey, A.R., Hennessey, P.A., Formica, M.A., Cox, C., and Walsh, E.E. 2005. Respiratory syncytial virus infection in elderly and high-risk adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 352, 1749–1759.
Falsey, A.R., Singh, H.K., and Walsh, E.E. 2006. Serum antibody decay in adults following natural respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Med. Virol. 78, 1493–1497.
Feltes, T.F., Cabalka, A.K., Meissner, H.C., Piazza, F.M., Carlin, D.A., Top, F.H.Jr., Connor, E.M., Sondheimer, H.M., and Cardiac Synagis Study, G. 2003. Palivizumab prophylaxis reduces hospitalization due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children with hemodynamically significant congenital heart disease. J. Pediatr. 143, 532–540.
Fong, A.M., Robinson, L.A., Steeber, D.A., Tedder, T.F., Yoshie, O., Imai, T., and Patel, D.D. 1998. Fractalkine and CX3CR1 mediate a novel mechanism of leukocyte capture, firm adhesion, and activation under physiologic flow. J. Exp. Med. 188, 1413–1419.
Fuentes, S., Tran, K.C., Luthra, P., Teng, M.N., and He, B. 2007. Function of the respiratory syncytial virus small hydrophobic protein. J. Virol. 81, 8361–8366.
Fujisawa, T., Chang, M.M., Velichko, S., Thai, P., Hung, L.Y., Huang, F., Phuong, N., Chen, Y., and Wu, R. 2011. NF-kappaB mediates IL-1beta-and IL-17A-induced MUC5B expression in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 45, 246–252.
Fulton, R.B., Meyerholz, D.K., and Varga, S.M. 2010. Foxp3+ CD4 regulatory T cells limit pulmonary immunopathology by modulating the CD8 T cell response during respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Immunol. 185, 2382–2392.
Funchal, G.A., Jaeger, N., Czepielewski, R.S., Machado, M.S., Muraro, S.P., Stein, R.T., Bonorino, C.B., and Porto, B.N. 2015. Respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein promotes TLR-4-dependent neutrophil extracellular trap formation by human neutrophils. PLoS One 10, e0124082.
Gan, S.W., Tan, E., Lin, X., Yu, D., Wang, J., Tan, G.M., Vararattanavech, A., Yeo, C.Y., Soon, C.H., Soong, T.W., et al. 2012. The small hydrophobic protein of the human respiratory syncytial virus forms pentameric ion channels. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 24671–24689.
Glezen, W.P., Taber, L.H., Frank, A.L., and Kasel, J.A. 1986. Risk of primary infection and reinfection with respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Dis. Child. 140, 543–546.
Graham, B.S., Bunton, L.A., Wright, P.F., and Karzon, D.T. 1991. Role of T lymphocyte subsets in the pathogenesis of primary infection and rechallenge with respiratory syncytial virus in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 88, 1026–1033.
Grosfeld, H., Hill, M.G., and Collins, P.L. 1995. RNA replication by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is directed by the N, P,and L proteins; transcription also occurs under these conditions but requires RSV superinfection for efficient synthesis of full-length mRNA. J. Virol. 69, 5677–5686.
Gruber, C. and Levine, S. 1983. Respiratory syncytial virus polypeptides. III. The envelope-associated proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 64 (Pt 4), 825–832.
Hall, C.B., Long, C.E., and Schnabel, K.C. 2001. Respiratory syncytial virus infections in previously healthy working adults. Clin. Infect. Dis. 33, 792–796.
Hancock, G.E., Speelman, D.J., Heers, K., Bortell, E., Smith, J., and Cosco, C. 1996. Generation of atypical pulmonary inflammatory responses in BALB/c mice after immunization with the native attachment (G) glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 70, 7783–7791.
Harcourt, J., Alvarez, R., Jones, L.P., Henderson, C., Anderson, L.J., and Tripp, R.A. 2006. Respiratory syncytial virus G protein and G protein CX3C motif adversely affect CX3CR1+ T cell responses. J. Immunol. 176, 1600–1608.
Haynes, L.M., Jones, L.P., Barskey, A., Anderson, L.J., and Tripp, R.A. 2003. Enhanced disease and pulmonary eosinophilia associated with formalin-inactivated respiratory syncytial virus vaccination are linked to G glycoprotein CX3C-CX3CR1 interaction and expression of substance P. J. Virol. 77, 9831–9844.
