Abstract
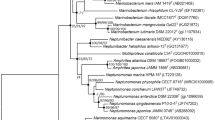
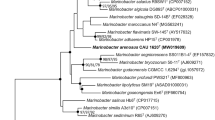
A novel bacterial strain, designated NA-09T, was isolated from a freshwater sample collected from the Cheonho reservoir, Republic of Korea. Colonies were creamy-white pigmented, translucent, and circular with convex shape. The isolate was Gram-staining negative, strictly aerobic, motile, and rod-shaped. The 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis revealed that strain NA-09T belonged to the genus Arenimonas and showed the highest sequence similarities with Arenimonas malthae CC-JY-1T (95.4%), A. oryziterrae YC6267T (94.9%), A. composti P2-12-1T (94.8%), and A. donghaensis H03-R19T (94.1%). The major fatty acids were iso-C16:0 (20.8%), iso-C15:0 (16.9%), summed feature 1 (13.2%), and iso-C16:1 ω7c alcohol (10.2%). The major isoprenoid quinone of the isolate was ubiquionone-8. On the basis of the data from the polyphasic characterization, the strain NA-09T represents a novel species, for which the name Arenimonas aquaticum sp. nov. is proposed (type strain NA-09T =KACC 14663T =NBRC 106550T).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aslam, Z., Park, J.H., Kim, S.W., Jeon, C.O., and Chung, Y.R. 2009. Arenimonas oryziterrae sp. nov., isolated from a field of rice (Oryza sativa L.) managed under a no-tillage regime, and reclassification of Aspromonas composti as Arenimonas composti comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.59, 2967–2972.
Bandelt, H.J., Forster, P., and Rohl, A. 1999. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol.16, 37–48.
Chun, J., Lee, J.H., Jung, Y., Kim, M., Kim, S., Kim, B.K., and Lim, Y.W. 2007. EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.57, 2259–2261.
Felsenstein, J. 1985. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution39, 783–791.
Groth, I., Schumann, P., Weiss, N., Martin, K., and Rainey, F.A. 1996. Agrococcus jenensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus of actinomycetes with diaminobutyric acid in the cell wall. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.46, 234–239.
Hall, T.A. 1999. BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser.41, 95–98.
Jin, L., Kim, K.K., Im, W.T., Yang, H.C., and Lee, S.T. 2007. Aspromonas composti gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of the family Xanthomonadaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57, 1876–1880.
Kimura, M. 1980. A simple method of estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol.16, 111–120.
Kwon, S.W., Kim, B.Y., Weon, H.Y., Baek, Y.K., and Go, S.J. 2007. Arenimonas donghaensis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from seashore sand. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.57, 954–958.
Lee, S., Oh, H.W., Lee, K.H., and Ahn, T.Y. 2009. Methylobacterium dankookense sp. nov., isolated from drinking water. J. Microbiol.47, 716–720.
Mesbah, M., Premachandran, U., and Whitman, W.B. 1989. Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol.39, 159–167.
Minnikin, D.E., O’Donnell, A.G., Goodfellow, M., Alderson, G., Athalye, M., Schaal, A., and Parlett, J.H. 1984. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods2, 233–241.
Moore, D.D. and Dowhan, D. 1995. Preparation and analysis of DNA. pp. 2–11. In Ausubel, F.W., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. (eds.), Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, Wiley, New York, N.Y., USA.
Olsen, I., Dewhirst, F.E., Paster, B.J., and Busse, H.J. 2005. Family I. Pasteurellaceae Phol 1981b, 382VP, pp. 851–856. In Brenner, D.J., Krieg, N.R., Staley, J.T., and Garrity, G.M. (eds.), Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology: the proteobacteria, part B: the gammaproteobacteria, 2nd ed. Springer, New York, N.Y., USA.
Smibert, R.M. and Krieg, N.R. 1994. Phenotypic characterization. pp. 607–654. In Gerhardt, P., Murray, R.G.E., Wood, W.A., and Krieg, N.R. (eds.), Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology, American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C., USA.
Tamura, K., Peterson, D., Peterson, N., Stecher, G., Nei, M., and Kumar, S. 2011. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol.28, 2731–2739.
Young, C.C., K⇐pfer, P., Ho, M.J., Busse, H.J., Huber, B.E., Arun, A.B., Shen, F.T., Lai, W.A., and Rekha, P.D. 2007. Arenimonas malthae sp. nov., a gammaproteobacterium isolated from an oil-contaminated site. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.57, 2790–2793.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplemental material for this article may be found at http://www.springerlink.com/content/20956.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12275-013-0728-x.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, A.R., Lee, S., Han, K. et al. Arenimonas aquaticum sp. nov., a member of the gammaproteobacterium, isolated from a freshwater reservoir. J Microbiol. 50, 354–358 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1301-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-012-1301-8