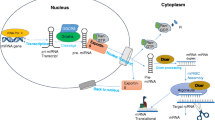
Abstract
Recent studies have examined gene transfer from bacteria to humans that would result in vertical inheritance. Bacterial DNA appears to integrate into the human somatic genome through an RNA intermediate, and such integrations are detected more frequently in tumors than normal samples and in RNA than DNA samples. Also, vertebrate viruses encode products that interfere with the RNA silencing machinery, suggesting that RNA silencing may indeed be important for antiviral responses in vertebrates. RNA silencing in response to virus infection could be due to microRNAs encoded by either the virus or the host. We hypothesized that bacterial expression of RNA molecules with secondary structures is potentially able to generate miRNA molecules that can interact with the human host mRNA during bacterial infection. To test this hypothesis, we developed a pipelinebased bioinformatics approach to identify putative micro-RNAs derived from bacterial RNAs that may have the potential to regulate gene expression of the human host cell. Our results suggest that 68 bacterial RNAs predicted from 37 different bacterial genomes have predicted secondary structures potentially able to generate putative microRNAs that may interact with messenger RNAs of genes involved in 47 different human diseases. As an example, we examined the effect of transfecting three putative microRNAs into human embryonic kidney 293 (HEK293) cells. The results show that the bacterially derived microRNA sequence can significantly regulate the expression of the respective target human gene. We suggest that the study of these predicted microRNAs may yield important clues as to how the human host cell processes involved in human diseases like cancer, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and others may respond to a particular bacterial environment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Refrerences
Akira S. and Takeda K. 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4, 499–511.
Alexiadis V., Waldmann T., Andersen J., Mann M., Knippers R., and Gruss C. 2000. The protein encoded by the proto-oncogene DEK changes the topology of chromatin and reduces the efficiency of DNA replication in a chromatin-specific manner. Genes Dev. 14, 1308–1312.
Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W., and Lipman D.J. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403–410.
Ambros V. 2004. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431, 350–355.
Azcarate-Peril M.A., Sikes M., and Bruno-Barcena J.M. 2011. The intestinal microbiota, gastrointestinal environment and colorectal cancer: a putative role for probiotics in prevention of colorectal cancer? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 301, G401–424.
Baulcombe D. 2004. RNA silencing in plants. Nature 431, 356–363.
Benson D.A., Karsch-Mizrachi I., Lipman D.J., Ostell J., and Wheeler D.L. 2008. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D25–30.
Cai X., Lu S., Zhang Z., Gonzalez C.M., Damania B., and Cullen B.R. 2005. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus expresses an array of viral microRNAs in latently infected cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 5570–5575.
Eccleston K., Collins L., and Higgins S.P. 2008. Primary syphilis. Int. J. STD AIDS 19, 145–151.
Ebby O.L. 2005. Community-acquired pneumonia: from common pathogens to emerging resistance. Emerg. Med. Pract. v7n12.
Farrar J.J., Yen L.M., Cook T., Fairweather N., Binh N., Parry J., and Parry C.M. 2000. Tetanus. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 69, 292–301.
Fire A., Xu S.Q., Montgomery M.K., Kostas S.A., Driver S.E., and Mello C.C. 1998. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in C. elegans. Nature 391, 806–811.
Freeman V.J. 1951. Studies on the virulence of bacteriophage-infected strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Bacteriol. 61, 675–688.
Fu G.K., Grosveld G., and Markovitz D.M. 1997. DEK, an autoantigen involved in a chromosomal translocation in acute myelogenous leukemia, binds to the HIV-2 enhancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 1811–1815.
Giannella R.A. 1996. Salmonella, chap. 21 pp. 295–302. In Baron S. (ed.), Medical Microbiology, 4th ed. University of Texas Medical Branch. Galveston, Tx., USA.
Gilmore T.D. 1999. The Rel/NF-κB signal transduction pathway: Introduction. Oncogene 18, 6842–6844.
Hamosh A., Scott A.F., Amberger J.S., Bocchini C.A., and McKusick V.A. 2005. Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, D514–517.
Han J., Lee Y., Yeom K.H., Kim Y.K., Jin H., and Kim V.N. 2004 The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing. Genes Dev. 18, 3016–3027.
Honda H., Inazawa J., Nishida J., Yazaki Y., and Hirai H. 1994. Molecular cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a novel protein-tyrosine phosphatase, HPTP eta. Blood 84, 4186–4194.
Huerta-Cepas J., Dopazo H., Dopazo J., and Gabaldon T. 2007. The human phylome. Genome Biol. 8, R109.
Huttenhofer A., Kiefmann M., Meier-Ewert S., O’Brien J., Lehrach H., Bachellerie J.P., and Brosius J. 2001. RNomics: an experimental approach that identifies 201 candidates for novel, small, non-messenger RNAs in mouse. EMBRO J. 20, 2943–2953.
Kavanaugh G.M., Wise-Draper T.M., Morreale R.J., Morrison M.A., Gole B., Schwemberger S., Tichy E.D., Lu L., Babcock G.F., Wells J.M., and et al. 2011. The human DEK oncogene regulates DNA damage response signaling and repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 7465–7476.
Kostic A.D., Gevers D., Pedamallu C.S., Michaud M., and Duke F. 2012. Genomic analysis identifies association of Fusobacterium with colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res. 22, 292–298.