Haynes, L.M., Moore, D.D., Kurt-Jones, E.A., Finberg, R.W., Anderson, L.J., and Tripp, R.A. 2001. Involvement of toll-like receptor 4 in innate immunity to respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 75, 10730–10737.
Heminway, B.R., Yu, Y., Tanaka, Y., Perrine, K.G., Gustafson, E., Bernstein, J.M., and Galinski, M.S. 1994. Analysis of respiratory syncytial virus F, G, and SH proteins in cell fusion. Virology 200, 801–805.
Hendricks, D.A., McIntosh, K., and Patterson, J.L. 1988. Further characterization of the soluble form of the G glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus. J. Virol. 62, 2228–2233.
Hoffmann, H.H., Schneider, W.M., and Rice, C.M. 2015. Interferons and viruses: an evolutionary arms race of molecular interactions. Trends Immunol. 36, 124–138.
Jansen, A.G., Sanders, E.A., Hoes, A.W., van Loon, A.M., and Hak, E. 2007. Influenza-and respiratory syncytial virus-associated mortality and hospitalisations. Eur. Respir. J. 30, 1158–1166.
Jenne, C.N., Wong, C.H., Zemp, F.J., McDonald, B., Rahman, M.M., Forsyth, P.A., McFadden, G., and Kubes, P. 2013. Neutrophils recruited to sites of infection protect from virus challenge by releasing neutrophil extracellular traps. Cell Host Microbe 13, 169–180.
Jin, H., Cheng, X., Traina-Dorge, V.L., Park, H.J., Zhou, H., Soike, K., and Kemble, G. 2003. Evaluation of recombinant respiratory syncytial virus gene deletion mutants in African green monkeys for their potential as live attenuated vaccine candidates. Vaccine 21, 3647–3652.
Jin, H., Zhou, H., Cheng, X., Tang, R., Munoz, M., and Nguyen, N. 2000. Recombinant respiratory syncytial viruses with deletions in the NS1, NS2, SH, and M2-2 genes are attenuated in vitro and in vivo. Virology 273, 210–218.
Johnson, C.H., Miao, C., Blanchard, E.G., Caidi, H., Radu, G.U., Harcourt, J.L., and Haynes, L.M. 2012a. Effect of chemokine receptor CX3CR1 deficiency in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus infection. Comp. Med. 62, 14–20.
Johnson, P.R., Spriggs, M.K., Olmsted, R.A., and Collins, P.L. 1987. The G glycoprotein of human respiratory syncytial viruses of subgroups A and B: extensive sequence divergence between antigenically related proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 5625–5629.
Johnson, T.R., Johnson, J.E., Roberts, S.R., Wertz, G.W., Parker, R.A., and Graham, B.S. 1998. Priming with secreted glycoprotein G of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) augments interleukin-5 production and tissue eosinophilia after RSV challenge. J. Virol. 72, 2871–2880.
Johnson, T.R., McLellan, J.S., and Graham, B.S. 2012b. Respiratory syncytial virus glycoprotein G interacts with DC-SIGN and LSIGN to activate ERK1 and ERK2. J. Virol. 86, 1339–1347.
Jorquera, P.A., Choi, Y., Oakley, K.E., Powell, T.J., Boyd, J.G., Palath, N., Haynes, L.M., Anderson, L.J., and Tripp, R.A. 2013. Nanoparticle vaccines encompassing the respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) G protein CX3C chemokine motif induce robust immunity protecting from challenge and disease. PLoS One 8, e74905.
Karron, R.A., Buonagurio, D.A., Georgiu, A.F., Whitehead, S.S., Adamus, J.E., Clements-Mann, M.L., Harris, D.O., Randolph, V.B., Udem, S.A., Murphy, B.R., et al. 1997. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) SH and G proteins are not essential for viral replication in vitro: clinical evaluation and molecular characterization of a cold-passaged, attenuated RSV subgroup B mutant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 13961–13966.
Kotelkin, A., Belyakov, I.M., Yang, L., Berzofsky, J.A., Collins, P.L., and Bukreyev, A. 2006. The NS2 protein of human respiratory syncytial virus suppresses the cytotoxic T-cell response as a consequence of suppressing the type I interferon response. J. Virol. 80, 5958–5967.
Kotenko, S.V., Gallagher, G., Baurin, V.V., Lewis-Antes, A., Shen, M., Shah, N.K., Langer, J.A., Sheikh, F., Dickensheets, H., and Donnelly, R.P. 2003. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat. Immunol. 4, 69–77.
Kurt-Jones, E.A., Popova, L., Kwinn, L., Haynes, L.M., Jones, L.P., Tripp, R.A., Walsh, E.E., Freeman, M.W., Golenbock, D.T., Anderson, L.J., et al. 2000. Pattern recognition receptors TLR4 and CD14 mediate response to respiratory syncytial virus. Nat. Immunol. 1, 398–401.
Lee, D.C., Harker, J.A., Tregoning, J.S., Atabani, S.F., Johansson, C., Schwarze, J., and Openshaw, P.J. 2010. CD25+ natural regulatory T cells are critical in limiting innate and adaptive immunity and resolving disease following respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Virol. 84, 8790–8798.
Ling, Z., Tran, K.C., and Teng, M.N. 2009. Human respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural protein NS2 antagonizes the activation of beta interferon transcription by interacting with RIG-I. J. Virol. 83, 3734–3742.
Lo, M.S., Brazas, R.M., and Holtzman, M.J. 2005. Respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural proteins NS1 and NS2 mediate inhibition of Stat2 expression and alpha/beta interferon responsiveness. J. Virol. 79, 9315–9319.
Lukacs, N.W., Moore, M.L., Rudd, B.D., Berlin, A.A., Collins, R.D., Olson, S.J., Ho, S.B., and Peebles, R.S.Jr. 2006. Differential immune responses and pulmonary pathophysiology are induced by two different strains of respiratory syncytial virus. Am. J. Pathol. 169, 977–986.
McLellan, J.S., Ray, W.C., and Peeples, M.E. 2013. Structure and function of respiratory syncytial virus surface glycoproteins. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 372, 83–104.
McMaster, S.R., Wilson, J.J., Wang, H., and Kohlmeier, J.E. 2015. Airway-resident memory CD8 T cells provide antigen-specific protection against respiratory virus challenge through rapid IFNgamma production. J. Immunol. 195, 203–209.
McNamara, P.S., Flanagan, B.F., Hart, C.A., and Smyth, R.L. 2005. Production of chemokines in the lungs of infants with severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis. J. Infect. Dis. 191, 1225–1232.
Melendi, G.A., Bridget, D., Monsalvo, A.C., Laham, F.F., Acosta, P., Delgado, M.F., Polack, F.P., and Irusta, P.M. 2011. Conserved cysteine residues within the attachment G glycoprotein of respiratory syncytial virus play a critical role in the enhancement of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses. Virus Genes 42, 46–54.
Mitra, R., Baviskar, P., Duncan-Decocq, R.R., Patel, D., and Oomens, A.G. 2012. The human respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein is required for maturation of viral filaments. J. Virol. 86, 4432–4443.
Moore, E.C., Barber, J., and Tripp, R.A. 2008. Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) attachment and nonstructural proteins modify the type I interferon response associated with suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins and IFN-stimulated gene-15 (ISG15). Virol. J. 5, 116.
Mukherjee, S., Lindell, D.M., Berlin, A.A., Morris, S.B., Shanley, T.P., Hershenson, M.B., and Lukacs, N.W. 2011. IL-17-induced pulmonary pathogenesis during respiratory viral infection and exacerbation of allergic disease. Am. J. Pathol. 179, 248–258.
Munir, S., Hillyer, P., Le Nouen, C., Buchholz, U.J., Rabin, R.L., Collins, P.L., and Bukreyev, A. 2011. Respiratory syncytial virus interferon antagonist NS1 protein suppresses and skews the human T lymphocyte response. PLoS Pathog. 7, e1001336.
Munir, S., Le Nouen, C., Luongo, C., Buchholz, U.J., Collins, P.L., and Bukreyev, A. 2008. Nonstructural proteins 1 and 2 of respiratory syncytial virus suppress maturation of human dendritic cells. J. Virol. 82, 8780–8796.
Murphy, B.R., Graham, B.S., Prince, G.A., Walsh, E.E., Chanock, R.M., Karzon, D.T., and Wright, P.F. 1986. Serum and nasal-wash immunoglobulin G and A antibody response of infants and children to respiratory syncytial virus F and G glycoproteins following primary infection. J. Clin. Microbiol. 23, 1009–1014.
Nair, H., Nokes, D.J., Gessner, B.D., Dherani, M., Madhi, S.A., Singleton, R.J., O'Brien, K.L., Roca, A., Wright, P.F., Bruce, N., et al. 2010. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 375, 1545–1555.