Kurreck J. 2006. siRNA efficiency: structure or sequence-That is the question. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 83757, 1–7.
Lander E.S., Linton L.M., Birren B., Nusbaum C., and Zody M.C. 2001. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921.
Marchesi J.R., Dutilh B.E., Hall N., Peters W.H.M., Roelofs R., Boleij A., and Tjalsma H. 2011. Towards the human colorectal cancer microbiome. PLoS ONE 6, e20447.
Marker C., Zemann A., Terhörst T., Kiefmann M.J.P., Kastenmayer Green P., Bachellerie-Brosius J.P., and Huttenhofer A. 2002. Experimental RNomics: identification of 140 candidates for small non-messenger RNAs in the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 12, 2002–2013.
Markham N.R. and Zuker M. 2008. UNAFold: software for nucleic acid folding and hybridization, chap. 1, pp. 3–31. In Keith J.M. (ed), Bioinformatics, volume II. Structure, function and applications, number 453 in Methods in Molecular Biology. Human Press. Totowa, N.J., USA.
Marshall B.J. and Warren J.R. 1983. Unidentified curved bacillus on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet 1, 1273–1275.
Marshall B.J. and Warren J.R. 1984. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1, 1311–1315.
Miller W.G., Parker C.T., Rubenfield M., Mendz G.L., and Wösten M.M.S.M. 2007. The complete genome sequence and analysis of the Epsilonproteobacterium Arcobacter butzleri. PLoS ONE 2, e1358.
Naimi T.S., Wicklund J.H., Olsen S.J., Krause G., Wells J.G., Bartkus J.M., Boxrud D.J., Sullivan M., Kassenborg H., Besser J.M., and et al. 2003. Concurrent outbreaks of Shigella sonnei and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infections associated with parsley: implications for surveillance and control of foodborne illness. J. Food Prot. 66, 535–541.
Okamoto K., Makino S., Yoshikawa Y., Takaki A., Nagatsuka Y., Ota M., Tamiya G., Kimura A., Bahram S., and Inoko H. 2003. Identification of I-kappa-BL as the second major histocompatibility complex-linked susceptibility locus for rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 72, 303–312.
Pfeffer S., Sewer A., Lagos-Quintana M., Sheridan R., Sander C., Grasser F.A., van Dyk L.F., Ho C.K., Shuman S., and Chien M. 2005. Identification of microRNAs of the herpesvirus family. Nat. Methods 2, 269–276.
Pfeffer S., Zavolan M., Grässer F.A., Chien M., Russo J.J., Ju J., John B., Enright A.J., Marks D., Sander C., and et al. 2004. Identification of virus-encoded microRNAs. Science 304, 734–736.
Reinhart B.J., Slack F.J., Basson M., Pasquinelli A.E., Bettinger J.C., Rougvie A.E., Horvitz H.R., and Ruvkun G. 2000. The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403, 901–906.
Riley D.R., Sieber K.B., Robinson K.M., White J.R., Ganesan A., Nourbakhsh S., and Dunning Hotopp J.C. 2013. Bacteria-human somatic cell lateral gene transfer is enriched in cancer samples. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9, e1003107.
Ruivenkamp C.A., Wezel T., Zanon C., Stassen A.P.M., Vlcek C., Csikos T., Klous A.M., Tripodis N., Perrakis A., Boerrigter L., and et al. 2002. Ptprj is a candidate for the mouse coloncancer susceptibility locus Scc1 and is frequently deleted in human cancers. Nat. Genet. 31, 295–300.
Saetrom P., Sneve R., Kristiansen K.I., Snove O.Jr., Grunfeld T., Rognes T., and Seeberg E. 2005. Predicting non-coding RNA genes in Escherichia coli with boosted genetic programming. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 3263–3270.
Samols M.A., Hu J., Skalsky R.L., and Renne R. 2005. Cloning and identification of a microRNA cluster within the latencyassociated region of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J. Virol. 79, 9301–9305.
Sasaki S., Takeshita F., Okuda K., and Ishii N. 2001. Mycobacterium leprae and leprosy: a compendium. Microbiol. Immunol. 45, 729–736.
Sullivan C.S., Grundhoff A.T., Tevethia S., Pipas J.M., and Ganem D. 2005. SV40-encoded microRNAs regulate viral gene expression and reduce susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells. Nature 435, 682–686.
Talya K., Tzvi T., Yoram K., Yedidya G., Colin D., and Vitaly C. 2001. Genetic transformation of HeLa cells by Agrobacterium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 1871–1876.
Voinnet O. 2005. Induction and suppression of RNA silencing: insights from viral infections. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6, 206–220.
Von Lindern M., Fornerod M., and Soekarman N. 1993. Translocation t(6;9) in acute non-lymphocytic leukaemia results in the formation of a DEK-CAN fusion gene. Baillieres Clin. Haematol. 5, 857–879.
Wightman B., Ha I., and Ruvkun G. 1993. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell 75, 855–862.
Zhang R., LiPuma J.J., and Gonzalez C.F. 2009. Two type IV secretion systems with different functions in Burkholderia cenocepacia K56-2. Microbiology 155, 4005–4013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/120956.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shmaryahu, A., Carrasco, M. & Valenzuela, P.D. Prediction of Bacterial microRNAs and possible targets in human cell transcriptome. J Microbiol. 52, 482–489 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-3658-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-014-3658-3