Narasaraju, T., Yang, E., Samy, R.P., Ng, H.H., Poh, W.P., Liew, A.A., Phoon, M.C., van Rooijen, N., and Chow, V.T. 2011. Excessive neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to acute lung injury of influenza pneumonitis. Am. J. Pathol. 179, 199–210.
Oshansky, C.M., Krunkosky, T.M., Barber, J., Jones, L.P., and Tripp, R.A. 2009. Respiratory syncytial virus proteins modulate suppressors of cytokine signaling 1 and 3 and the type I interferon response to infection by a toll-like receptor pathway. Viral. Immunol. 22, 147–161.
Polack, F.P., Irusta, P.M., Hoffman, S.J., Schiatti, M.P., Melendi, G.A., Delgado, M.F., Laham, F.R., Thumar, B., Hendry, R.M., Melero, J.A., et al. 2005. The cysteine-rich region of respiratory syncytial virus attachment protein inhibits innate immunity elicited by the virus and endotoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 8996–9001.
Puthothu, B., Forster, J., Heinzmann, A., and Krueger, M. 2006. TLR-4 and CD14 polymorphisms in respiratory syncytial virus associated disease. Dis. Markers 22, 303–308.
Ramaswamy, M., Shi, L., Varga, S.M., Barik, S., Behlke, M.A., and Look, D.C. 2006. Respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural protein 2 specifically inhibits type I interferon signal transduction. Virology 344, 328–339.
Ren, J., Liu, T., Pang, L., Li, K., Garofalo, R.P., Casola, A., and Bao, X. 2011. A novel mechanism for the inhibition of interferon regulatory factor-3-dependent gene expression by human respiratory syncytial virus NS1 protein. J. Gen. Virol. 92, 2153–2159.
Rixon, H.W., Brown, G., Aitken, J., McDonald, T., Graham, S., and Sugrue, R.J. 2004. The small hydrophobic (SH) protein accumulates within lipid-raft structures of the Golgi complex during respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 85, 1153–1165.
Roberts, S.R., Lichtenstein, D., Ball, L.A., and Wertz, G.W. 1994. The membrane-associated and secreted forms of the respiratory syncytial virus attachment glycoprotein G are synthesized from alternative initiation codons. J. Virol. 68, 4538–4546.
Rueda, P., Garcia-Barreno, B., and Melero, J.A. 1994. Loss of conserved cysteine residues in the attachment (G) glycoprotein of two human respiratory syncytial virus escape mutants that contain multiple A-G substitutions (hypermutations). Virology 198, 653–662.
Saitoh, T., Komano, J., Saitoh, Y., Misawa, T., Takahama, M., Kozaki, T., Uehata, T., Iwasaki, H., Omori, H., Yamaoka, S., et al. 2012. Neutrophil extracellular traps mediate a host defense response to human immunodeficiency virus-1. Cell Host Microbe 12, 109–116.
Sen, G.C. and Sarkar, S.N. 2007. The interferon-stimulated genes: targets of direct signaling by interferons, double-stranded RNA, and viruses. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 316, 233–250.
Shingai, M., Azuma, M., Ebihara, T., Sasai, M., Funami, K., Ayata, M., Ogura, H., Tsutsumi, H., Matsumoto, M., and Seya, T. 2008. Soluble G protein of respiratory syncytial virus inhibits Toll-like receptor 3/4-mediated IFN-beta induction. Int. Immunol. 20, 1169–1180.
Spann, K.M., Tran, K.C., Chi, B., Rabin, R.L., and Collins, P.L. 2004. Suppression of the induction of alpha, beta, and lambda interferons by the NS1 and NS2 proteins of human respiratory syncytial virus in human epithelial cells and macrophages [corrected]. J. Virol. 78, 4363–4369.
Spann, K.M., Tran, K.C., and Collins, P.L. 2005. Effects of nonstructural proteins NS1 and NS2 of human respiratory syncytial virus on interferon regulatory factor 3, NF-kappaB, and proinflammatory cytokines. J. Virol. 79, 5353–5362.
Suhara, W., Yoneyama, M., Kitabayashi, I., and Fujita, T. 2002. Direct involvement of CREB-binding protein/p300 in sequence-specific DNA binding of virus-activated interferon regulatory factor-3 holocomplex. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22304–22313.
Swedan, S., Andrews, J., Majumdar, T., Musiyenko, A., and Barik, S. 2011. Multiple functional domains and complexes of the two nonstructural proteins of human respiratory syncytial virus contribute to interferon suppression and cellular location. J. Virol. 85, 10090–10100.
Swedan, S., Musiyenko, A., and Barik, S. 2009. Respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural proteins decrease levels of multiple members of the cellular interferon pathways. J. Virol. 83, 9682–9693.
Tal, G., Mandelberg, A., Dalal, I., Cesar, K., Somekh, E., Tal, A., Oron, A., Itskovich, S., Ballin, A., Houri, S., et al. 2004. Association between common Toll-like receptor 4 mutations and severe respiratory syncytial virus disease. J. Infect. Dis. 189, 2057–2063.
Tawar, R.G., Duquerroy, S., Vonrhein, C., Varela, P.F., Damier-Piolle, L., Castagne, N., MacLellan, K., Bedouelle, H., Bricogne, G., Bhella, D., et al. 2009. Crystal structure of a nucleocapsid-like nucleoprotein-RNA complex of respiratory syncytial virus. Science 326, 1279–1283.
Teng, M.N., Whitehead, S.S., Bermingham, A., St Claire, M., Elkins, W.R., Murphy, B.R., and Collins, P.L. 2000. Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus that does not express the NS1 or M2-2 protein is highly attenuated and immunogenic in chimpanzees. J. Virol. 74, 9317–9321.
Teng, M.N., Whitehead, S.S., and Collins, P.L. 2001. Contribution of the respiratory syncytial virus G glycoprotein and its secreted and membrane-bound forms to virus replication in vitro and in vivo. Virology 289, 283–296.
Triantafilou, K., Kar, S., Vakakis, E., Kotecha, S., and Triantafilou, M. 2013. Human respiratory syncytial virus viroporin SH: a viral recognition pathway used by the host to signal inflammasome activation. Thorax 68, 66–75.
Tripp, R.A., Jones, L.P., Haynes, L.M., Zheng, H., Murphy, P.M., and Anderson, L.J. 2001. CX3C chemokine mimicry by respiratory syncytial virus G glycoprotein. Nat. Immunol. 2, 732–738.
Tripp, R.A., Moore, D., Jones, L., Sullender, W., Winter, J., and Anderson, L.J. 1999. Respiratory syncytial virus G and/or SH protein alters Th1 cytokines, natural killer cells, and neutrophils responding to pulmonary infection in BALB/c mice. J. Virol. 73, 7099–7107.
Vareille, M., Kieninger, E., Edwards, M.R., and Regamey, N. 2011. The airway epithelium: soldier in the fight against respiratory viruses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 24, 210–229.
Varga, S.M. and Braciale, T.J. 2013. The adaptive immune response to respiratory syncytial virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 372, 155–171.
Ventre, K. and Randolph, A.G. 2007. Ribavirin for respiratory syncytial virus infection of the lower respiratory tract in infants and young children. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. CD000181.
Whelan, J.N., Tran, K.C., van Rossum, D.B., and Teng, M.N. 2016. Identification of respiratory syncytial virus nonstructural protein 2 residues essential for exploitation of the host ubiquitin system and inhibition of innate immune responses. J. Virol. 90, 6453–6463.
Whitehead, S.S., Bukreyev, A., Teng, M.N., Firestone, C.Y., St Claire, M., Elkins, W.R., Collins, P.L., and Murphy, B.R. 1999. Recombinant respiratory syncytial virus bearing a deletion of either the NS2 or SHgene is attenuated in chimpanzees. J. Virol. 73, 3438–3442.
Yoon, J.S., Kim, H.H., Lee, Y., and Lee, J.S. 2007. Cytokine induction by respiratory syncytial virus and adenovirus in bronchial epithelial cells. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 42, 277–282.
Zeng, R., Cui, Y., Hai, Y., and Liu, Y. 2012. Pattern recognition receptors for respiratory syncytial virus infection and design of vaccines. Virus Res. 167, 138–145.
Zhang, G., Zhou, K.F., and Lu, Z.H. 2016. Interleukin-17 enhances the removal of respiratory syncytial virus in mice by promoting neutrophil migration and reducing interferon-gamma expression. Genet. Mol. Res. 15, gmr7002.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, M.E., Varga, S.M. Modulation of the host immune response by respiratory syncytial virus proteins. J Microbiol. 55, 161–171 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7045-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7045-8